Orange World, Elastic Space: An Interview With Karen Russell
Karen Russell is a short story sorcerer. And with each collection, her powers grow. In Orange World, her third, out tomorrow from Knopf, she whisks the reader through time and space—from a snowy Oregon mountain lodge during the Great Depression to a future Florida flooded by an engorged sea. In one story the reader is swept off to a medieval village in Croatia plagued by corpses not content to rest in peace. As in all of her stories since her debut, St. Lucy’s Home for Girls Raised by Wolves (Knopf, 2006), the real and the fantastical blend without seam. This literary alchemy starts with the core elements, her words—nouns are wielded as verbs—and builds fractal-like as the narrative progresses. Sentences that begin as simple declarations leap into the figurative, landing as poems. Historical fiction twists into speculative horror. A lover’s walk through the desert becomes a meditation on the borders between people and their environment. The supernatural morphs into a grand metaphor on motherhood. Nothing is as it seems to be.
As high as Russell’s imagination soars in the eight new pieces in Orange World, the characters keep one foot on the reader’s throat. Though it’s chilling to tour the drowned cities of post-climate Florida by gondola, the driver—a lonely mutant girl who navigates by echolocation and lives in a seaplane hangar with her three sisters—is the narrative lodestar. Such intricately drawn characters require space to run, and the stories in Orange World stretch long, bringing to mind the ambitious tales of Kelly Link and George Saunders.
I’ve had the pleasure of talking with Russell, who has also published a novel, Swamplandia! (Knopf, 2011) about her inventive work before, and over the course of a few weeks, as the weather shifted from brutally cold to delightfully warm and the air became laden with petals and pollen, we exchanged a series of e-mails about her new collection.
The title of each one of your books—St Lucy’s Home for Girls Raised by Wolves, Swamplandia!, Vampires in the Lemon Grove, and now Orange World—references a place. In this new collection, the story settings feel even more diverse than in your previous ones, and exquisitely described, and so integral to the tales that you tell. How does setting work in regard to your process?
When I’m writing, I nearly always begin with setting; characters come later, and I wouldn’t be able to imagine them if I didn’t have a sense of where they lived, or in some cases, how far from home they had traveled. I was just on a wonderful panel with Luís Alberto Urrea and Emily Fridlund and we discussed the fictional and real landscapes to which we keep returning: swamps, forests, borders. Luis said, “There’s place, the physical location. And then there are the stories you tell about that place.” I’m so interested in how the sight lines, soundscapes, flora and fauna of our childhoods shape us—how those earliest encounters with the land become part of our private, interior vocabularies of dream and thought. And I love novels and stories where geography shapes plot and gives rise to character. I think the question “What’s possible or impossible for this human personality in this landscape?” is a good starting place for fiction.
With short stories it feels possible to hop across time zones and zip into new skins; also to take risks that I think would prove unsustainable for the length of a novel. World-building is such a pleasure for me, as a writer and as a reader, and I love story collections because they feel like a miniature universe, with all these interrelated worlds-in-progress. Do you ever find yourself feeling that peculiar deja-vu as a traveler, as if a memory is returning to your body of some place you’ve never been, in this life? Or do you find yourself haunted by scenery that feels both remote from your lived experience and strangely familiar to you? I love that feeling and am always looking for it, in life and in books.
I thought of Orange World as being primarily a collection of long landscape stories, where setting is not a static, painted backdrop for human dramas but where nonhuman nature intersects with a character’s interior world. So, for example, a woman finds herself trying to navigate the surreal, slippery topography of new motherhood during an extreme Portland winter. Two honeymooners lose sight of their horizon in a literal desert. And I miss Florida every day, so there is a story here, “The Gondoliers,” set on the canals of a drowned South Florida in the floating future. It’s true that the landscapes in this collection are far flung, relative to my earlier collections, and I was happy to return to my home state, which really is the ur-landscape for me.
I hope that the human animals here feel like one element of a much larger story, because it’s that interaction between human and nonhuman nature that truly fascinates me; and the bad trouble people get into when they fail to respect their own and nature’s limits.
You’ve set one story, “The Bad Graft,” in Joshua Tree National Park. This struck me as unusual. It seems like you often pass a location through an imaginary filter, but Joshua Tree is a real place, and you situate the story within a geography that actually exists. How did this story come about?
I went to Joshua Tree National Park on my first date with my now-husband, and while this story is in no way autobiographical, I do associate the vastness of the desert with the vertiginous feeling of falling in love with him. I had never been to the desert before and never seen a Joshua tree; I felt like those Joshuas were only holding their poses, waiting until our backs were turned to wave into new shapes. The millions-year long co-evolution of the Joshua tree and the yucca moth is stranger and more beautiful than anything I could ever dream up, and I was grateful to find this living metaphor for a love-and-horror story about our interdependency.
Though “The Bad Graft” does feel slightly closer to contemporary consensus reality than some of the other stories, it also features a tree spirit possession. Maybe here the imaginary world is that overlapping Venn between Angie, Andy, and the Joshua tree, and the real desert was sufficiently mysterious to me that I didn’t need to make any fun-house mirror alterations to move out of my ordinary perspective into fiction.
One thing I love about all of the characters in this collection is that, like Angie and Andy in “The Bad Graft,” they’re not wealthy. They worry about money, and they work hard for it. The grifters in “The Prospectors,” Clara and Aubergine, for instance, are as much victims of societal oppression as the twenty-six impoverished men of the Oregon Civilian Conservation Corps who built the grand Emerald Lodge and then died in it when an avalanche swept the building away. On the surface, “The Prospectors” reads like a classic ghost tale, and yet at heart it strikes me as a political story. Do you think of yourself as an overtly political author? Or am I projecting too much?
I don’t think you’re projecting at all, although I rarely have a wholly conscious ambition for a story when I begin, beyond a wish to explore a certain collision of landscape and character and desire. I did have an inkling, when I began “The Prospectors,” that the catalyst for the story would be two young women who were prospectors, treating their future together like speculators, panning for golden horizon light somewhere far from home. And that we’d watch their early hope darken into a kind of desperation, and see how hunger, figurative and literal, can underwrite many forms of denial and delusion.
Shortly after I moved to Oregon I visited the Timberline Lodge on the side of Mt. Hood, “an architectural gem atop a natural wonder,” the showpiece of the Works Progress Administration (made famous by that ominous aerial shot that opens The Shining, to which this story certainly owes a debt). I was so moved by the black-and-white photos of the WPA and CCC crews, these bony young men trying to hoist themselves and the nation out of the Depression by building a fantasy ski resort. These boom and bust cycles in American history fascinate me; today, Oregon’s coastline is haunted by once-bustling ports and timber towns. The Columbia River bar is home to so many shipwrecks it’s known as “the graveyard of the Pacific.” I am always interested in the dreamers who navigate the shoals, who discover, often belatedly, that their dream is poorly suited to the reality in which they find themselves. The West is rich in stories of those dreamers who succeeded, but there are so many nameless others who got mowed under, and today we have a president who talks about “winners” and “losers” as if the entire onus for success or failure is on individuals, when in fact from birth onward the deck is stacked so profoundly against millions of people in our country.
I hope “The Prospectors” has contemporary resonance for readers, both insofar as it explores the way financial insecurity can transform interior and exterior landscapes, and because it looks at the way that women are often tasked with supporting an entire infrastructure in unacknowledged, uncompensated ways (in this story, Aubby and Clara do their “prospecting of the prospectors” by quite strategically propping up male egos and underwriting a ghostly world of male power and ambition, siphoning off wealth’s remainders, long before they are called upon to donate their life force to the phantom lodge and the ghosts inside it, minting them into reality). The precarity of the women’s position on the mountain, the careful way they maneuver through that party, is not so distant, I think, from the existential and economic calculations many women must make today in our tilted world.
Throughout the collection, these political and symbolic dimensions never compromise the narrative. By which I mean, your stories open themselves up to interpretation, they seem to invite it, and yet they’re always first and foremost gripping, expertly told tales. When writing, do you consider the figurative elements of the story, and what the reader might see in it? Or are you simply trying to tell the tale?
A friend of mine whose work I adore, Kevin Brockmeier, recently told me, when I asked him a question about his new book, “It’s as open to my discovery as it is to the reader’s.” I do feel that if a story is working at all, that has to be true; there has to be some mysterious and uncontrolled dimension to it that continues to offer itself up to interpretation. At the same time, I usually begin with at least a shadowy notion of what the story’s concerns might be; and then in the best-case scenario, a story eludes my initial ambitions for it and takes on a life of its own.
You’re a parent now, and I’m curious to know if that’s affected your work in any way, both practically—in terms of carving out time for writing—and creatively. We’ve bonded over our appreciation of Stephen King before, and I’m especially a fan of Pet Sematary, which explores the dark side of a father’s desire to keep his family intact; he literally violates the laws of nature, bringing his dead son back from the grave. Helen Phillips’s excellent forthcoming novel The Need covers similar terrain. The fantastical situations in these narratives shed light onto the shadows of parenting that realism can’t illuminate quite as effectively, I think. For me, your story “Orange World” exists on this same level.
I love Pet Sematary too, for the same reason, the deeply human wish at its core and the shadow side of the father’s love. I reread recently, and am still haunted by, Doris Lessing’s maternal horror story The Fifth Child. And I just started Helen Phillips’s The Need this very week, and it is wonderful. Her previous novel, The Beautiful Bureaucrat, was such a good friend to me when I was pregnant with my son.
My son has changed everything for me, in ways that I am still finding difficult to articulate without defaulting to cliché. I felt quite muted by the experience and I was very grateful when I began, slowly, to write fiction again. Perhaps half the stories in Orange World were written during my pregnancy and the early months of our life together; I turned the book in a couple months before his second birthday. I’m pregnant right now, with a daughter, due the first week of August, and I will tell you that the most notable way this has affected my work is by making me a much slower writer. But I also feel more like a writer, if that’s not too contradictory—a writer who is having a hard time finding her rhythm on paper at the moment, maybe, but I do think I’m paying a new kind of attention to this place.
I want to say here that I don’t want to give accidental support to the pernicious old story that motherhood is somehow a woman’s highest calling; innumerable stories of love and transformation are currently unfolding on our planet and this is one of many. But I do feel transformed, on a cellular level. Wrenched open, and riveted to my skin, and zipped into the present moment with my son in a way that reminds me strongly of my own early childhood, when one’s home was the size of the Universe and everything had a particularity and sheen and shadow to it—a unique life, because nothing had a precedent yet.
That might be my way of disclosing that a practical change is that I spend a lot of time at home with our son right now. So there’s the exigencies of diaper-changing and feeding and the repetitive fear that causes me to comb over our stairs for potential hazards, and this is not my favorite use of the imagination, whatever scenario-generator now compels me to view the bathtub and the playground and etc. as possible Lands of Present Hazards and Future Regrets. If you were to look at a day’s itinerary, it would seem happy and boring, and in no way revelatory of the intensely bright and also shadowy emotional landscape we are living. It also would fail to suggest the atmospheric pressures and shared global and local concerns of our surreal epoch, where so many lives impinge on our own thanks to new technologies, and yet the reality of others’ suffering often gets flattened into pixels on the screen. I remember looking down at my phone a few months ago to see, stacked in my push notifications, “Migrants tear-gassed on the border” and “Get the most out of Cyber Monday!”
I desperately need speculative fiction right now, as a writer and a reader, to open up an elastic space where it’s possible to represent all of the dimensions of love and of horror, the utopias and dystopias co-evolving on this planet. So if there’s something crazy happening—a huckster demon with a thirst for mother’s milk shows up, say—it’s in the service of a kind of extreme emotional realism. Or as Flannery O’Connor says, where “the truth is not distorted…. but rather a distortion is used to get at truth.”
Brian Gresko is a widely published writer and editor of the anthology When I First Held You: 22 Critically Acclaimed Writers Talk About the Triumphs, Challenges, and Transformative Experience of Fatherhood. He cohosts Pete’s Reading Series, the longest running literary series in Brooklyn, New York.
Orange World by Karen Russell
Karen Russell reads an excerpt from her new story collection, Orange World, published by Knopf in May.
A Great Good: An Interview With Jacqueline Woodson
Jacqueline Woodson is the author of more than two dozen acclaimed books for young adults, middle graders, and children—a body of work that places African American characters at the center of richly drawn narratives that have helped young readers engage with real-life situations such as interracial relationships, child abuse, poverty, and homosexuality.
Her own childhood story—she was a precocious daughter of parents in a troubled marriage, who found solace in the imaginative world of books, and eventually in writing—forms the basis of her New York Times best-selling memoir Brown Girl Dreaming (Nancy Paulsen Books, 2014), which won a National Book Award, the Coretta Scott King Award, the Newbery Honor Award, an NAACP Image Award, and the Sibert Honor Award. Brown Girl Dreaming also traces Woodson’s journey from Ohio to South Carolina to Brooklyn, an eye-opening childhood in which she learns, among other things, about the regional differences of the black experience during the 1970s.
With the release of Another Brooklyn (Amistad), her first adult novel in twenty years, Woodson revisits that important period of dramatic social changes. August, a young black girl who moves with her father and brother from Tennessee to the culturally rich Brooklyn neighborhood of Bushwick, comes of age during a time when her empowerment as a black woman offers new freedoms as well as familiar demons: classism, racism, and sexism. Another Brooklyn follows August as she learns the hard lessons of adolescence, uplifted by the strength of her girlhood friendships and guided by her family’s religious conversion. All the while, the terrible truth of her mother’s fate back in Tennessee weighs heavily on her emotional well-being.
I sat down with Jacqueline Woodson at her home in the Park Slope neighborhood of Brooklyn for a conversation about her new book, New York City’s literary legacy, gentrification, Islamophobia, and happiness.
The dedication of Another Brooklyn reads “For Bushwick (1970–1990) In Memory,” which covers the span of August’s coming-of-age in the novel. The reader also gets to observe Brooklyn come of age, as it negotiates the changes and challenges of those eras, through the perspective of a young black woman—a point of view that’s relatively absent from the portrayals of Brooklyn in literature. What drew you to tell this story at this stage of your career? Why this book now?
The Bushwick that’s on the page is a true place, as it exists in the book. I wanted to put that on the page in its true existence because when a neighborhood becomes gentrified, its new inhabitants think they’ve discovered someplace new, but that place had a story before them. Bushwick is its own character, and this book is one of its biographies. I wanted to pay homage to the Bushwick I grew up in, so my dedication also suggests this book is an elegy to a place and time that is no longer with us. Overlaid on that biography is the narrative of the four girls, which is fiction. After having written Brown Girl Dreaming, which is a memoir, I really wanted to move away, just for a moment, from children’s literature and explore something I felt was invisible, which is the story of the black girl in Brooklyn.
In the novel, we meet August as an adult looking back at the place where she grew up. But what does Jacqueline Woodson have to say about the Bushwick of today?
August in the book is looking back with a kind of melancholy or longing for this intensity of that period she lived through. Jacqueline Woodson looking at the place now—I look at it in wonder because I still go to my old neighborhood a lot and I’m just surprised by the fact that I grew up with white flight. Most of New York City was on the edge of white flight at the time, but now I’m watching the reverse of white flight, with white folks coming back into the neighborhoods their ancestors fled from. It makes me marvel at how cyclical everything is.
I’m trying to place Another Brooklyn as part of the borough’s writer-of-color lineage. I see Paule Marshall’s Brown Girl, Brownstones, published in 1959, and there are a few contemporary works, such as Daniel José Older’s Shadowshaper, but one has to really dig hard to find those narratives that are not centered on white characters. What areas need that literary attention in order to expand what is celebrated as Brooklyn’s—and New York’s—cultural heritage?
There is so much territory left to explore in New York City in general. I feel like Brownsville is not on the page, East New York is not on the page; there are stories from the Bronx and Harlem, but since Down These Mean Streets by Piri Thomas not enough books about the black NYC experience are getting talked about. DJ does a great job in Shadowshaper, writing the black Latino perspective on the page, but we need more. Even in the Bushwick I grew up in there was a larger Dominican, Puerto Rican, and Ecuadorean population—I would love to see those stories, that Brooklyn.
And I’m even remotely interested in the vision of the kids of the hipsters who are growing up in those neighborhoods now. I know their stories are not going to be my story because of our differences in class and race, but I feel they too are part of all of these deep pockets that are not represented. I’m waiting for more stories from Queens—from Jackson Heights and the Hindu population. There’s so much that still needs to be told in order to shape this city in a way that’s nuanced. We still have a pretty flat narrative.

There are a few parallels between Jackie’s story in Brown Girl Dreaming and August’s in Another Brooklyn: Both young black women have roots in the South and eventually journey north with one parent. One gives shape to her memories through her affinity for language, the other comes to terms with her losses through her knowledge as an anthropologist of the rituals of death and dying. Agency is an important fire in your work. So is memory. How do you see these as critical components of a young black woman’s experience?
Starting with memory, when you look at who we are as a people and how we got here and what we were allowed to hold on to: We were allowed to hold on to our spirit—a certain amount—and we held on to our memory. No one could take that away unless they beat us unconscious. I believe in genetic memory, that our ancestors are pretty much with us. And I believe in asking questions about the past to make historical connections because that’s what gives us strength. And in terms of agency, I grew up in the 1970s, which was so much about black power—taking your power, owning your power, making yourself visible in the world even if the world wasn’t reflecting you back. So as a writer I feel that every time I sit down to tell a story it is to create that mirror for myself and for other readers who have historically not seen themselves in the pages of literature, and to talk about how badass we are, because there’s so much strength in being a person of color and having survived.
Another Brooklyn is being marketed as an adult novel. But with contemporary YA novels being edgier, taking risks that keep their stories ahead of their time, could you imagine your younger fans reaching for the latest Jacqueline Woodson title? Is the YA designation fast becoming a fuzzy category?
Oh, I think I see my audience reaching for this book the way I once reached for Judy Blume’s Forever—“Wait, she has an adult book? There might be some sex in it!” So I definitely see that happening. Also, having been publishing for twenty years, my population has grown up now, they’re adults. So I definitely see them reading it. But I do think that distinction between YA and adult is fast becoming a fuzzy line in terms of subject matter. There are still differences in the approaches to writing the two narratives, but today’s YA author is claiming more permission to take risks in order to keep up with a changing world, which is why our books continue to be banned.
Is Another Brooklyn an adult novel because of the treatment of sexuality? Not only August’s own sexual desires but also all of the lessons August learns about women and their bodies: from Muslim women, from prostitutes, from her own friends who are experimenting and pushing boundaries. Why is this still important work to do on the page?
For too long we were given the wrong messages about our bodies, especially as women of color, and I wanted to show that a girl’s sense of her body is really shaped by the outside gaze, by the mirrors in her community. But I also wanted to show her agency and the way women can come together more powerfully. At one point in the book I have August with her girlfriends, and she’s thinking about how boys don’t understand why girls cover themselves even when they’re alone. It’s important work to do on the page because we are sexual beings and we have a right to be so and to walk through the world with these bodies. Living in the age of Beyoncé is really exciting for me—she’s not only celebrating the black body, but also the big body. I grew up with Twiggy as an idea of what is a beautiful body, but thankfully I also had Angela Davis and Diahann Carroll. I was informed differently, but when I’m coming to the page—because the narrative is so much bigger than real life—I have a responsibility to write what I believe in, in terms of representing more fully who we are as women.
There are so many rich layers to the life of August—her girlfriends, her brother, her love interest, the father’s love interests. She’s at the center of a complex support network, but one character who really stands out is Sister Loretta, who guides the family through their conversion to Islam. August says, “My Muslim beliefs lived just left of my heart,” meaning she understood everything that religion was providing for her and her brother, including structure and a mother figure. Was this a decision that came about given this country’s escalating Islamophobia? What do you hope readers take away from this encounter with a black Muslim family?
It’s really a scary time to be living in. And Islamophobia happens when people are thinking, “Muslims are those people over there and have nothing to do with us.” Putting their humanity on the page was really important to me. We exist in all kinds of religions and this is the religion of this family, and the book deals with how this girl is taking in this religion because she’s negotiating it against this space and time of friendships and sexuality and puberty and adolescence. And faith. That’s all part of August’s journey.
I was talking to a friend about the shooting in Orlando, and during these times of crisis it’s so hard to remember the kind of work we do as artists. It’s nonstop. Much of it is economic, but so much of it is also emotional and at the core of who we are. Like Audre Lorde said, “We must wake up knowing we have work to do and go to bed knowing we’ve done it.” And writers, especially, every time we sit down to work we are working to impact a great good. And even though I am not always conscious about what is happening, when I sit down to create the narrative I know that all the information coming in from the world is informing that narrative.
The four young women at the center of Another Brooklyn—August, Sylvia, Angela, and Gigi—create such a special bond that it’s difficult to see those friendships begin to crumble. You once said that one question you wanted to explore through writing was “what is the happily ever after?” After completing this novel, dozens of books into your career, and as times change, what have you come to understand about happiness?
That it ebbs and flows like every other emotion we have. I think that if I were happy all the time I’d be the most boring person in the world. The nuance comes from working towards happiness and not always getting there, or some days getting there surprisingly so. That I can wake up in the morning and get to write is amazing to me, so the mere fact that I’m here and that I’m able to tell my story is the happily ever after for me.
Rigoberto González is a contributing editor of Poets & Writers Magazine.
The Emotional Realist Talks to Ghosts: A Q&A With George Saunders
In the late spring of 2000, on my first feature assignment as a twenty-seven-year-old editorial assistant for this magazine, I took the five-and-a-half-hour train ride from New York City to Syracuse, New York, to interview the author of one of that summer’s most highly anticipated books, the story collection Pastoralia (Riverhead Books). George Saunders had not yet received the kind of popular acclaim and critical recognition that followed him in the years to come, in the form of a MacArthur Fellowship, the so-called Genius Grant; the PEN/Malamud Award for Excellence in the Short Story; an Academy Award from the American Academy of Arts and Letters; the Story Prize; and so many other honors. He had not yet appeared on The Late Show With Stephen Colbert or This Week With George Stephanopoulos, or been named by Time magazine as one of the hundred most influential people in the world. He had not yet delivered the convocation address at Syracuse University that was posted on the website of the New York Times and then, within days, shared more than a million times on social media.
Back in 2000, when the author had published just one collection, CivilWarLand in Bad Decline (Random House, 1996), and his second was just starting to gain momentum, the name George Saunders was already on every critic’s tongue, but the literary world had yet to discover the true depth of the author’s talent. Seventeen years later, we still haven’t touched bedrock, though his subsequent books—two more story collections, In Persuasion Nation (Riverhead Books, 2006) and Tenth of December (Random House, 2013); a novella, The Brief and Frightening Reign of Phil (Riverhead Books, 2005); a children’s book, The Very Persistent Gappers of Frip (Villard, 2000); and a collection of essays, The Braindead Megaphone (Riverhead Books, 2007)—have added to the already overwhelming evidence that we are in the presence of a writer whose boundless imagination, laugh-out-loud humor, moral acuity, and, though he would protest the characterization, generosity of spirit truly set him apart.
Saunders’s soaring talents are once again on display in his long-awaited debut novel, Lincoln in the Bardo, published in February by Random House. Presenting a kaleidoscopic panorama of voices (the audiobook employs a cast of 166 narrators), Lincoln in the Bardo is set in a graveyard, over the course of a single night in 1862, where President Abraham Lincoln grieves the death of his eleven-year-old son, Willie, while the boy’s ghost confronts a congregation of other spirits in a strange purgatory—called the bardo, in Tibetan tradition. It is a wonderfully bizarre and hilariously terrifying examination of the ability to live and love with the knowledge that everything we hold dear will come to an end.
Seventeen years ago, Saunders offered to spend more of his time with me than any professional obligation or friendly courtesy required of him. It was my first, and fortunately not my last, opportunity to get to know this bighearted, wholly original writer. In December we met again, at a hotel on the Upper East Side of Manhattan, where we spoke for several hours about emotional realism, humor as a form of honesty, the flexibility of form, and, because this is George Saunders, poop jokes.
In 2000, I asked you if you’d ever tried to write a novel, and you replied, “Most of those stories in Pastoralia started out as novels. I’ve tried and I just recently got to the point where I’m not going to try anymore. If it happens, it’ll happen organically.” Here you are with your debut novel—so, did it happen organically?
The idea for Lincoln in the Bardo had been around for a long time, and I found myself saying, “Well, I’ll do it, but I’m not sure it’s going to be a novel. I’m hoping it isn’t. I’m going to push against it whenever it starts to bloat.” And that principle seemed to be a good compositional principle, you know? If something tries to push its way into the book, you give it a stern look and say, “Are you just here because you think this is a novel? Because that’s next door.” So that meant, too, that all the moves I developed [writing stories] over the years were of course the ones that I used. How could it be otherwise, you know? But about halfway through, I said, “Oh, this is a novel only because it’s on a bigger stretcher-frame.” But each of the individual sections was being executed by the same principles as a story would be. So that was a relief.
You just treated it like pieces of a story.
Yes. And I don’t know if other writers do this, but there’s that moment where you go, “Oh my God, I’m writing a novel. Anything goes!” And a couple of times I got in trouble because that mind-set took over. And then I would get that back in the box and say, “No, it’s by the same principles as all these stories: efficiency, one section producing and then leading to another. That’s it.” And then I would get back on track. So it was like the more I said, “The principles don’t change, but maybe the scale changes,” then I could do it. It was really a comfort to know that, in art, form is a way of accommodating one’s natural inclinations. If your natural inclination is to make small, concise structures, then form shows up and says, “Would you like me to help you link your small, concise structures?” And then form seems organic; it doesn’t seem whimsical. It doesn’t seem arbitrary. It seems organic, because it’s what allows you to accommodate your strengths.
Actually, at one point, a long time ago, I tried to do sort of a third-person version of this. And it was just dull, you know? “Lincoln walked into the graveyard. It was a dark and stormy night.” And sometimes you get into a zone like that, and you recoil. Like, no, no, no, I’m not using that voice. I can’t do it.
How far did you go using that voice?
A page. Maybe two pages. It just felt creepy. And it was funny, because I loved that idea, but the prose was doing nothing to get me into a happy zone vis-à-vis that idea. It was just, like, typing about Lincoln. So that was no good. But I did try, over the years, to write a play. Kind of the same thing: It made me more convinced that there was definitely a story there, but that wasn’t it. The play wasn’t it, for sure.
That wasn’t the form that was going to allow you to tell the story.
No. And strangely enough, the book is kind of playlike. But it was just, you know, sometimes you think—for me, for example, when I think, “I’m going to write a poem today,” it’s a guarantee that bullshit will come out of my head, because I’ve said I’m going to be a poet, and I just don’t have that gift. So my “poems,” in quotes, sound like poems in quotes. They’re just not good. The play was like that. It had a certain kind of faux-dramatic quality that just wasn’t interesting.
And how far did you get into the play?
I finished it. I did twenty or thirty drafts. I kept thinking, “I’m going to figure out something here that makes this work.” At one point I put a big sign across it: Don’t Touch It! Just stay away.
That makes me think of something Colson Whitehead said when we talked for a recent episode of our podcast, Ampersand, about The Underground Railroad and how the idea for that was something he’d had fifteen years ago. And he just put it aside. He said he wanted to wait because he didn’t feel like he could do the idea justice. He wanted to become a better writer before he tackled that subject matter.
That’s exactly the feeling I had about this…. I feel like my whole trajectory has been as a person of quite limited talent who’s a little strange and learns to harness that strangeness to accent the talent. So then you’re walking on a pretty thin ledge for the first two or three books. I think the thing has been trying to make my work—I’ve said as “happy” as I am, but I’m not sure I’m really that happy—I’m trying to make my work more like me. And so, over the past twenty years, the process has been trying to expand my toolbox to allow access to these different emotional valences that I didn’t really have access to early on. Or, I had access to them but only through a really dark route. I don’t think those early stories are particularly not hopeful. I think they’re kind of hopeful, but you’ve got to go a long way to get there, you know?
I suppose it’s like one’s personality: When you’re young, you’re a little insecure, you’re a little stealthy, and you try to find your way in the world, so you start embracing certain approaches and eschewing other ones. Then maybe at some midlife point, you go, “Wait now, I wonder if there’s more to me than this,” and you start to try to become more expansive, or maybe just get a little more comfortable in your skin, and you go, “Okay, I’m going to reconsider.” So for me it was an artistic enactment of that, which happened when I started writing essays. Especially the travel essays. Andy Ward, whom I worked with at GQ, had a really nice way of encouraging me when I would get into a place where I wasn’t relying on humor quite so much. And that in turn led to the Tenth of December and a couple of stories where suddenly I was drawing more directly on my real life…and finding that you could actually do that and still have a good prose style. Those kinds of things were the ladder that led me to be able to try this book.
What was the initial germ of the idea for this novel?
We were in D.C. and driving by Oakhill Cemetery, and my wife’s cousin just casually pointed up and said, “That crypt up there…” I don’t know if we could actually see the crypt, or if we could just see the graveyard, but he said, “Lincoln’s son was buried up there.” And at that point, I didn’t even know Lincoln had a son. I’m not exactly a history major. And then she said, “Yeah, you know, he died while Lincoln was in office, a very low moment in the presidency, and Lincoln was so bereft that he apparently snuck out of the White House, crossed the city at night, and then newspapers at the time”—I’ve verified this since—“said that he had touched or held the body several times.” So that’s just one of those weird historical things. One, that a president at that point in history could leave the White House. This was during the Bill Clinton years, so you thought, “Bill Clinton’s not coming out at night.” And then also, as a father, just this sense of loss, and also the idea that, at that time, to touch and hold a body wouldn’t have been considered quite as morbid as we consider it. And this doesn’t happen to me, I’m not a real visual person, but there was just a pop of that image of Lincoln with the body across his lap—the Pietà, a monument or memorial or whatever. And then your mind goes, “Oh, that’d be a good story,” and I just had a feeling like, “Yeah, not for you.” Because maybe at that point…what year did we see each other?
That was 2000.
So it would be around that time. A little earlier than that, because Clinton was president. At that point I had just gotten up on my feet a little bit with a certain voice and a certain approach to material that for me was very new. So when I just did the mental transposition of that material with what I thought was my voice at that point, it’s almost like sparks: “Nah, that isn’t right.” So I put it aside. I’m not sure I was so confident I ever would write about it. But I remember kind of thinking, “Yeah, there are people who could do that, but in this life, maybe it’s just not me.” And there are lots of stories in the world; I just happened to hear that one. No problem. But it definitely persisted. And the way I knew it was, I have a range of, like anybody, happiness and not-happiness, and whenever I’d be happy, that idea would almost come stand behind me and go, “Would you please?”
But every time I thought of it, I got that uncomfortable feeling like it was more than I could do. I’m not sure I was quite as confident as Colson that I would get there, but I just wasn’t able to get over it. So that’s interesting: an idea that just refuses to be boxed. That’s kind of weird. And I hadn’t actually ever had that feeling before. I normally don’t even think in ideas. So I felt a trap was being set, because when I was a younger writer, I would have those kinds of ideas: A novel in which…
The grand elevator pitch.
Right. And then nothing would happen. So I was really resisting it. But when I have an idea like that, it’s trying to summon me into some new artistic ground. I was permitting parts of myself into the book that I had been keeping out all these years—genuine parts, and parts that I wanted to have in there. And somehow the idea went, “Come here, come here, come here. Trust me, trust me.” And I’m like, “I don’t know, I think it’s a trap.” And the idea said, “It is! It’s a good trap!”
And suddenly, you find yourself in really interesting, dramatic situations where the only way out is to summon up those previously suppressed or denied parts of your psyche that can finish it. And for me, those tended to be the more hopeful parts, actually. Or, hopeful and narratively straight, being comfortable with drama, no need to turn around and make jokes, just stay in that zone a little longer than I would normally be comfortable with. And then turn around and make the joke. It was a great experience.
I listened to an interview you gave around the time Tenth of December came out. And you were talking about how you were a little nervous about the reception of it, because you felt like it had more realism in it than your earlier work. Do you see this as a kind of trajectory, that you’re kind of pushing toward more realism?
It’s funny, in talking about writing, I think people tend to make binaries. I don’t know why, but a student will come in and say, “I don’t know if I want to be funny or serious.” Or sometimes they’ll link it to people: “I either want to be Kerouac or Flannery O’Connor.” I don’t know why these writing problems present as binaries, but they seem to be neurological. So then of course one of the things you can do is, you can destabilize the binary. If you like O’Connor and Kerouac, put them on one side of the binary, and who’s on the other side? In this new novel, it’s a kind of realism, but when I think about writing a truly realistic book, I don’t have any interest in it. So I would say it’s emotional realism. And the goal has always been—that’s actually what it is, that’s the first time I’ve realized that: It’s just to have the fiction somehow simpatico with my actual emotional life, or let’s say with our actual emotional lives. I think that was always the goal. In CivilWarLand, that’s what I was trying to do. I was in a pretty rough patch. But I think the idea would be to say, “Okay, I’m going to try to remember every emotional state I’ve ever been in, and then assume that there are a bunch I haven’t been in, and that out in the world, all the ones I’ve ever experienced are still going on. It’s not like being a depressed eighteen-year-old went away because I turned nineteen.” So then you try to experiment, to imagine all those coexisting [states]; develop a style that would allow you to talk about that. I don’t really care much about realism, except in that sense. What does the human mind actually produce for us? What experiences and prejudices and impulses and desires? How do those desires actually play out in the real world? To get to the point where you could actually accommodate that would be the goal. And that makes sense for my work, because this novel isn’t—there are only three living people in the book, so I don’t know if we could really call it realism, but I think it certainly felt like I had more room to be emotionally realistic. In other words, to be able to write about grief not glancingly but rather directly. There’s some of that in the early books, but it’s always just a quick hit and move on, almost like a marker of grief. To be able to turn directly to it for three hundred pages feels to me like a step in the direction of emotional capaciousness, let’s say. So the goal would be, when I’m three hundred years old and I’m finishing my last book, that to anybody who walked in I’d be able to say, “Oh yeah, I get that. I love you, I understand you. Let’s have a book about you.” Whereas even now, there are some areas of human experience where I’m just like, “Yeah, I don’t know enough.” Or maybe I don’t have enough generosity of spirit.
In the interview you did with Random House—the one that appears in the back of the ARC—you talking about this book being a sort of chorus of voices. And you say, “These are people who did not in life manage to bring forth what was within them.” Where did that come from? It’s a psalm, I think.
It’s the Gnostic Gospels, yeah. In some ways it’s just traditional ghost theory, which is, “Why are you here?” “I want my liver back!”
Unfinished business.
That kind of thing. And that kind of melded with the Tibetan bardo idea, which is to me the more interesting and scarier idea: whatever way that your mind works in real time, right this minute, right this second. The body’s going to drop away, and that’s going to continue, but exaggerated. So with Heaven and Hell, it becomes a little complicated. It’s not: “Turn left, you’re in Heaven; turn right, you’re in Hell.” It’s: “Where are you right now?”
There’s that binary you were talking about again.
Exactly. There’s something that’s Heaven-esque maybe. So if a person had gotten into a relationship with their thoughts in this life in a way that made them mostly pretty loving and happy, then I guess the idea would be that when you kicked off, that would continue. Or if you were an intensely self-flagellating, suspicious, greedy person whose every thought was sort of infused with that, then when you die, that could continue. That’s the theory. But the fun thing about this book was, your temptation was to say, “Well, let’s figure out what the afterlife is, and I’ll put it in a novel.” Well, I’m pretty sure that whatever it is, it’s not what you think it is. So part of it was fun. To make the afterlife surprising was a pretty natural thing for a comic writer to do. You know how to make things weird and surprising, so to take the afterlife and just make it a little bit strange. I didn’t want it to look like the Christian Heaven, I didn’t want it to look like the Buddhist Heaven. I wanted it to look like nothing you’d seen before, to simulate the idea that if you went there, you’d be like, “Oh my God, what is this?”
You’re referencing Heaven a lot.
They’re not in Heaven.
I read this novel as much darker. It inhabits a much darker space.
Yes, that’s true.
Back when we first talked sixteen years ago, you said that you could only write comic fiction. You said, “Humor, I don’t know, but comic.” So, is this a comic novel?
Yes. I think so. But…I got to certain places where, in early rounds, the material was so straight. Sort of slavishly straight. It just had a History Channel vibe in the early drafts. And that panicked me a little bit, because that’s where it looked like it wasn’t emotionally honest. It was something else. So I kind of panicked and dropped in a couple funny things. And they just didn’t belong in that book. They were kind of funny, but they also were…it’s like somebody in the middle of a marriage proposal who senses he’s going to get a “no,” so he does a fart joke. You know? You think, “Well, that’s a desperate move.” So then I had a few days of just saying, “Okay, wait a minute now.” Again, in the binaries: I was saying funny versus not-funny. Then I thought to myself, “Is there a way to turn that? And whatever it is that I have always thought of in my work as funny, or people have thought of as funny, can we rename that a little bit?” Just to give myself a little bit of room. And I thought, “Well, all right: How does a joke work in fiction?” I think the way it works is, you and I are walking through the story together, reader and writer, writer and reader, and there’s something I’ve said behind us, and I suddenly remember it. As we’re going into the apartment building, I eat a banana, I drop the peel. And then we’re coming out of the building, and I remember that, you know? And you have just said something really arrogant to me, and then you step on the peel and you fall. That’s comedy. But really, at its essence, it’s the writer remembering what he said. In other words, it’s a form of narrative alertness. So then I thought, “Okay, since this draft is a little straight, is there a way that I’m not being narratively alert enough?” And I could show you, there’s one particular moment where I had the three ghosts arriving, and I’d forgotten that they all had these crazy features, these physical manifestations. Just by the act of putting those descriptions in, the text came alive, and the text coming alive made me hear them better. And I gave them a couple funny lines. So the whole thing came alive, but with, I would say, narrative alertness. So then suddenly it gives you a little more freedom to do things that don’t break the tone of the scene. From then on, I’m like, “Oh yeah, you don’t have to be funny.” People like it when narrative alertness becomes funny, but there’s a lot of forms of narrative alertness. Cormac McCarthy is the most narratively alert person you could ever ask for. Not particularly funny, but when he’s moving through a landscape, he doesn’t forget anything that he’s made. It all comes home in that beautiful language.
The Orchard Keeper.
Unbelievable. And he sometimes can be very funny actually. But you can see that he’s not addicted to or looking for that. He’s just 100 percent alive in his fictive reality. Actually, Toni Morrison—I taught Sula this year: same. She can be very funny. But the main thing I feel with her is that the fictional world is just crackling with life, and the author is just generously looking around, blessing it all, and asking, “What do I need?” And that question means: What will make the most beautiful sentence I can put in front of you to make you feel as alive in the fictive reality as I am? So whether it’s humor or not is maybe a low-level understanding of that kind of interaction between reader and writer.
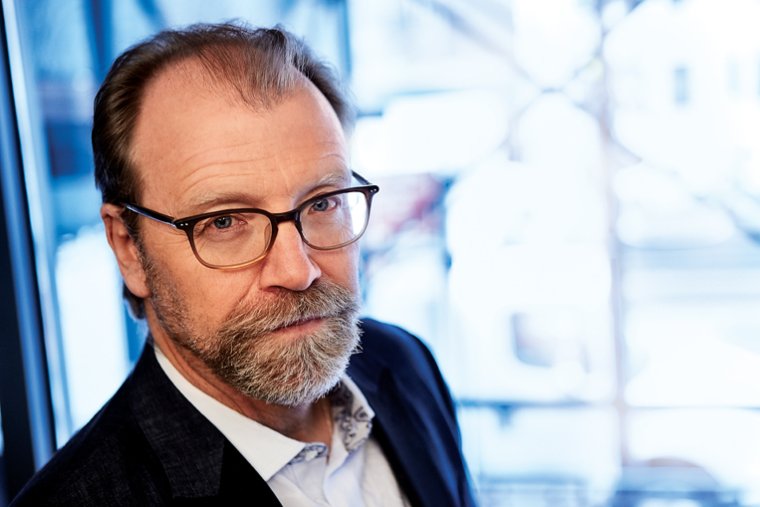

Well, I’ll tell you, when I started reading this I wasn’t sure what to do. Because I know you, and I’ve read all your books, and then here’s this novel. And it’s had such big fanfare. “George Saunders has a new novel, and I have all the feels,” that sort of thing. And I was reading along, and pretty early on you write, “When we are newly arrived in this hospital yard, young sir, and feel like weeping, what happens is, we tense up ever so slightly, and there is a mild toxic feeling in the joints, and little things inside us burst.” And so I stopped for a second, because so much of it, too, is that when a reader enters your work, so much depends on where the reader is as well. You don’t have complete control over the reader.
Not at all, no.
So at that phrase—“little things inside us burst”—I guess I was feeling emotional, and I knew I was about to read a novel about a father losing his son. And I have young kids. You know, it’s all those little things that are happening in the reader. So I read that sentence, and it’s like, “Oh, the dead are weeping.” And there are very real emotions in here that I’m thinking through as I’m reading. But then the very next sentence is, “Sometimes, we might poop a bit if we are fresh.” And right there we realize we’re in George Saunders’s world.
It’s so funny you should pick that out, because in the manuscript, that’s said on page two. In the galley, it’s deeper, but in what I worked on for many years, it was two. And I remember thinking, “I just hope my readers will make it to the poop joke.” And that’s my weakness, but I was just thinking, “That’s where I’m signaling that I’m all here.” I didn’t turn into a super-straight realist guy, which is a fear of mine, because humor came into my writing as a form of emotional honesty. We’re talking about when I was really young. I kept it out when I was trying to be Hemingway, which is a form of emotional dishonesty. My wife and I got married, we had our kids, we were having a great time, but we were pretty poor, all working really hard. The humor came back in at that point as “Holy shit, what’s going on here? This is really hard.” So that was honest. My fear is always that as you get old and august, the world actually stops being so difficult, and it’s not that funny anymore. Please note that I’m saying this in a British accent. [Laughter.] So in that case, again, that would be a form of emotional dishonesty. Just because it’s not happening to you doesn’t mean it’s not happening. In that first long section I hope my readers don’t think I’m that guy now, that I’m just indulging in a straight historical narrative with capital-R Romantic tendencies. For me, that joke was a place to sort of breathe a little. You with me? I didn’t leave anything behind. I’m still doing it.
You did it.
But it sounds like you could have used a few more beats of the emotional stuff before the poop stuff.
You get a great mix of both in this novel. In all of your work.
You know what it reminds me of? If you were a Led Zeppelin fan, and then, what’s the album, the one with “Over the Hills and Far Away” on it?
Houses of the Holy.
There are parts of that album where you think, “Oh my God, where’s Jimmy Page? Where’s the guitar?” And they know that, and they’re kind of setting you up a little bit with those swelling strings, and then all of a sudden it starts. So to me, it was a little bit like, let’s make sure we don’t leave anything behind.
Let’s go back to something you said earlier about the essays that you were writing. You had mentioned that those gave you an opportunity to do a little bit of work on writing about your own emotional responses to things, which is in your fiction, but it’s not you, George Saunders, saying, “I feel this way.” There’s a part in the “Buddha Boy” essay, which a lot of people talk about because it’s a terrific essay….
Oh, thanks.
Do you mind if I read it?
Yeah, no, I love it.
“You know that feeling at the end of the day when the anxiety of that-which-I-must-do falls away, and for maybe the first time that day, you see with some clarity people you love and the ways you have during that day slightly ignored them, turned away from them to get back to what you were doing, blurted some mildly hurtful thing, projected instead of the deep love you really feel, a surge of defensiveness or self-protection or suspicion. That moment when you think, Oh God, what have I done with this day? And what am I doing with my life? And how must I change to avoid catastrophic end-of-life regrets? I feel like that now, tired of the me I’ve always been, tired of making the same mistakes, repetitively stumbling after the same small ego-strokes, being caught in the same loops of anxiety and defensiveness.” I love that you had the presence and the courage to write that. I really connect with that notion. I think anybody who is sentimental, as you said that you are…
I am.
Perhaps nostalgic…
Yes.
And is very busy and maybe has kids, as we do, you can’t help but feel that way. Some of us feel that way a lot more often than others.
Those would be the good people.
But to push that idea a little further, I have those feelings, exactly what you’re talking about there. And it’s this tremendous feeling of guilt, because I have those moments, and then I even think of myself having those moments, like, “Oh, okay, at least I’m aware enough to be feeling this.”
Yeah, I think that’s true, actually.
But then an hour later, I’m checking my phone and looking at tweets. Yet it’s a wonder I ever leave the house and let my kids and my wife out of my sight. You know what I mean?
I do. I do. I think that you’re right, first of all, that the awareness that one is less loving or less present than one would wish is actually pretty good awareness, you know? Because there were times in my life when I didn’t even have that awareness. I just was…right. I think that’s where, for me, a person’s desire to get better on that score is what leads them to something. For some people, it’s a spiritual push, meditation or prayer. But I think just to be aware of that is huge. But as you say, it doesn’t change.
It doesn’t solve anything.
I know I can’t run a marathon, and I still can’t.
I could go out and train.
I could do that. But I’m aware I don’t want to. And I think that’s part of art. Part of fiction writing is a small training in assessing how good your awareness is. You come back to the page you’ve written, and you’re reacting to it by reading it. And the critical thing is: How fine-tuned and honest are your reactions to your own work? So a part gets slow; do you notice it? Do you honor the fact that you noticed it? Are you willing to try to fix it? And then the second level is: You’re aware of your reaction to the work, then outside of that you’re also aware that that reaction is also temporary and may change. So how then do you revise? You go ahead and make the change. But then the next day you come back and do it again. And at some point, you reach a steady state where your reaction to the piece is pretty consistent. Then you’re good. But for me, that mimics the process of being in the world. How are you feeling right now? How reliable is your feeling about how you’re feeling right now?
I want to say one thing parenthetically about the GQ pieces, because you are right that I was able to turn to my own emotional state to write about them. The other thing that I learned is just the simple mechanics of…describing the setting, which I don’t usually do in my fiction. I feel like I can’t get anything going with that. Well, when you have to do it, you find that you can get something going. So there was a part of me that got more comfortable with the power of just describing physical stuff. That was something I had been suppressing. So the idea that I would spend a couple lines describing someone’s looks or something, I usually wouldn’t do it, except if I could get a little joke in there. But now I have more confidence that if I am given the task of describing your face or this street outside, I’ll be able to come up with some language that is interesting in its own right. That is something I learned from magazine writing. You’re driving through South Texas for three hours, and it’s gorgeous. You think, “Do I have something I can say about this?” Once I gave myself permission to do that, I found that, sure, your years of writing have made your language skills good enough to describe a mountain.
I want to refer to something in an essay you wrote, “My Writing Education: A Time Line,” about your experience earning a master’s degree in creative writing at Syracuse University in the 1980s. You wrote about a meeting you had with one of your teachers, Doug Unger, and basically that he didn’t pull any punches in telling you that your thesis was essentially not…it was “crap,” I think, is the word he used.
He didn’t say it was crap; he just didn’t say it wasn’t.
Right. [Laughter.] And your response was that it was difficult to hear, of course, but that he had the respect to do such a thing for you, to not just feed you a line about how brilliant you are. That’s one of the things an MFA program can offer: respect. Because for a creative writer, where else can you go in today’s society where everyone around you respects what you’re doing—maybe they don’t necessarily like your work, but the act of writing is respected. That sort of validation for writers is something we try to provide at Poets & Writers, too: What you’re doing is important. I’m wondering if you could talk a bit about your experience teaching at Syracuse. When we talked in 2000, you had been teaching there for maybe three or four years. Did you have a sense then that you were going to be there for twenty years or more?
I hoped so. Yeah, those early years were really rich, and they still are. There’s something to be gained by staying in the same place for a long time. But I like this idea of respect. That’s correct. And I think, also, what Doug gave me in that moment and what I got from my whole time there was just that standards don’t move, you know? This thing that we are doing is actually really hard, and there are no guarantees that anybody will be able to accomplish anything. So when you get to an MFA program and you realize that there actually are standards that aren’t being imposed by your teachers; they’re being imposed by the world, by culture, and the rabbit hole you have to go down is very, very deep. There are levels of exertion and understanding that you haven’t even touched yet. And the whole purpose for that journey is so you can be most uniquely yourself. That’s what it should do. It should be neither a teardown nor a feel-good factory. But just to say, this thing that you’re doing is really, really difficult, really, really essential. You don’t even know yet. “Know you do not yet” [in Yoda voice]. You’ve got to say, “Actually, this is even harder than you think, and also, we don’t know how it’s going to be hard for you in particular.” To set that up I think is really useful. In some ways, it’s maybe like going to medical school—except for the money—but in the sense that someone teaching young doctors doesn’t say, “It’s all right. You don’t have to worry about tonsillectomies, because you probably will get only about six in your career, so don’t bother.” You know? That’s not a thing. The way you’d know a culture was going down the shitter would be if someone was doing that. I think it’s the same with the arts. But it’s complicated, because part of that process is to nurture, but part of the process is to not over-nurture, which I think can be a problem in MFA programs. You come to love these people so much, and the delivery of bad news is not fun. But respect is the key thing, because if you really loved a young writer and you saw that she was doing something contrary to achieving her full potential, it would definitely be an act of love to put up a sign to stop her from doing that, in whatever way worked. Basically, my prayer is: “Let me positively inflect this person once or twice while she’s here.” More, if possible, but once or twice would be great. If I could just have one interaction so that five years down the line, she goes, “Ah! I now know what he was talking about.” Or the best is when students have walled off certain material that they don’t want to do, they don’t want to do it, but it’s essential to them, and you somehow help them take the wall down. That’s really wonderful. Or when they have been hurt or maybe diminished by some life situation, and you can make them see that that actually is their material, and it’s all right.
Have you noticed any changes in how writers are approaching the MFA?
There are two observations. One is that the relation of the young writer to the MFA program has changed certainly since I was a student. At that time, the idea was kind of like, “Oh, that’s freaky. Let’s be outlaws and do this thing that isn’t actually going to make us richer or whatever.” And there weren’t very many programs. I’d never heard of one until the week before I applied. I didn’t know they existed. And then there’s the false and damaging assumption that if one wants to be a writer, you must go to an MFA program. And the related one, which is, if you go to an MFA program, you’ll definitely be a published writer. That whole suite of assumptions makes a lot of pressure for students. It’s what we call “professionalization,” and I think that’s not so good, and I predict there’ll be some kind of backlash against it. I predict there will be—there probably already is—a group of people who say, “I’m not going to an MFA program; I’m going to do it on my own.” And then we’ll have a series of successes from those writers, and the pendulum will swing. There’s nothing wrong with it, but the most damaging thing is when a student doesn’t get in and thinks, “Therefore I’m not a writer.” That is not true. And it’s a function, at least in our program, of the numbers. We get 650 applications for six spots. We have six spots because those are all that we can afford to fully fund, which we feel is kind of ethically or artistically important. So if you’re number seven, you’re great. It doesn’t matter that you didn’t get in.
Another thing you mentioned in that essay is that when you first got to Syracuse and were studying with Tobias Wolff, who is just an amazing writer, a master—
He’s a genius.
But you had the realization that he’s also a real person. He creates this amazing art for four hours in the morning, and then he goes grocery shopping or picks up the laundry or whatever. And that leads into something I want to talk about, which is how to respond to success. Because here you are, and if people see you picking up your laundry, it’s like, “Wow, George Saunders has this normal life.”
Not as often as you’d think. Mostly they’re just like, “Hmm, who’s that bald dude?”
You’ve been the cover story in the New York Times Magazine and appeared on talk shows; you sang a song with Stephen Colbert. You’ve achieved a very high level of success in this field. And literary journalists and bloggers and everyone on social media will pump that up, rightly so, but we don’t often talk about how, as a writer, you are supposed to respond to that sort of thing.
That’s a great question. I think one thing you can do is watch it. I’ve said before, if you eat a bunch of beans, you’re going to fart. That’s it. It wouldn’t be a disgrace, but you might notice it. So I think anybody, at any level, who has gotten any attention knows this syndrome, which is the birthday syndrome. You get something published, you tell your friends, they get excited, and you get elated, which, as a word, has positive connotations. But I actually see it as kind of a negative. You get elated: You can’t think about anything else and you want more. It’s like a sugar buzz. And then the next day, it’s not your birthday anymore, and you’re like, “What the fuck is wrong with all these idiots?” You know? That’s just the human mind responding to stimuli. So I think part of it is to ask yourself, “Where am I on that scale right now? How full of shit am I based on this attention that I’m getting?” And by the way, that would also go the other way; if you were being criticized, you would have anti-elation.
Deflation.
It’s the same thing, though, because you’re still thinking about only you and your hurt feelings. I think part of my deal is to sort of take everything in my life and subjugate it into the goal of using my talent wisely. So if success starts to occur, go on full alert to the ways in which your natural biologic reactions to success might screw up your work. One way is, you get into the rarefied-air syndrome, where you’re only in cool places being praised. That’s death. You can’t do that. The other thing would be believing that it’s objectively true that you did well. That’s anathema to an artist. Even after a work is done, you have to be going, “I should have done better; I know I could have.” That’s how you get to the next thing. I think most of it is just not believing in it too much, and maybe if you still have a little skill left you say, “Let me also not enjoy it too little, because it doesn’t happen all the time; it doesn’t happen to everybody.”
If we think about talent, talent is like a flower. I wasn’t doing publishable work until about thirty-three. Well, the odds are, it’s going to wilt. It may very well wilt before I die. So you have to treat it as something that you were gifted with briefly, and it may or may not be around. But I also think of it as kind of a fun adventure; especially in this time, I feel like it’s not a bad thing for a writer to work herself into a more public role, to kind of push herself into the public mind a little more so as to push back against some of the stuff that’s going on. But it’s like everything else. Anything that happens to you is going to have some effect on your artistic abilities, so I think part of it is to manage. Even when we met the last time, I had just come out of that period when I’d written a book at work, and the way I understood that was, okay, this is part of it. This is part of the artistic journey. I don’t have enough money, and my hours are getting burned up doing this work. All right, I accept. And then it becomes ennobled. And I found myself empowered by that. If I thought, “Ah, I’m getting cheated by the world,” then that’s disempowering. But to say, “This is part of my writer’s journey,” then suddenly you can take more of it.
We have a little more time, and there are two topics that I want to touch on: One is the election and the other is death.
Wait, there was an election? Oh, you saved the good one for last.
It was very interesting to go back and reread, “Who Are All These Trump Supporters?” which was published in the New Yorker last July. I’ll confess that when I first read it—and this is maybe part of the problem—but my reaction was one of curiosity, almost like being at the zoo or something. Who are these creatures? What’s happening? It was almost a morbid curiosity. Now, rereading it, I think, “Why didn’t we see this coming?” I personally thought good would prevail. And it didn’t.
It did numerically.
It did numerically, but the system did not.
Well, that piece was really hard for me to finish, and I think it was exactly for the reason you’re naming. I went there thinking it was kind of a fringe—at the time, I think 40 percent of people who were going to vote said they would vote for Trump. But I thought it was kind of a fringe thing that would burn out. In other words, I found myself in the position of somebody who takes on the story, “Some People Like Football Better Than Baseball: Who Are They?” Well, they’re everybody. Or it’s a mix of all kinds of people. So I went in with this idea that I was going to try to pinpoint or diagnose this slender, fading movement, but in fact it’s half the people who voted. I’m still puzzling over it, actually. The one thing I’m sure of is this: The people who supported trump were either willing to ignore or could not see the humiliation and fear that he was causing in good people: Muslims, Mexicans, Mexican Americans, gay people, black people, any people of color. You’d have to be sort of willfully blind to not see the anxiety his rhetoric was causing in those people. So the thing that I think a lot of progressives are struggling with is, how could you discount that? Now, that’s an interesting question. Because the first-level answer is, they’re racist. I think it’s responsible to take that and try to break it apart a little bit, and one Gallup poll recently suggested an interesting answer, which was that most of the Trump supporters had a relatively low level of interaction with the other. They didn’t live near the border; they didn’t live near undocumented communities; they didn’t have a lot of friends of color. So it’s sort of a projection. When they have a fear about an undocumented person, it’s almost all projection.
And how were they getting their perspective on these matters? Fox News?
Well, this is the interesting thing, because that’s what my assumption was, so I would do these little fishing questions like, “So, where do you get your news?” And they’d say, “I get my news from all over.” And it’s funny, at the time, last spring, I took that to mean they also watched CNN or something. But now, in retrospect, I think they meant Fox and Breitbart and alt-right sites. They were seeing Fox as a little bit left of center. In the reporting, I would get these weird refusals of data sets to intersect. We’d be talking about something, and their facts were coming from somewhere I didn’t know about. And at the time, I don’t think that network of right-wing sites was as widely known. That explains a lot of the data in that piece. So I’m still puzzling over it.
But I think for writers, it’s a time…I feel kind of excited about writing. I don’t think I’ve ever felt in my life that it was a more essential task. When there’s leadership in place that is purposefully encouraging anti-factuality, that got elected on repeatedly being as nonspecific as possible, constantly invoking linguistic tropes, meaningless linguistic tropes, using these rhetorical stances to alienate and terrify groups of people, that’s when language shows up and goes, “I did matter all along! You writers knew about it.” So, right is still right, virtue is still virtue, and I feel a little bit energized about it. Now, the one thing I noticed during this thing that scares me is that this left-right divide is getting fatal. I went with these Trump supporters, and I got along with everybody and had a really nice time. They were very friendly; we chatted; I insulted them and they insulted me. But one thing that was funny—if I was feeling insecure, I’d drop the fact that I’m a New Yorker writer, in general. And I don’t think there was a single Trump supporter—there might have been one guy in Wisconsin—who knew what that was.
I expected, “Oh, that liberal rag.” Not even that. “Is that some liberal thing?” sometimes. But they didn’t know what it was. So that means then I went home and worked five months on a ten-thousand-word piece trying to be very measured but not a pushover and all this stuff. Who read it? We read it. Now, I’m a fan of preaching to the choir; the choir needs to huddle around the most profound version of our ethos. But it was weird to think, “If I wanted to bust out and really speak directly to Trump supporters, how would I do it?”
That’s the question.
It’s a big question.
You mentioned that you feel hopeful and energized now. That’s a very good message, this idea that language does matter now. Maybe now more than ever. But the hard thing is trying to reconcile the fact that no one really gave a shit about the language Trump was using during the campaign.
I would break that down, because many of us, including you, care deeply about it.
Of course. It didn’t have an effect, though. When I was hearing him say some of these things—“Grab them by the whatever”—I was like, “Oh, well, it’s over now,” because there’s no way someone’s going to vote for that.
It’s disqualifying, right, right.
But they did.
Yeah. And that’s a deep well. One thing I’m trying to tell myself in order to stay hopeful is that heartbreak is the difference between what you thought the world was and what the world actually turned out to be. So you thought this person loved you; they didn’t. Aww. Well, actually, that’s on you, in a sense. So those of us who are feeling crestfallen or heartbroken at this time, I’m trying to say to myself, “That’s your problem! You were out there in the rallies, why didn’t you know?” So then isn’t it literary to say, “I’m going to adjust my view because it was too small. I misunderstood America. I misunderstood the country.” That’s okay. You’re allowed to misunderstand. Also, America is allowed to be as fucked up as it wants to be. My perceptions just can’t be out of sync with that. That’s one thing.
Now, we talk about specificity. With this thing, a fifth of the country voted for Trump. That’s a pretty small number. To elect someone else would take a sliver of about 15 percent. Say 15 percent of the population would have to flip over into an anti-Trump stance. That’s really easy.
Or just vote at all.
Right. But part of me is wanting to say because of our election procedure, this looks like the country has totally changed, but the truth is—and this is something I left out of the piece because it didn’t come into focus—so many of those people I talked to were as much anti-Hillary as for Trump. To me, that’s mystifying, but that was their position. So I would imagine if you just plunk in Joe Biden next time, it all shifts. So I’m not hopeless. It’s still depressing, mostly because it makes me sad to think of all the people I met on this trip down in Phoenix, and so many wonderful Mexican Americans and also Mexican immigrants who were so humiliated by this. You know, they work so hard, and now the country is sort of turning them into enemies. And that’s heartbreaking. That’s disgusting, actually, and it makes me sad. But the other thing it does is it backlights our whole history a little differently. You talk to any African American and you say, “America’s racist!” they’ll go, “That’s not news.” So I think part of the sadness but also maybe the invigorating thing for me as an older person is to go, you know what? I maybe never saw this country correctly. And as you get older, a little bit of an Aaron Copland vibe gets in your head, like, “Oh, this lovely country that’s been so good to me.” It’s a time for me to maybe reconsider, for everyone to reconsider, and say, “Yeah, this is not new, this kind of oppressive rhetoric and this kind of knee-jerk, reactionary demagogue thing. We’ve been fighting it a long time.” I think heartbreak comes from the fact that many of us felt that that was in its death throes and that this next administration would be the end of it, or at least a good movement towards the end of it, and now we have to wait.
It’s also perhaps naive for some of us to have thought that we understood this country. It’s a huge country. There are so many people, so many different kinds of people, and to think that we know who we are as one united…
Right. And so much of that comes from our mind, what we want to see. But to turn it back to writers: What an incredible moment to say, “Okay, we don’t know.” And let’s just generalize: “We don’t know the Midwest.” Well, that’s a good project, because it’s full of human beings and therefore full of literature. I remember coming the other direction; I was in Amarillo before I came to the Syracuse program, and I’d been working in a slaughterhouse, and we’d been having a lot of drama in our circle of friends and family—real deaths and drugs and all kinds of dark stuff. And I came out here very hopeful that that would give me a badge of authenticity, kind of like when Kerouac met Neal Cassidy. I came out, and I found that a lot of the people I met in the artistic community hadn’t had much experience there, and so therefore it didn’t hold much interest. It was sometimes just a one-line joke, you know? “Oh, Amarillo, I drove through there. Bunch of currency exchanges.” And I remember, it was maybe one of the most heartbreaking moments of my life to see that I wasn’t going to get in there with that. There was no understanding that there was an entire human community there that I loved, and they were suffering. So now, it’s a tremendous literary mission to say, “Can we reimagine our country?” It’s going to take some legwork, and it’s going to take some curiosity, which is in short supply these days, in both directions.
Well, shifting gears here—
Let’s move on to death!
Let’s move on to death. It seems like the perfect place to end our conversation. You’ve mentioned that you find death such an interesting and terrifying thing to write about. It’s in all of your work, but this book in particular, because all but three people are dead. And a horse.
Thank you for noting the horse. [Laughter.] I think it’s because I have a reasonable level of belief that it’ll actually happen to me. I remember, as a kid, being in my grandparents’ house in Texas, and it was a smallish house, and I could hear their sleep-noises, and it hit me really hard—and they were in their sixties, so they were old to me at that time—and I couldn’t sleep, and I thought, “They’re going to die, my God.” And that just-woke-up sort of confusion: “What if they die right now? They could. Well, they could. They’re going to, and they could.” I don’t think I’m fascinated with it, but I kind of feel like, you know, if you’re on the tracks and you distantly hear a train, come on! I’m not fascinated with the train, but—
It’s a fact, coming.
Yes.
I guess another way to phrase the question here is that, similar to how taking the election as this sort of negative and looking at it as a positive, which you so beautiful did, it’s a similar thing with death. I think that the kind of general feeling about death is that it’s a negative. And yet it’s going to happen to every one of us. And you seem to have taken the positive view, which is that it makes life, life.
Yes. Let me put it another way: As with the election, it’s not that you think the thing itself is positive, but being willing to accept the reality of the thing is positive. Then you accommodate it. It’s kind of like—actually, it’s sort of anti-denial. Denial is something I’m very prone to, and it’s always gotten me in trouble. Okay, look, death seems to be, as far as I can tell, it’s going to come for me. So is there any way I can accommodate that knowledge? No matter what, whether it enriches your life or fucks it up, it’s still healthy to acknowledge. So if you go to a party, and you know everyone is leaving at midnight, it should affect the way you pace yourself, or the way you are there.
I think what happened with me is, again, because of that thin ledge of talent I have, I’m not a writer who could write a story about something that has no urgency for me. There are really talented writers who say, “Oh, I’m going to imagine that I live in that apartment.” I can’t even do it, something so casual. I flounder in that mode. So I have to make sure that my stories get on something that really matters to me. Death would be one. I always quote Flannery O’Connor: “A writer can choose what he writes, but he can’t choose what he makes live.” So coming at that idea from the other direction, if your prose is flat, that means you’re not writing about—well, it means your prose is flat. And it means you better stop that. So for me, what that means is, when I get off into something where the prose starts jangling, then full-speed ahead, don’t worry about what it’s about. But that tends to be about mortality. And it might just be a lack of subtlety. I’m not too good at making a story in which nothing big happens. I mean, the masters do. Chekhov, he always can do that. I think I’m maybe just not that subtle. So for me, peril, death, has to be there for me to get the necessary energy.
This whole novel is predicated on death. Did anything about writing it surprise you?
Oh, yeah. So much. But mostly it’s—this is Poets & Writers, so we can talk about it—but mostly it was the internal dynamics. If you’re writing a story as over-the-top as this one, it’s all in the doing. It’s all in the line-to-line and section-to-section transfers. And my thought was, if ever once I got too cheesy or on the nose, all the air goes out of the balloon. So much of the editing work was: If I juxtapose this speech with this speech, what does it feel like? If I cut this speech and move this one up? I just finished section nine; which way am I going? And the constant enemy was kind of—I was going to say “banality,” but it’s not really that. I think a lot of the energy is, as a reader, going, “What the fuck’s going on here? Who are these people?” And then, just about the time they figure out who they are, then I have to keep moving it. The idea was to keep the reader always a little bit behind me but interested. So sometimes if you make a too-obvious structural move, the reader passes you. “Oh, it’s a ghost story.” That’s really hard to talk about, but it’s all the micromanaging of text and transitions and the way the speech is made, which I really like, because if my attention’s on that stuff, the big questions come in anyway, and they come in naturally. So the surprises—there were thousands of things that surprised me.
I have to ask you about one of the voices in the book: the hunter.
Yeah.
Where did that come from?
I don’t know.
You pause on that character it seemed to me in a slightly different way. It was more detailed in terms of what he had to do in the afterlife. All the thousands of animals he killed during his lifetime were gathered around him, and he had to hold them all, one by one, “for a period ranging from several hours to several months, depending on…the state of fear the beast happened to have been in at the time of its passing.”
I mean, I could make something up, but the truth is, this is what I love about writing. Basically, they’re going from Point A to Point B; they need to pass some people. What I love is to suspend the part of your mind that says, “Well, who should they pass?” and just go, “No, who do they pass.” And that guy just showed up. I don’t know why. I honestly…the only true answer is: I don’t know. He just showed up. And in that space…it’s funny: You’re walking through the woods, and you go, “Okay, I need somebody to show up on the left,” your mind turns there, and it supplies. That’s the difference between someone writing well and someone not. And I don’t think you can say much more than that. But you do train yourself, I think. I’ve noticed the training is mostly been to repress the side of me that wants to figure it out. Who should I have show up? No. Maybe just a vague turning in that direction that’s informed by everything that’s behind you, and then a trust that whatever the little intuitive leap is, is actually coming from the subconscious in a deeper way. But it’s literally like training yourself in putting up a little roadblock to your conscious mind and saying, just stay back a little bit. You don’t have to go away, but just stay back. And then veering over here and seeing what you’ve got. I mean, how do you talk about that?
You don’t want to look behind the curtain.
No, you don’t. But it’s also years of being in that exact space and being somewhat confident. And I would even say, in that moment when you turn away from the conscious, there are several different strands of other things. There are several candidates going, “I’m over here! I’m over here!” And there’s a micro-moment where you can go, “No, no, no, no, yeah.” So it’s really freaky.
Well, this book is full of those moments. As you say, it’s a comic novel, but when I was reading it, moments like that are haunting.
Oh, thanks.
Your work is full of those moments where it’s comic, laugh-out-loud moments, and then this little twist.
Part of that, again, is that alert[ness]. I’m trying to imagine where you are. Now, again, you can’t exactly, but it’s surprising how you sort of can. So if, on a micro-level, you feel like you just landed a very nice, profound, serious moment, and I’m watching Kevin—what if I do the poop joke? So it’s interesting, you know? You’re enjoying the pleasure of that deep, literary, serious moment. Now, you know, if we just left it alone, does that trail off? And if we follow it with another one, do you now feel like it’s becoming predictable? It’s a challenge of teaching in an MFA program, or teaching writing in general: Those little skills are so small and subrational, in a certain way. You can’t teach those moments, and yet everything abides in them. So that’s why I do a lot of close line-editing with my students, because in that way you can sort of communicate, if you have a sentence that’s this way, and you can edit it and make it this way, and that way’s better, you’ve kind of engaged that moment a little bit. That’s very interesting. And the danger is, in school, we’re always analyzing the effect after the fact, in analytical language. Which may or may not have anything to do with how Tolstoy did it in the first place. That’s the thing. I try to remind myself of that, that we’re talking about literature often from the wrong end of the telescope. That’s the conundrum of a writing education.
I was saying earlier how you can never know the mess of neuroses and emotions and everything that a reader is bringing to it, but on the other hand, just in my case, I’m not feeling anything new. I’m not going through anything so special that hasn’t been gone through by other people, you know?
Think of it this way: If we’re walking down the street, you’re having your thoughts, I’m having mine, somebody gets hit by a car; suddenly, we’re both in exactly the same space. So I think in art and writing, you can do the same thing, sometimes just with a simple sentence, you know? “They crossed the river.” You might be having a bad day, but suddenly, you’re crossing a river.
Kevin Larimer is the editor in chief of Poets & Writers, Inc.
The Very Persistent Mapper of Happenstance: A Q&A With George Saunders
Don’t tell George Saunders you can’t get there from here. En route to an enviable writing career, he traveled from a working-class childhood in south Chicago to the oil fields of Indonesia, a slaughterhouse in Amarillo, Texas, and the stuffy office of an environmental company in Rochester, New York. Along the way he collected an MA in creative writing from Syracuse University, where he studied with Tobias Wolff, and a degree in geophysical engineering from the Colorado School of Mines.
Saunders readily admits he didn’t chart his course, and he approaches the writing of fiction the same way—with no particular destination in mind. As a result his stories end up in some unexpected places: a prehistoric theme park; a future world where citizens belong to two classes: “Normal” or “Flawed;” and a self-help seminar where participants learn to identify who has been “crapping in your oatmeal.” Ask him why his stories, at once hilarious and macabre, are littered with severed hands, dead aunts, see-through cows, and Civil War ghosts and he’ll share your curiosity. “Where does this shit come from? I don’t have an answer.”
Today Saunders teaches creative writing in the graduate program at Syracuse University. He lives with his wife of 13 years and his two daughters, ages 9 and 12. His first collection of short stories, CivilWarLand in Bad Decline, was published in 1996 by Riverhead Books. In May, Riverhead published his second collection, Pastoralia. Villard will publish his modern fairy tale “for adults and future adults,” The Very Persistent Gappers of Frip, illustrated by Lane Smith, in August.
Recently I visited Saunders in Syracuse. During lunch at Erawan Restaurant and over coffee in his sunny Victorian home, he revealed two qualities that make him so popular among his students—a friendliness and a generosity one wouldn’t necessarily expect to find in someone at this stage of a successful writing career. He also displayed a quality one would expect to find in the author of such stories as “The 400-Pound CEO” and “Downtrodden Mary’s Failed Campaign of Terror”—the uncanny ability to find humor in unlikely places.
One of the things that’s immediately intriguing about you as a writer is your sort of non-traditional background—
That’s a nice way to put it …
Well, it doesn’t seem like you’ve been stagnating in some university setting.
No, that started up here. It was kind of an inadvertent path. When I look back I’m always a little bit embarrassed because it’s not like I had any sense. I had such a malformed sense of the world at each point that I ended up making some stupid decisions without really realizing what the options were. I grew up in Chicago in a pretty working-class neighborhood so writing wasn’t something…well, I didn’t really know who did it. It never occurred to me that I might do it. But I never even read a whole lot. I remember reading Johnny Tremain—that was a big watershed. I got a degree in geophysical engineering from the Colorado School of Mines. This was at the height of the oil boom, so I went over to Sumatra and worked for a couple years in the oil fields. After that was a period of just bombing around with no real sense of what was going on. I worked in a slaughterhouse for a while in Amarillo, Texas. I was probably twenty-four or twenty-five. In that town if you wanted to get some money quick that’s where you went, and they would hire anybody and you could stay for as short as you wanted.
What did you do at the slaughterhouse?
I was a knuckle-puller. It’s a leg thing. It would come in on a hook. It would look like a big chicken leg. There was this complicated series of cuts. You had a hook in one hand and a knife in the other. The cuts were very surgical, some of them. When that was done you just sort of heaved it across onto this conveyor belt. It was like this big Rube Goldberg thing and it would go somewhere else. At one point I got demoted because I was too slow and I went to this place where all the stuff that was left over at the end came by on this big belt and you had to separate it. There was one box that was for bone and one was for fat and one for miscellaneous. The story was that the bone went to make pizza toppings, and fat was for marshmallows. It wasn’t too good.
So you were de-knuckling the leg. Of what animals? Cows?
Oh, cows, yeah. It was hard to tell. It could’ve been brontosaurus for all I know.
You’re a vegetarian now.
Yeah, but that’s pretty recent. One wasn’t a result of the other.
How did these kinds of experiences inform your work?
I always wanted to write but had never read anything contemporary. When I was in Asia there were all these great things to write about during the oil boom, but I didn’t have the vocabulary. I found myself drifting and not knowing how to put the stuff that was happening into the work because I had never seen it done before. But then I read that story “Hot Ice” by Stuart Dybek and that was basically my neighborhood where I grew up. To see that in prose… I couldn’t pretend that only Hemingway mattered after that. Dybek was a big breakthrough because I could for the first time see what you had to do to reality to make it literature, because I knew the neighborhood and I knew the people and I could see what he’d done to it.
You played guitar in a bar band in Texas.
A really bad bar band. We were called—it’s really embarrassing—we were called Rick Active and the Good Times Band. It was along Route 66 in Amarillo, where they had these drunk palaces where you’d go to drink and they’d pay us each $50 a night and we’d play the same set six times over and over again, never practice, no original songs. This was 1986. I should’ve known better then. In a way it’s like half of your mind is saying, “It’s okay, I’m just slumming, I’ll write about this some day,” and the other half is just that there weren’t a whole lot of other options.
Were there any other early influences?
Monty Python was a huge influence—the way that they would get at something archetypal through a side door was always really interesting. We just turned our kids on to that recently. The argument sketch. Do you remember that one? “I’m here for an argument.” “No you’re not.”
I remember watching Monty Python with my father. He was really busy and we didn’t do a lot together, but every Sunday night we’d watch that. In our neighborhood, a very working-class neighborhood, jokes were really a currency. If you could tell a joke or even if you could imitate somebody it was a really big deal. Junot Díaz, who teaches here at Syracuse, has this great theory that writers come out of any kind of situation where language equals power. So in his case, in the Dominican Republic, English was clearly a meal ticket. And I think that’s true. So that combined with just sitting there with my father roaring at Monty Python…somehow humor became validated. But for years, like a lot of working-class people, writing was that thing which I could not do. It had to be just beyond my grasp or it didn’t count, right? So it was only when that sort of dropped that I could really have fun with it. But that was relatively recently.
Humor is obviously a very big part of your writing. Humor combined with sentiment. I’m thinking of the ending of the short story “Isabelle” in CivilWarLand in Bad Decline. It’s heartbreaking.
I’m increasingly happy to be a funny writer. What I find really funny is the straight faces that people keep in spite of the fact that life is so full of suffering. I think of the poses people strike, and the hatred that they develop in spite of the fact that in fifty years we are all going to be dust. We have to occupy those places so that’s really funny to me. Whenever I try to write hard and earnestly it always comes out like that. I have to sort of trust it. I can’t write anything that isn’t comic—I don’t know about funny—but comic. Earnestness is my enemy.
You’ve written short stories and a novella. Have you ever tried to write a novel?
Most of those stories started out as novels. I’ve tried and I just recently got to the point where I’m not going to try anymore. If it happens it’ll happen organically. I’m not going to sweat it because in the past when I tried to write a novel I thought, “I’ll have to do something fundamentally different, I’ll have to stretch things out.” But if I have any gift it’s for compression. At forty-one I’m like, “Well it’s nice that I can do something. I don’t have to do everything.” We’ll see what happens.
When I was working as an engineer at the environmental company there was just no way that a novel was going to happen. When I was in that job I was desperately trying to figure out another way because not only was it not a lot of money, but not a lot of time with the kids. There’s that great quote by Terry Eagleton: “Capitalism plunders the sensuality of the body.” That was such a beautiful lesson because you come home half despising yourself because you’ve done such stupid things with your day. You’ve groveled and you’ve not even groveled efficiently. Then you come home and you’re exhausted and you’re not capable of generosity and I find it really sad.
A lot of your stories, like “Pastoralia” and “CivilWarLand in Bad Decline” take place in this beaurocratic, artificial universe. Disneyland gone wrong.
I think it’s mostly that job I worked at the environmental company. It was a provincial office of a medium-sized company that was based in Texas so it had all the rigidity with none of the brilliance. There were probably thirty people there and they were all pretty anxious and by the time I got there they were shrinking the place down. It wasn’t huge enough that it was faceless. We all knew each other. There was quite a bit of inside space where there was no natural light. My own ego, my youthful arrogance, and my own high expectations of myself were put suddenly in conflict with this because, you know, by then I had two kids. I was maybe thirty-three or thirty-four and nothing was going as planned. I hadn’t won the Nobel Prize yet and Hollywood wasn’t calling because I hadn’t published anything, so there was something about that that made it seem absurd. It was a pretty petty place and there were a lot of rules. I mean at one point I was sending stories out and I got a nice rejection from the New Yorker and I was so excited because an actual person had responded and in a fit of madness I mentioned this to my supervisor at the end of the day. And he got this stricken look on his face and he said, “Well actually, George, it’s come to our attention that you are using corporate resources to produce your ‘writing’ so we’d like you to discontinue that.” And this was a guy who knew me and he knew my kids. So that wasn’t too good.
How are you able to negotiate some of the awful things that happen in your stories—death, dismemberment—with humor?
That’s a South Side of Chicago thing because our whole world—communicating anything emotional—was to be sarcastic. If you wanted to say you loved somebody you’d punch him in the crotch. My impulses are always very sentimental, I mean mawkishly, sit-comishly so. So in some ways I think it’s a cloaking mechanism. If you have in one scene a kid getting his hand cut off, I think in some funny way you’re more willing to accept a sentimental scene. I don’t know if you’re more willing to accept it, but maybe the juxtaposition of those two things is more interesting. As a writer I’m really aware of my defects and how much I have to find other things to substitute, so humor helps. It’s got its own inherent energy so if you can sustain funniness you almost always have to sustain something else. Pure funny you see sometimes in humor columnists who are just funny, but in fiction to keep funny going you almost always dredge something else up. I think.
For some reason I think of Charlie Chaplin.
Yeah, The Great Dictator. I think partly it’s ritualized humility. If you think of the great evils: When China invades Tibet they’re not funny, they’re not self-doubting. There’s no trace of humor in what they’re doing. And Hitler: not a guy who’s at all prone to see funniness in himself. One of the great things about fiction is that if I write an asshole into a story it has to be me. I can’t generate him. And it’s always funny in the reviews they say my stories are full of losers. I know where I got all those things. I didn’t just make them up. I think it’s ritualized humility.
In your stories, one thing that continually strikes me is guilt. I’m thinking of “Winky” in Pastoralia, and just about every story in CivilWarLand in Bad Decline.
Well, I think it’s the Catholic background. The binary that got set up was that you were either doing good or you were doing evil, and you were never doing good. If you actually appeared to be doing good there was probably something wrong with your intentions. I think if you have any moral tension, guilt is part of it. If a person can feel guilt they are at least cognizant of a moral interplay. It’s a powerful emotion—one, because it implies you’ve done wrong, and two, that you know you’ve done wrong.
When I was a kid in Chicago, the big thing was to go to a Bears game because it was expensive and people didn’t really do it. But this family that lived two doors down from us—they were maybe ten years off the boat from Poland and they didn’t have much money and they lived in a house that was completely bare, no furniture. It always smelled like noodles and they were always kind of barking at each other. One day the kid came over and said “I got Bears tickets.” It was like someone in the poorest neighborhood saying they had a house in the Hamptons. So I said, “Great, we’re going to go.” It was his father, his uncle, Greg, and me. It was a big journey with trains and buses, and we stopped at other Polish relatives and there was a lot of cheek-pinching. But I was going to endure it all to see Gale Sayers and Dick Butkus. So we finally got to Wrigley Field and just before we go in the father says, “All right, boys, we’ve got a little problem which is that we only got two tickets, but don’t worry about it we got it figured out. The Andy Frain guys they never look up when they take your ticket.” So they picked each one of us up—we were maybe ten or eleven—picked us up and put us on their shoulders. And in those days they were still wearing those big overcoats, and they had us put our feet down their overcoat and they buttoned it up. And so the plan was that they were going to walk in and they would take our tickets and not look up. Now I was the all-time Goody Two-shoes, straight A, never had an evil thought. And I was just appalled to be cheating, and cheating publicly. Then the father says, “Now if they do look up, all you got to do is look retarded.” And he was serious. The idea was that if they thought you were retarded they would let you in for free. So he says, “Now let’s see how you’re gonna do it.” So we had to practice. And we started in. What I was really deeply ashamed of afterward is how willing I was. I was not going to get caught. If they busted us, I was going to go into the retarded thing, I was going to do what he said.
Something of that is in my writing too. When I’m getting ready to send something out, I get really intensely self-critical. To my credit I get really fanatical about revising, but sometimes that can bleed over to just lock-up.
I think sometimes you can find yourself frightened of what you’re going to find if you look at it too closely too soon. I finish something and I think it’s good and I don’t want to go back to it too early. How many times do you wake up the next morning and say, “That’s trash,” you know?
I think you’re right. Part of being a writer is to know when to trust yourself. I know I’m going to have a cycle. I’m going to love it more than it should be loved at first, hate it more than it should be hated later. You let your ecstatic side have it for a while, then you let your neurotic, self-doubting side. For me it was a breakthrough to realize that that wasn’t abnormal, that you weren’t right or wrong in either of those two, that you were right in both and wrong in both, and you just had to let it have a long shelf life and then it would start to make sense. Part of it, too, is knowing when to quit.
When I start to write a story I always have a simple design that would make it sort of classic and beautiful, but I can’t do it. I have some kind of weird thing that twists it, but the twist isn’t meaningless. Somehow the distortion that always happens if I work hard is useful. It’s like having this dog and going out in the field and saying, “Bring me back a pheasant.” That dog is your talent, and it runs out and and it comes back with the lower half of a Barbie doll. But if every time it brings back the lower half of a Barbie doll, you put those things together and you think, “That’s kinda good.” I don’t fight it anymore.
You write on a computer. You also said you revise a lot. How do you trust your ecstatic instinct electronically?
The kind of writing I do I wouldn’t be able to do without a computer. Until I get to the end part of a story I work on the screen almost exclusively. Any time something strikes me I just put it in or cut it or whatever. If there is anything significant that happens I’ll save it. But the main thing I do is to try to keep it really free. Nothing is ever lost. I can always go back to it. It’s like those fast motion pictures of trees growing. I don’t know if it’s true with trees or not but let’s pretend it is. You sort of see this thing accreting and parts disappear and come back in but in the long run it’s working in a general direction. I couldn’t do that on hard copy.
For me, writing has become—it sounds a little pretentious but sort of true—a spiritual practice. If you’re open to whatever the story presents with no attachments to what you did yesterday or any attachments to what you want the thing to be or how you want to be perceived, but just open to the needs of the story, that’s kind of ecstatic. It’s really beautiful to say, “What I did yesterday or for the last twenty years might be shit but that’s okay.” It’s interesting to see how the artistic form teaches you. It instructs you on your own shortcomings as a person. I love that writing can really help me turn back the spiraling neurosis. It can help me be a little bit less stupid, less judgmental and unkind.
You said it is important to be there when you’re writing, not thinking about yesterday or tomorrow. Is that harder for you now that you have a couple books?
It was really hard after the first book because I just thought I had squeaked through a door. “The Falls” was the first story of the new book that I wrote and it was a real lucky sort of breakthrough because it was so different from the other book. And I remember writing it and thinking, ‘No I shouldn’t send it out because it’s not like the other ones.’ But when the New Yorker took it I thought maybe whatever it is I have to offer is not totally manifest in that book, it’s something different, and that was a nice feeling to think it’s not really about style but something else you have to offer.
And maybe you don’t even know what it is yet, and maybe you never will. Maybe you’ll be eighty and you just keep cranking stuff out and you’re good enough and then you die. When you’re young you think, “I want my work to last,” and then you see that nothing lasts. Shakespeare doesn’t last, nothing does. The moment of doing it is really all there is. Everything else is all delusion. It’s hard to remember, especially now when books are coming out.
Tell me a little about The Very Persistent Gappers of Frip.
I have two daughters, and I would tell them these made-up stories about this little girl and they were funny and in some ways they were funnier than anything else. They were freer and not so programmatic. And I wrote it. It’s basically a short story really. And I liked it. There was something Monty Pythonesque about it. I didn’t have to worry about any realism and I had a really good time working on it and I sent it to Daniel Menaker at Random House and he bought it. As kind of an extra bonus he sent it to Lane Smith and Lane had read CivilWarLand in Bad Decline and said, “Yeah, I’ll do it.” So that instantly became more of an important book than it was. That was really a thrill. I’d go down to his studio in New York and there would be a whole wall of sketches. Not only were they true to my work, they were twice as good as I could’ve ever dreamed of. One, he understood that the book is an exaggeration, but two, he understood the flavor of the exaggeration. It was really a thrill for someone who is not a bit visual. It was a good lesson for me because he is the least neurotic person I’ve ever met. He goes into the studio every day habitually and gets it done. I’m sort of a Catholic, “I think it’s good but it probably isn’t.” The Eeyore School of Literature.
Are you currently working on more stories?
I’ve got one that Lane Smith and I might do if I can get it to be good enough. It used to be a novella. It seems to be pretty funny. It started to be a kid’s story and then it extended to be about genocide. So unless there’s a big need for a child’s guide to genocide it won’t be that. I’m sure this summer I’ll be working. I don’t really make too many plans. I just sort of see what develops.
Kevin Larimer is the assistant editor of Poets & Writers Magazine.

Fiction writer George Saunders in Syracuse, New York, in the spring of 2000. (Credit: Jayne Wexler)
Which Story Will You Tell? A Q&A With Alexander Chee
Sometimes it pays to procrastinate. It took Alexander Chee fifteen years to complete his second novel, The Queen of the Night, and about seven years in, during a particularly bad case of writer’s block, he spoke to his agent, Jin Auh at the Wylie Agency, about putting together a collection of essays instead. “It was one of many moments where I was like, ‘Is there anything I can do to get out of writing this novel?’” Chee says. While, thankfully, he persevered and completed The Queen of the Night, which was published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt in 2016 to much critical acclaim, Chee continued to gather his previously published and discarded essays during the slow periods in his fiction writing. “It was this weird shadow creature that grew in the process of writing both my first and second novels,” he says, “almost like a back passageway to them.”
Chee has made his name as a fiction writer. His first novel, Edinburgh (Picador, 2001), which tells the story of a Korean American boy who is forced to deal with the devastating effects of being molested by his choir teacher as a young teen, won the $50,000 Whiting Award. The Queen of the Night, a sweeping period novel in which an orphan moves from America to Europe to become one of Paris’s most famous opera divas, was a national best-seller and a New York Times Editors’ Choice. But for as long as he has been writing fiction, Chee—who is an associate professor of English and creative writing at Dartmouth College in New Hampshire—has also been quietly publishing essays in venerable journals and magazines such as n+1, Guernica, and Out. And with the release of his first essay collection, How to Write an Autobiographical Novel, out this month from Mariner Books, his “shadow creature” has stepped fully into the light.
The collection, which includes both previously published essays and new works, covers a wide range of subjects, all explored through the lens of Chee’s own life—from performing in drag, to a rose garden he grew outside his Brooklyn apartment, to a stint as a caterer for conservative socialites William F. and Pat Buckley. But as disparate as some of the topics are, they all circle back to one central question: How do we live and write truthfully? For Chee, a Korean American gay man growing up in a small white town in Maine, who came out at the height of the AIDS epidemic, the answer to that question has been fraught. But in his essays Chee explores the ways in which, despite tremendous external resistance, he forged a more consistent, authentic self both in life and on the page. The book is part memoir, part writer’s guide: While Chee mines the territory of his own life, he also offers useful advice about how other writers might do the same. In his essay “100 Things About Writing a Novel,” for instance, he offers this sage bit of wisdom for fiction writers: “The family of the novelist often fears they are in the novel, which is in fact a novel they have each written on their own, projected over it.” Many of the essays also include writing advice from Chee’s mentors, including his beloved undergraduate teacher Annie Dillard, and Deborah Eisenberg, his first professor at the Iowa Writer’s Workshop. In some ways, the book is far less a back passageway than it is a map, leading the reader to a deeper connection with both herself and the risky, rewarding act of creation.
I spoke with Chee about his new book, a lively conversation during which we discussed how to keep working during bouts of self-doubt, methods for successfully spying on yourself, and whether dancers do in fact make the best writers.
How do essays function for you in relation to fiction?
I studied with Annie Dillard, and that set the tone for how I came to think about essays and their possibilities. Annie told us, and I didn’t realize how radical it was for her to say this, that you make more money from nonfiction. If you become good at essays you can sell them while you’re working on your fiction. If you’re trying to start a writing career, you can use a finished essay as both a writing sample and an introduction to an editor, and while that editor may not like what you’ve written specifically, it might create a relationship that will yield work in the future. Everyone else [who taught in my writing programs] had a kind of, “I don’t talk about business in class” mode, which, I think, is unfortunately quite common in creative writing. And I say unfortunately because the truth is that one of the ways you democratize literature is by teaching people how to make some money so that they can get by.
Yes, and how to talk honestly with each other about the money they are making.
Yes, and how to stand up for the money that they are making. Annie encouraged us back then to have all of those conversations, taught us the format for submitting work, taught us to use the Best American anthologies as a guide to the places we should be submitting work to, taught us even to double check the addresses in the mastheads because some of them used codes to sort out who was only combing Best American anthologies for their address. Annie Dillard is no joke.
You’ve said before that we are living in a more “essay friendly” time. Can you say more about that?
The irony of the Internet, which was supposed to rob us of our attention span and be the death of journalism, is that it has actually promoted a new passion for longform nonfiction. It’s also given us more opportunities to find and discover poets, who are a big part of the movement towards essays as well, since they are doing work that is increasingly hybrid. In general, the best thing I can say about social media and the Internet is that it has allowed a lot of people to bypass the gatekeepers, such that I don’t know if there’s a real gate any more.
You say in the book, and you’ve mentioned this on social media before, that readers often want to know what’s “true” in fiction. What is your relationship to “the truth” in writing, and does it vary between mediums?
I think fiction is the thing you invent to fit the shape of what you learned and nonfiction is the thing you invent to fit the shape of what you found or maybe even what you can’t run away from. One thing that I noticed during the editing process of this book was how often it felt like I was dying. [Laughs.] It was just soul crushingly depressing and difficult work and it took so much longer than I thought it would. I had this kind of idea of, “Oh, I’ve published a lot of these essays before and this won’t take a lot of time.” Boy was that naive. It was shocking how naive that was. I think that’s because when you do it right, and this goes back to what Annie used to say, it’s a moral confrontation the writer has with the truth of their experience. That is no joke, and that is not a thing you can just rush through. In literary fiction I think you’re watching someone else in a landscape, wondering if they’re ever going to figure out who they are. In nonfiction of this kind, what you’re doing for your reader is riddling through the ways you lie to yourself and others and trying to get at what you actually believe.
Yeah, it’s horrible.
And that’s why you feel like you’re dying, because the part of you that your ego has held is saying, This is me, while the essay is saying, Well, it’s nice that you think that, but…
You’re actually over here, in this big pile of shit.
Right. Mary McCarthy wrote this essay collection Memories of a Catholic Girlhood. In between each of the essays she has a few pages about what she made up, what she lied about, what she didn’t mention, and she just calls herself on all of it. And it was this interesting early lesson when I read it about how much you have to be on your guard about yourself.
What were some of the lies you had to let go of in writing this book?
I engaged in a kind of forensics of the self. It was something that, again, Annie had taught. An early exercise of hers was called something like, So you think you know your hometown? And she asked us: “Do you know the major populations in your hometown, do you know the major industries, do you know the flora and fauna of the different seasons, do you know the historical events that shaped the founding of the town? How much do you know and how much are you actually just around for?” I continued to take that approach with myself. I reread my journals and all my e-mails. I look at my social media “likes” history to find out what I’m actually paying attention to, and my browser history for the things I won’t even allow myself to “like” publicly. I act like a spy on myself, like someone who doesn’t love me and is just going to report on me. It’s a trust-but-verify relationship to the self.
In the book you write about how Annie Dillard said to you, “Sometimes you can write amazing sentences and sometimes it’s amazing you can write a sentence.” Has getting that kind of feedback helped with this honest relationship to the self?
[Laughs.] I had a high school English teacher who said to me, “What I love about you is, I can knock your head off, hand it to you, and you just put it back on, straighten it and keep going.” And I think my ability to just hear people say those things and figure myself out in relationship to what they’ve said has made a big difference. As I’ve learned from a long teaching career, not everyone is built that way, and I’m very glad [my English teacher] identified that early on. He once took a paper of mine and read it aloud without telling me he was going to read it and at the end he just said, “This is an example of what not to do with metaphors.” I could have been upset but I thought, “Okay,” because I respected him and I knew I was showing off what I could do with words in a way that was overblown.
In this collection, was there a hardest essay or an easiest essay, or were they all hard and easy in different ways?
That’s a good question. They all presented different challenges. Some of them were written in the nineties and abandoned and then revisited and abandoned again. “The Guardians” and “Autobiography of My Novel” were, for a long time, one essay and then I turned them into two essays. I started [the original piece] when I was about to finish my first novel, Edinburgh, and it was originally going to be one of those essays you publish in support of your novel—which has become this weird tradition that my essayist friends really hate because they’re like, “Who are these fiction writers showing up, thinking they can write an essay and flooding the market with low quality pablum?” And it’s true that writing a novel, writing a short story, and writing an essay are distinct skills.
My essay “Girl” was one that I actually workshopped initially at Iowa. I worked on it for a few years before deciding it was possibly juvenilia and set it aside. And then every few years I would pick it up and think, “This is pretty good, I should do something with it,” and I never would. And finally Guernica reached out to me and said, “Do you have anything about gender?” And I sent them that essay. I think I was like a lot of my students. I thought success in grad school or in a writing class was a kind of low bar, that it didn’t mean anything about success in the world, which to my mind had to be so much harder, and so I talked myself out of submitting a lot of work that I could have submitted earlier and who knows what would have happened. I think in this culture there’s such a value placed on hard work that your inherent talent can seem like something silly. So I ignored it for a while.
In “After Peter,” you talk about your involvement in the activist group Act Up and growing up in San Francisco during the AIDS epidemic. I’m wondering, how did coming of age in that time affect your sense of your body and sex and intimacy?
I think intimacy is always fraught but it was differently fraught because of the AIDS epidemic. At that time, in the nineties, I was also just starting to experience the return of memories I discuss [in the essay] about being abused, and so my body was a kind of unfamiliar territory. Dustin, my husband, has memories of being in Hell’s Kitchen during the same time and seeing guys going up to the rooftops to jack off and watching each other at a “safe distance.” He said it was like jerking off in silence with the biggest condom of all, this gap of space between buildings.
Do you feel like writing has changed your relationship to your body?
I think, in general, I often ignore my body because of writing, to my own detriment. So I’m trying right now to reinhabit my body. But I have noticed that students of mine who have a background in dance are often quite talented at writing as well. There’s some way of thinking about how the body can be articulate that translates into how you tell stories on the page. I don’t know if it goes the other way. I’d love it if it did. The body is the instrument for the essayist in particular. It’s the instrument by which the events are recorded; it’s the instrument on which the events are replayed. It’s a very complicated, interdimensional relationship we have with our bodies when we’re nonfiction writers.
You’ve written about your family in different ways in this collection. The line of what writers will share and won’t share about family is always different and I’m wondering where that line is for you.
One thing I know is true for Asian and Asian American families is there’s a lot of intergenerational silence, so my mom [who is white] is the source of a lot of the stories I have about my dad’s family, which she learned when we were in Korea, because she doesn’t have any of those social taboos. There is also the silence of my father’s death, which is certainly a profound one for me—I’ve spent a lot of time in relationship to my memories of him and my imagination of him. One of the first essays I wrote, which I almost put in this collection but held back, is a confrontation with the memory I have of my father and what would happen if I told him I was gay, because he died before I could come out. That early experience of having to think through that and write what his reaction would be, which also meant writing about my mother and my sister, got my family used to the idea that I was going to write this book. And my mom read it and offered some insights into what she felt I’d gotten wrong about her, but she said, “It’s your truth.”
“Girl” was such a powerful example of all the ways you’re straddling different worlds: boy/girl, gay/straight, Korean/Korean American/white. Does writing feel like it creates bridges or synthesis, or is it just an observation of the gaps that are there?
I have come to view writing as a sort of prism. Early on, at a time when I was experiencing a crisis, I had a therapist who said, “You are different with different people because you are uncertain whether you can be whole with any of them, and the result is that you feel inauthentic with all of them and you may even feel inauthentic to them. So you need to pursue a complexity in the relationships you want to be your core relationships and that will help you feel more authentic to yourself.” That was the source of a profound breakthrough because what I was experiencing as depression was a kind of self-rejection predicated on my imagined sense of other people’s rejection.
At some point you have to make a choice about which story you are going to tell about yourself. Are you going to tell a story of you as a failure who never did the thing that you wanted to do—which is the story you essentially tell yourself, a kind of private theater of pain—or are you going to tell the story that you’re working on, a story that can actually reach other people and connect outward to the world? If you’re busy telling yourself that other story about your own failure, chances are you aren’t writing. You may think you are protecting yourself by keeping yourself from writing, but that’s really not protection at all. That’s just another story trying to talk you out of being yourself.
Listen to Alexander Chee read an excerpt from How to Write an Autobiographical Novel.
Amy Gall’s writing has appeared in Tin House, Vice, Glamour Magazine, Guernica, Brooklyn Magazine, and PANK, among others, and in the anthology Mapping Queer Spaces. Recycle, her book of collage and text coauthored with Sarah Gerard, is out now from Pacific Press. She is currently working on a collection of linked essays about sex, violence, and bodily return.

Novelist Alexander Chee, author of the new essay collection, How to Write an Autobiographical Novel, out this month from Mariner Books. (Credit: M. Sharkey)
Blind Ambition: A Q&A With Gregory Pardlo
If nothing succeeds like success, Air Traffic: A Memoir of Ambition and Manhood in America is Gregory Pardlo’s noble attempt to show what becomes of the people who die trying. “My father’s world operated on homespun destiny,” Pardlo writes about his late father, Gregory Pardlo Sr., who lost his job as an air traffic controller during the Professional Air Traffic Controllers Organization (PATCO) Strike in 1981, “the kind of destiny that was dictated by character and the inevitability of Hollywood endings.” While it was this belief in the inevitability of Hollywood endings that fueled Greg Sr.’s decision to see the strike to its end, president Ronald Reagan’s firing of the 11,345 air traffic controllers who refused to return to work two days later was a dismal reminder that life ain’t a movie. That for all we, as Americans, want to believe in the Dream; here is our rude awakening.
The essays in Air Traffic, published this month by Knopf, function like someone who jumps up from sleep, thinking the nightmare is over, only to discover this is reality. Pardlo’s rendering of his life and the people in it takes on a quiet nobility because the author resists the temptation to achieve any simple resolutions. There are no grand statements to be made. No fortune cookie wisdom. No moral to the story. If Greg Sr. was driven to death by the promise of the Hollywood ending, Pardlo is in the parking lot of life doing donuts. This is where Air Traffic succeeds.
Instead of showing the ways in which Greg Sr.’s ambition makes his family exceptional, Pardlo undermines that ambition by highlighting the ways in which the paternal failure makes them like everyone else. Pardlo’s understanding that he is nothing “special” enables him to come to terms with some of his own failures as a father, husband, and poet.
I interviewed Pardlo at his home in Bed-Stuy, Brooklyn, where we talked about his aversion to happy endings, his disillusionment with narratives of progress, complicated relationship to his Pulitzer win, and why alcoholism is like religion.
One of the first things I want to talk about in regards to Air Traffic is that the book ends without any real sense of closure. As if the wounds you’re describing haven’t healed yet. What was your intention in ending the book this way?
My aesthetic in general is not to pursue a conclusion. Real early on in my writing development, I read Lyn Hejinian’s essay, “The Rejection of Closure.” That essay had a big impact on me in thinking about how to avoid the Disney kind of happily ever after ending. Life doesn’t work that way—particularly when you’re talking about an addiction or recovery narrative. The idea that one can be sick, and be healed, and be done with it is not a narrative that works in terms of recovery. There is no recovery. Just a lifetime of maintenance.
One of the strategies I had when I started writing the book was to look for the opposing ideas. Where I have one argument being made affirmatively in place, I want to make an opposing argument in another. I’m working against the idea of a narrative having a teleological arc; this idea that the story is moving towards something.
This is a book about manhood, and a lot of it is focused on your father, but I was wondering: What was behind your decision to not write about your mother as much? Not only do you describe her as the one who holds the family together, but it’s difficult to talk about manhood in all its nuances without the women who help to contextualize what that manhood means.
If I’m going to be honest, it’s garden-variety sexism that the role of the mother, in the family, was always a secondary presence. Although she was most certainly a primary presence in my day-to-day life, in my imaginative life she was a supporting character. It sounds awful to say that but flat off, the impulse was to deal with my dad.
When I first started this book, I was most interested in the PATCO strike and the labor history around it. The more I learned about the strike, the relationship between the FAA and the controllers became more clearly paternal—so that theme of the father-son relationship pulled me in that direction. Then I discovered I’m not really dealing with my dad; I’m dealing with myself.
While I was writing this book, I was regularly visiting my therapist. One of her questions early on was, “When are you going to write the essay about your mom?” I didn’t know how [to write an essay about her] because my mother has always been a far more complicated character to me than my father. Case in point, for the intervention piece—which is not only the last piece of the book, but also the last piece that I wrote—I interviewed my mother. I wrote the piece and sent it to her. She wrote back that she loved it but felt that my depiction of her was a little harsh. My depiction of her was in service of her own ego, but that is the logic I applied to my dad. It doesn’t apply to her. So I’m still trying to find the emotional framework to render her fully.
Though the book is labeled a memoir, it reads so much more like essays in that the writing seems to be more concerned with the journey than any particular destination. There’s this very subtle way in which your father’s wanting to be the center makes you feel like you’re the supporting character in your own life. And you write every essay as though you’re experiencing your life through the eyes of someone else as opposed to your own.
Even the way you describe your drunk episodes, they seem sort of like they’re just treated as incidental. I felt it was an honest depiction of how our problems tend to happen in real time. They manifest themselves in the background. If it were something that you’re going to take hold of and keep in your eyesight it probably wouldn’t be a problem. I don’t know if you did that on purpose, but the most insidious things that happened in your life are the things you don’t see. You’re so focused on your father and brother, you lose sight of yourself.
That’s absolutely right. One of the things I love about the essay is that I can have that kind of dual presence as author and character. In terms of the tension of the book, obviously there are points in there where I, as a writer, am not going to see what I’m doing entirely. There is no omniscient narrator, but there are many points in the book where I am conscious of how I’m allowing my “I” character to be flawed.
We can see the patterns of my dad’s big, tragic moment set against my own tragic moment and my brother’s tragic moments. If not explicitly, “narrativizing” the blind spot is definitely an agenda of the book. It is a strategy of mine to read the character of “I” as a character, which means there are flaws that I, the writer, am aware of after the fact. As a writer I can see the thing my character “I” did and say, “Oh, well that was stupid,” but it’s not for me to go back and correct it. I don’t need to protect him. I don’t need to justify him.
That being said, the book does have this sort of arc where the beginning is so much more “ambitious” than the end. In the first essay we’re introduced to your father, who is determined to die in this grand way. But as the book goes on, ambition is subdued—in that everything, in comparison to your father’s death, just seems so much smaller. I’m wondering if that’s a question that this book is concerned with: What happens when you have too much ambition in a world that doesn’t make space for it, or doesn’t believe certain people—like your father—should have any?
You’re right. I think it’s my disillusion with the narrative of progress altogether. By damn near every metric of the American Dream, my life is a success story, but there is no point at which I want to stop and say, Alright we’ve made it. We think about the narratives of black progress, of uplift, and how that narrative has this teleology. What is the end game of the black uplift story?
How do we know when we’ve made it? My frustrations with that narrative—and how that narrative keeps us thinking about racism as the one dominating presence in the lives of black folks—was a distraction. There’s some shit there obviously. But I realized that so much of our family narrative was distracted by racism, by larger sociopolitical narratives, so that we didn’t pay attention to the ways that we interact generationally.
When I say this I’m thinking about Gayle Jones’s Corregidora. How the great-grandmother’s trauma gets passed down so that generations later, you still hate the slave master ’til the point that you’re unable to focus on what you’re doing in your own life. The extent to which I worship my father is a direct consequence of the way he makes himself a hero in my life. I grow up believing that his progress, his narrative, is more important than mine. I am a supporting character in his story. His story is the story of black uplift. His story is the civil rights story. My generation and on, however, are just there to bear witness to that narrative—and I realize that my father couldn’t see how he was part of this intergenerational story that was supposed to go beyond him because, in his mind, his story ends with him.
This goes back to narrativizing my own blind spot. As an artist, as a writer, as a person in the world, how do I claim my life, in service of my life, as opposed to being this subordinate character in my father’s? Or in service of the civil rights narrative? Or in service of some class, racial uplift narrative? How do I just do what I want to do and not feel beholden to some larger American narrative?
So is ambition something that you actually come to own or is it something that you inherit like debt? You inherit this sense that you have to do something bigger than yourself to prove that you have a right to exist. In this sense, any grand scale achievement, like your Pulitzer win, becomes a symbol of “progress.”
Right, when people come up to me and say, “You being a black Pulitzer Prize winner is important for the community,” I’m like well, that’s awesome, but I also just like writing poems. And I would also like to be congratulated for writing nice poems.
When you won the Pulitzer what was your honest response to it? Block out the white noise of everyone else responding to you. How do you, Gregory Pardlo, feel?
Fear, because I am sensitive to the ways other people’s narratives inhibit my ability to craft my own.
So if the larger narrative is about this black man who wins the Pulitzer and whatever else we turn this into for our own gain, what would be the Gregory Pardlo narrative about winning the Pulitzer?
It would be: We gotta read these poems more closely, and talk about these poems more, which, of course, is a consequence of the Pulitzer. But I think the larger, predominating narrative is “Look at this black man winning this historical prize.”
One of the things I heard a lot after it was announced that I was awarded the Pulitzer was, “When I found out you won, I felt like I did too,” which is great. I don’t resist that narrative, but what that also feeds into is me being a kind of inverted sacrificial lamb. That what I have done was in service of this larger thing that has nothing to do with me. As soon as I try and answer that question, I find myself reaching for somebody else’s narrative about my potential.
It also sounds like what you describe your father did anytime he wasn’t the center of attention: He found a way to steal it. It’s not really your win; it’s everybody’s win, which is to say no one won. But that doesn’t fully answer my question about what you would want the narrative of the Pulitzer win to be. I think this is the central difficulty of what this book is trying to articulate: How do you think outside of those contexts that define you?
As much as I want to wrest control of my own narrative, it is ultimately dependent on the larger context from which I derive my identity. I cannot be an isolated person in the world. My enjoyment of life, my sense of self-worth, is tied up in the ways I feel that I contribute to other people’s lives.
Something that I didn’t get around to writing about, but is probably in one of the early drafts and notes, is that having children was so important to me [because] that…was my father’s story. My great-grandfather, grandfather, and my dad all had kids—and I didn’t want to be the one to drop the ball. I can’t isolate my loving my kids from the pride I take in being a father as part of this lineage of fatherhood.
But at the same time, the contradiction there is I do say that I wish I was standing at the podium holding this trophy, not for the sake of the larger community, but to get my father’s acknowledgement. The trophy is a measurement of success that my father would recognize.
In the essay “Intervention” you ask your younger brother, Robbie, how he wants to be remembered when he’s no longer here. I’m going to ask you the same question—how do you want to be remembered?
Having had this conversation and thinking about my legacy, an ambitious telling would be to have Gregory Pardlo High Schools around the country. What that symbolizes for me is a sense of permanence.
In this same essay, you also described your alcoholism as being the closest thing you have to religion. What did you mean by that?
That is the only place that I feel it’s necessary to acknowledge helplessness. If the ambitious me feels like I can contend with whatever happens in the world outside, the thing that I cannot promise myself with any sense of security is that I’m going to be sober tomorrow.
Alcoholism is the one clear space in my life where my ambition is neutralized. There is no external narrative there. I am entirely in relation to myself. And the only way that I can even look forward to being sober tomorrow is by acknowledging that I have no control over that promise. It’s necessary for me to humble myself in the face of that threat.
Yahdon Israel is a writer, from Bed-Stuy, Brooklyn, who has written for Avidly, the New Inquiry, Brooklyn Magazine, LitHub, and Poets & Writers. He graduated from the MFA Creative Non-Fiction Writing program at the New School. He is the Awards VP of the National Book Critics Circle; runs a popular Instagram page which promotes literature and fashion under the hashtag Literaryswag, and host a web show for writers called LIT.
Photographs by Rog Walker.
In Technology We Trust: A Q&A With Victor LaValle
Whenever I read a book, I try my best to read it on its own terms. To not allow my understanding of what I think I know—or expectations for what I think should exist—compromise what’s right in front me. What I mean is I try to get out of a book’s way; I try to get out of the writer’s way. Instead of leading, I allow myself to be led, bearing witness to the journey.
In the same way that it’s “easier to build strong children than to repair broken men,” in the words of Frederick Douglass, it’s easier to make mistakes than it is to admit them. This is certainly true for me and, after reading Victor LaValle’s newest novel, The Changeling (Spiegel & Grau), I see I’m not alone. Borrowing its basic premise from folklore, The Changeling is a story that lends language to what happens, or what can happen, when a father, in this case a man named Apollo, is blinded by the fiction that he knows best, even when reality suggests otherwise. Under his nose, and on his watch, Apollo’s son, Brian, is switched out with the baby of a troll, but it is only his wife, Emma, who suspects it—not that she suspects their baby is a troll per se, but Emma knows the child they have is not theirs. Apollo isn’t convinced. This is where social media and technology enter the narrative.
For Apollo, Facebook is the site for which the fiction of his fairytale fathering can be turned into fact. He floods his feed with pictures of his newborn son. Some are clear, others blurry. He receives Likes and comments about what a good father he is, and it’s the Likes that blind him from what should’ve been obvious. The fact that Apollo’s own baby could be switched without his noticing wouldn’t only mean father doesn’t know best, and that Emma knows better, but also: that he knows very little at all. The simmering tension between Apollo and Emma boils over when Emma chains Apollo to a radiator, beats him bloody, kills the troll baby, and disappears into the New York City night. How does Apollo, a man intent on maintaining appearances, figure out that things aren’t always what they appear to be? How does he recover that which he has lost? He learns to listen. No longer to the chamber of voices that echo only what he wants to hear—the language of social media—but to those voices that were always there, telling him what he needed to hear, even when he did not want to hear it.
While reading The Changeling I started to become self-aware of the dependency of my generation (often referred to as “millennials”) on social media—its ability to make us seen and “likeable.” And by the end I realized that the most important technology we have is our ears, our ability to listen to one another. The photographs of me and LaValle, taken periodically during our interview, perfectly illustrate this realization. You’ll notice that there are times when either I’m not listening to LaValle, or he’s not listening to me, but that’s because we each have something in our hands that prevents us from doing so. “If the concept of God,” James Baldwin wrote, “has any validity or any use, it can only be to make us larger, freer, and more loving. If God cannot do this, then it is time we got rid of Him.” This is how I’ve learned to feel about anything that’s been given to us with the intention of making us “better” and ultimately failed—whether it’s technology, social media, or even literature. Only when we put down those things that can oftentimes obscure our vision can we truly see—and hear—what’s right in front of us.
LaValle is the author of three three previous novels, The Ecstatic (Crown, 2002), Big Machine (Spigel & Grau, 2009), and The Devil in Silver (Spiegel & Grau, 2012), as well as a collection of stories, Slapboxing With Jesus (Vintage, 1999), and the novella The Ballad of Black Tom (Tor, 2016). He teaches writing at Columbia University and lives in New York with his wife, author Emily Raboteau, and his two sons.
How long have been working on The Changeling?
About three years. I was trying to take a page from writers who are not super precious with their work. They just produce and produce and produce—and every second or third book might be great, the second one is really damn good and the third one is garbage. But so what? You’re just working through your stuff. I put out The Ballad of Black Tom last year; The Changeling is this year; I’ll have another one next year. This is so I don’t get too fussy.
The first draft of this book, my editor, Chris Jackson, told me, “No one’s gonna sign up for that.”
What was the book when you gave it to him?
It literally began with the scene in the kitchen where his wife locks [Apollo] up and is beating the hell out of him and killing the baby. And it just went from there. My publisher, editor, and I all went to lunch together. The publisher, she says, “I’m not going to let Chris buy this book if it starts like this because I can’t imagine anyone who would get into it—and she had good reasons: “You’ll break a lot more people’s hearts if it feels like this is happening to them,” my publisher told me. “I’m not telling you to make it nicer. Right now, you’re doing the equivalent of a horror movie where it’s a gory beheading versus you’re an hour into the movie and you start to really care about these people and then it means more. If you do that, we’ll buy the book.” It was very good advice.
That makes sense because the first hundred pages are like a family history, explaining the circumstances that conspired to make Apollo and Emma’s marriage feel real. What I appreciated was your ability to create a timeline that felt to me like it was happening as it happened to the character.
Sometimes, as readers, we have access to certain information that the character doesn’t. That’s not the case here. The bomb drops on the reader and character at the same time. There’s very little shelter. It really shows how we, as people, move about the world with the information we have—and how that information is often very limited. And the people who withhold information from us, often our parents thinking they’re protecting us, but they’re also putting us in unforeseeable danger as well. I feel like we’re always learning about things that anyone outside of the situation assumes we should already know. You’re just now learning that the thing that you thought didn’t happen actually did. How much of this book is art imitating life? How often do you find yourself navigating moments like the ones Apollo navigates?
Well I always feels like I’m catching up, finding out information late, if at all. I’m always surprised about what I don’t know that I should’ve known—about family members, myself, my kids. And I definitely want the reader to feel like Apollo, in that most of the time he doesn’t know what the hell is going on.
And the irony of that is he’s named after a god. I mean, he’s also named after Carl Weathers’s Apollo Creed, but that is a god’s name. So Apollo, the character, is always at the mercy of what he can’t see. And what’s funny is, every time he tries to assert his authority, a woman usually subverts him. What struck me was the amount of empathy you had for your female characters.
For the past three years I’ve been reading books by men, and thinking about how they write women differently. And it all started when I read The Women by Hilton Als. It’s a 135-page critical memoir about how he basically didn’t realize who his mother was until she died. And not who his mother was in terms of her role in his life. He realized that all he had ever seen of her was as his mother, completely neglecting the fact that she had an interior life. You give each of the women characters a rich interior life. Is that something you knew you wanted to do?
I was trying to think about two things: The particular fairytales about changelings are almost always exclusively about mothers who realize their children had been switched and what they do as a result; and the unstated implication of that is the fathers wouldn’t care or wouldn’t notice because they weren’t present. And my thinking about that bonded with this idea of the “new dad.” Of a certain age and younger there are these men who go, “I’m going to change those diapers,” “I’m going to be at the school.” And the danger of being those new dads—and this is my opinion—I get so much credit for being little more than a minimal dad. I show up for school on Family Fridays and the mothers and teachers are like,“Oh! It’s so good to see you! Oh you’re such a good dad!” and the mothers who are always there volunteering and basically giving blood to the kids are stepped over just so I can be told I’m a good dad—and I haven’t been there for six months! And so I was really thinking about this idea. But as I tried to step up my game, and as Apollo in the book tries to step up his game, as a man and as a father, the seesaw Apollo is walking up, there’s still a bunch of women standing on it so that he can ascend, completely convinced that it is not going to drop out on him at all. And that lead me to thinking, “Well what if we told this fairytale in way that did not go, ‘Oh look how great the dad is,’ and instead the dad is doing his part,” but…these women have been doing this very thing for thousands of years.
Another reason the women characters feel full is because of my wife, Emily Raboteau. I was telling her about how Emma kills the changeling baby and then just runs. Emily asked me, “Well why did she kill the changeling baby?” And I was like, “because she has to, because the plot needs it.” And she was like, “Now that I’m a mother, even if I saw a demon baby I don’t know that I could kill it. It would be too hard.” And this led me to think about how there needs to be message boards where these mothers are sharing info about how to get their babies back. Some Reddit group where they’re talking about the old myths. Then it evolved into something more than her just killing the baby because she was angry at Apollo. The first version was Emma killing the baby because she was angry at Apollo. And Emily asked, “Why would she kill her baby if she’s mad at Apollo? Why doesn’t she kill Apollo?”
And that’s a way to still make the man the center of the narrative.
Exactly! So I asked her, “Well what would be a good reason?” and she said, “The only reason I would ever kill some other baby is if it meant I got my baby back—and it would still kill me to do it.” And so those conversations, her just sort of pushing back, filtered into the book in a lot of good ways that make all the women present in a real way.
Although the book follows Apollo, which by default should suggest he’s the protagonist, Emma strikes me as the protagonist. She’s the real MVP. I feel like Apollo is the threshold for which we get to see Emma be great. In that, the book strikes me, if nothing else, as a love letter/apology to Emily, your wife, for years of, I can only imagine, you not listening to her. This book seems to be saying, “For all the years I haven’t been listening, I am now.” I used to think all that mattered in a conversation was being right. Now I realize people want to be understood. Listened to. Believed.
Sometimes with fiction, readers try to interact with a book on a cosmetic level—plot, character, theme, etc.—to avoid the emotional logic on which the book operates. And that’s the level I think this book is working on—this remorse, this understanding of your place in the world as a father. That for doing so little you get so much, in contrast to the women, the mothers, who do so much but get so little.
I agree with you. At a certain point, I started treating Apollo as the antagonist and Emma as the protagonist so that I could get rid of the male ego thing, but also so that when Apollo says [to Emma], “You’re what’s wrong with this family,” when he think she’s gone crazy for not believing the troll to be their baby, that would only happen if he is the antagonist, and have everyone just sort of hate him. And then when Emma runs, after she kills the baby, the reader maybe responds, “I thought she was the one I’m supposed to like.” And then she’s gone and maybe this gives you time to begin to like Apollo. Part of Apollo’s journey is going from the man who tells his wife, “You’re what’s wrong with this family” to a man who at the end says, “We can’t win without each other.”
Yahdon Israel has written for Avidly, the New Inquiry, LitHub, Guernica, and Brooklyn Magazine. He graduated from the New School with an MFA in creative nonfiction. He currently serves as the VP of Awards and Membership for the National Book Critics Circle and runs a popular Instagram page that promotes literature and fashion under the hashtag #literaryswag.
Photographs by John Midgley.
In Technology We Trust: A Q&A With Victor LaValle
Whenever I read a book, I try my best to read it on its own terms. To not allow my understanding of what I think I know—or expectations for what I think should exist—compromise what’s right in front me. What I mean is I try to get out of a book’s way; I try to get out of the writer’s way. Instead of leading, I allow myself to be led, bearing witness to the journey.
In the same way that it’s “easier to build strong children than to repair broken men,” in the words of Frederick Douglass, it’s easier to make mistakes than it is to admit them. This is certainly true for me and, after reading Victor LaValle’s newest novel, The Changeling (Spiegel & Grau), I see I’m not alone. Borrowing its basic premise from folklore, The Changeling is a story that lends language to what happens, or what can happen, when a father, in this case a man named Apollo, is blinded by the fiction that he knows best, even when reality suggests otherwise. Under his nose, and on his watch, Apollo’s son, Brian, is switched out with the baby of a troll, but it is only his wife, Emma, who suspects it—not that she suspects their baby is a troll per se, but Emma knows the child they have is not theirs. Apollo isn’t convinced. This is where social media and technology enter the narrative.
For Apollo, Facebook is the site for which the fiction of his fairytale fathering can be turned into fact. He floods his feed with pictures of his newborn son. Some are clear, others blurry. He receives Likes and comments about what a good father he is, and it’s the Likes that blind him from what should’ve been obvious. The fact that Apollo’s own baby could be switched without his noticing wouldn’t only mean father doesn’t know best, and that Emma knows better, but also: that he knows very little at all. The simmering tension between Apollo and Emma boils over when Emma chains Apollo to a radiator, beats him bloody, kills the troll baby, and disappears into the New York City night. How does Apollo, a man intent on maintaining appearances, figure out that things aren’t always what they appear to be? How does he recover that which he has lost? He learns to listen. No longer to the chamber of voices that echo only what he wants to hear—the language of social media—but to those voices that were always there, telling him what he needed to hear, even when he did not want to hear it.
While reading The Changeling I started to become self-aware of the dependency of my generation (often referred to as “millennials”) on social media—its ability to make us seen and “likeable.” And by the end I realized that the most important technology we have is our ears, our ability to listen to one another. The photographs of me and LaValle, taken periodically during our interview, perfectly illustrate this realization. You’ll notice that there are times when either I’m not listening to LaValle, or he’s not listening to me, but that’s because we each have something in our hands that prevents us from doing so. “If the concept of God,” James Baldwin wrote, “has any validity or any use, it can only be to make us larger, freer, and more loving. If God cannot do this, then it is time we got rid of Him.” This is how I’ve learned to feel about anything that’s been given to us with the intention of making us “better” and ultimately failed—whether it’s technology, social media, or even literature. Only when we put down those things that can oftentimes obscure our vision can we truly see—and hear—what’s right in front of us.
LaValle is the author of three three previous novels, The Ecstatic (Crown, 2002), Big Machine (Spigel & Grau, 2009), and The Devil in Silver (Spiegel & Grau, 2012), as well as a collection of stories, Slapboxing With Jesus (Vintage, 1999), and the novella The Ballad of Black Tom (Tor, 2016). He teaches writing at Columbia University and lives in New York with his wife, author Emily Raboteau, and his two sons.
How long have been working on The Changeling?
About three years. I was trying to take a page from writers who are not super precious with their work. They just produce and produce and produce—and every second or third book might be great, the second one is really damn good and the third one is garbage. But so what? You’re just working through your stuff. I put out The Ballad of Black Tom last year; The Changeling is this year; I’ll have another one next year. This is so I don’t get too fussy.
The first draft of this book, my editor, Chris Jackson, told me, “No one’s gonna sign up for that.”
What was the book when you gave it to him?
It literally began with the scene in the kitchen where his wife locks [Apollo] up and is beating the hell out of him and killing the baby. And it just went from there. My publisher, editor, and I all went to lunch together. The publisher, she says, “I’m not going to let Chris buy this book if it starts like this because I can’t imagine anyone who would get into it—and she had good reasons: “You’ll break a lot more people’s hearts if it feels like this is happening to them,” my publisher told me. “I’m not telling you to make it nicer. Right now, you’re doing the equivalent of a horror movie where it’s a gory beheading versus you’re an hour into the movie and you start to really care about these people and then it means more. If you do that, we’ll buy the book.” It was very good advice.
That makes sense because the first hundred pages are like a family history, explaining the circumstances that conspired to make Apollo and Emma’s marriage feel real. What I appreciated was your ability to create a timeline that felt to me like it was happening as it happened to the character.
Sometimes, as readers, we have access to certain information that the character doesn’t. That’s not the case here. The bomb drops on the reader and character at the same time. There’s very little shelter. It really shows how we, as people, move about the world with the information we have—and how that information is often very limited. And the people who withhold information from us, often our parents thinking they’re protecting us, but they’re also putting us in unforeseeable danger as well. I feel like we’re always learning about things that anyone outside of the situation assumes we should already know. You’re just now learning that the thing that you thought didn’t happen actually did. How much of this book is art imitating life? How often do you find yourself navigating moments like the ones Apollo navigates?
Well I always feels like I’m catching up, finding out information late, if at all. I’m always surprised about what I don’t know that I should’ve known—about family members, myself, my kids. And I definitely want the reader to feel like Apollo, in that most of the time he doesn’t know what the hell is going on.
And the irony of that is he’s named after a god. I mean, he’s also named after Carl Weathers’s Apollo Creed, but that is a god’s name. So Apollo, the character, is always at the mercy of what he can’t see. And what’s funny is, every time he tries to assert his authority, a woman usually subverts him. What struck me was the amount of empathy you had for your female characters.
For the past three years I’ve been reading books by men, and thinking about how they write women differently. And it all started when I read The Women by Hilton Als. It’s a 135-page critical memoir about how he basically didn’t realize who his mother was until she died. And not who his mother was in terms of her role in his life. He realized that all he had ever seen of her was as his mother, completely neglecting the fact that she had an interior life. You give each of the women characters a rich interior life. Is that something you knew you wanted to do?
I was trying to think about two things: The particular fairytales about changelings are almost always exclusively about mothers who realize their children had been switched and what they do as a result; and the unstated implication of that is the fathers wouldn’t care or wouldn’t notice because they weren’t present. And my thinking about that bonded with this idea of the “new dad.” Of a certain age and younger there are these men who go, “I’m going to change those diapers,” “I’m going to be at the school.” And the danger of being those new dads—and this is my opinion—I get so much credit for being little more than a minimal dad. I show up for school on Family Fridays and the mothers and teachers are like,“Oh! It’s so good to see you! Oh you’re such a good dad!” and the mothers who are always there volunteering and basically giving blood to the kids are stepped over just so I can be told I’m a good dad—and I haven’t been there for six months! And so I was really thinking about this idea. But as I tried to step up my game, and as Apollo in the book tries to step up his game, as a man and as a father, the seesaw Apollo is walking up, there’s still a bunch of women standing on it so that he can ascend, completely convinced that it is not going to drop out on him at all. And that lead me to thinking, “Well what if we told this fairytale in way that did not go, ‘Oh look how great the dad is,’ and instead the dad is doing his part,” but…these women have been doing this very thing for thousands of years.
Another reason the women characters feel full is because of my wife, Emily Raboteau. I was telling her about how Emma kills the changeling baby and then just runs. Emily asked me, “Well why did she kill the changeling baby?” And I was like, “because she has to, because the plot needs it.” And she was like, “Now that I’m a mother, even if I saw a demon baby I don’t know that I could kill it. It would be too hard.” And this led me to think about how there needs to be message boards where these mothers are sharing info about how to get their babies back. Some Reddit group where they’re talking about the old myths. Then it evolved into something more than her just killing the baby because she was angry at Apollo. The first version was Emma killing the baby because she was angry at Apollo. And Emily asked, “Why would she kill her baby if she’s mad at Apollo? Why doesn’t she kill Apollo?”
And that’s a way to still make the man the center of the narrative.
Exactly! So I asked her, “Well what would be a good reason?” and she said, “The only reason I would ever kill some other baby is if it meant I got my baby back—and it would still kill me to do it.” And so those conversations, her just sort of pushing back, filtered into the book in a lot of good ways that make all the women present in a real way.
Although the book follows Apollo, which by default should suggest he’s the protagonist, Emma strikes me as the protagonist. She’s the real MVP. I feel like Apollo is the threshold for which we get to see Emma be great. In that, the book strikes me, if nothing else, as a love letter/apology to Emily, your wife, for years of, I can only imagine, you not listening to her. This book seems to be saying, “For all the years I haven’t been listening, I am now.” I used to think all that mattered in a conversation was being right. Now I realize people want to be understood. Listened to. Believed.
Sometimes with fiction, readers try to interact with a book on a cosmetic level—plot, character, theme, etc.—to avoid the emotional logic on which the book operates. And that’s the level I think this book is working on—this remorse, this understanding of your place in the world as a father. That for doing so little you get so much, in contrast to the women, the mothers, who do so much but get so little.
I agree with you. At a certain point, I started treating Apollo as the antagonist and Emma as the protagonist so that I could get rid of the male ego thing, but also so that when Apollo says [to Emma], “You’re what’s wrong with this family,” when he think she’s gone crazy for not believing the troll to be their baby, that would only happen if he is the antagonist, and have everyone just sort of hate him. And then when Emma runs, after she kills the baby, the reader maybe responds, “I thought she was the one I’m supposed to like.” And then she’s gone and maybe this gives you time to begin to like Apollo. Part of Apollo’s journey is going from the man who tells his wife, “You’re what’s wrong with this family” to a man who at the end says, “We can’t win without each other.”
Yahdon Israel has written for Avidly, the New Inquiry, LitHub, Guernica, and Brooklyn Magazine. He graduated from the New School with an MFA in creative nonfiction. He currently serves as the VP of Awards and Membership for the National Book Critics Circle and runs a popular Instagram page that promotes literature and fashion under the hashtag #literaryswag.
Photographs by John Midgley.
Where Big Books Are Born: Tayari Jones on the Ucross Foundation
Getting to Ucross is not easy. There aren’t many direct flights into Sheridan, Wyoming. You have to fly to Denver, where there may or may not be a tiny plane waiting to take you the rest of the way. After that, budget another forty-five minutes by car. Unless it’s snowing. If that is the case, you’ll get there when you get there, but once you do, it’s paradise. I have a theory about artists residencies: They are helpful only if they provide something that you don’t have at home. A friend of mine who has a big family says that a retreat is any place her kids are not. When I was a young writer accustomed to writing on a desk shoved into a closet, a room with a window constituted luxury. By my fourth novel I had a room of my own, but I didn’t have peace and natural wonder. Ucross is situated on the open prairie. As an early riser, I delighted in glorious purple-streaked sunrises. Just outside my studio, deer pranced like jackrabbits. Needless to say this was a far cry from my life in Jersey City, where I once looked out of my window just in time to see a greasy raccoon scurry up a lamppost for a better look at the drunks tussling in the middle of the street. In the quiet dawn of Wyoming I solved a major problem in my novel An American Marriage. There in my studio, completely alone, I decided to experiment with an epistolary format. The solitude of Ucross lent itself perfectly to the idea of separated lovers communicating by post. The helpful staffers provided me with a typewriter so I was able to duplicate the way my hero would write letters from prison. Each morning for a month I awoke filled with anticipation. I tiptoed downstairs to my studio where my characters waited for me to break the silence of the dawn with the sharp click of a typewriter, scoring their words onto clean paper.
Three Points of Productivity:
1. It’s multidisciplinary. There’s less of a sense of competition—and less pressure to network, or to be networked—when folks aren’t in the same lane.
2. Meals are provided. Until you don’t have to feed yourself, you don’t realize what a hassle it is to feed yourself; also, good healthy food makes for a strong writing day.
3. The hikes are gorgeous. A daily sojourn into nature became a way to loosen up knots in my story; it was a meditation of sorts.
Tayari Jones is the author of four books, including the novel An American Marriage, published by Algonquin Books in February.

Ucross Foundation: Two- to six-week residencies from March through early June and from mid-August through early December to poets, fiction writers, and creative nonfiction writers on a working ranch in Ucross, Wyoming. Residents are provided with lodging, studio space, and meals. Next deadline: March 1. Ucross Foundation Residency Program, 30 Big Red Lane, Clearmont, WY 82835. (307) 737-2291. www.ucrossfoundation.org (Credit: Stephen G. Weaver)
Where Big Books Are Born: Danez Smith on the Millay Colony
I left the Millay Colony with a new relationship to deodorant and a new respect for wild turkeys, but it was my second collection and the relationships with my friends and collaborators that were born anew in that beloved barn. My month at Millay was split between a four-week individual residency and a weeklong group residency with the Dark Noise Collective, my artistic and chosen family. I showed up to Millay a lotta bit nervous but curious about what doors in my work would open up there, out of my element. (I’m very much used to being Black&FreeInTheCity, not Black&LostInTheWood.) Thankfully the staff and the land itself, which seems infused with some soft blessing by Edna herself, make it hard not to settle in and let the work take you. Millay is where my book became a book. I had time and space to play in new forms, get to the questions I didn’t always have the time to think. I got to the bottom of myself there. Millay offered comfort and the space for deep meditation and investigation. During the group residency, our relationships to one another and our work had no choice but to deepen, having been given so much time to be with one another, away from noise and worry. Millay is held up in my heart as one of the best places artists can go to toil and dance in the hard labor that feeds them most.
Three Points of Productivity:
1. The cooking is excellent, the groceries for all other meals are provided, and the kitchen is great for dancing.
2. The land surrounding the residency is perfect for people who love nature and people who are new to it and scared of it just the same.
3. If you’re ever feeling low on inspiration, you can just Google all the writers and artists who have carved their names into the doorframes to get some juice.
Danez Smith is the author of two books, including Don’t Call Us Dead, published by Graywolf Press in 2017.

The Millay Colony: Two- and four-week residencies from April through November for poets, fiction writers, and creative nonfiction writers at Steepletop, the former estate of Edna St. Vincent Millay in Austerlitz, New York. Residents are provided with lodging, studio space, and meals. Next deadline: March 1. Millay Colony for the Arts, 454 East Hill Road, P.O. Box 3, Austerlitz, NY 12017. (518) 392-3103. www.millaycolony.org (Credit: Whitney Lawson)
Craft Capsule: Every Novel Is a Journey
This is the twenty-fourth in a series of micro craft essays exploring the finer points of writing. Check back each week for a new Craft Capsule.
***
Last week I wrote about how I came to make Roy the protagonist of my new novel, An American Marriage. The decision was frustrating because I came to this tale seeking to amplify the muffled voices of women who live on the margins of the crisis of mass incarceration. So imagine how hard it was for me to make the Roy’s story the main color of the take and relegate Celestial’s point of view to a mere accent wall. It nearly killed me. I was prepared to pull the novel from publication.
Luckily, I had a craft epiphany.
Roy is a great character. He’s like Odysseus, a brave and charismatic man returned home from a might battle. He just wants to get home and be taken care of by a loving wife and sheltered in a gracious house. His voice was very easy to write because he is easy to like; his desires and decisions make it easy to empathize with him. He is a wrongfully incarcerated black man. What decent person wouldn’t root for him?
Celestial was bit more challenging. She’s ambitious. She’s kind of stubborn. And most important, she isn’t really cut out to be a dutiful wife. Back when she was the protagonist of the novel, I used to say, “I am writing a novel about a woman whose husband is wrongfully incarcerated…” and everyone would expect the novel to be about her fight to free him. And it wasn’t. It was about her decision not to wait.
On the level of craft, it just didn’t work. For one thing, you can’t write a compelling novel about what someone doesn’t do. (There is a reason why Bartelby doesn’t get to narrate his own story.) Second, as I wrote last week, Roy’s crisis is just too intense and distracting for the reader to care about any other character as much.
So, what to do?
I foregrounded Roy. He is the protagonist and readers find him to be very “relatable” (my very least favorite word in the world). I took Roy on the journey, and I invite readers to accompany him. As the writer, I came to the table understanding that the expectations put on women to be “ride or die” are completely unreasonable; furthermore, there is no expectation of reciprocity. But rather than use Celestial’s voice to amplify my position, I allowed Roy the hard work of interrogating his world view, and the reader, by proxy, must do the same.
The result is a novel that was a lot harder to write, but the questions I posed to myself and my readers were richer, more complex, and I hope, more satisfying.
Tayari Jones is a contributing editor of Poets & Writers Magazine. She is the author of four novels, including An American Marriage, forthcoming in February from Algonquin Books. Her website is www.tayarijones.com.
Craft Capsule: Finding Your Story
This is the twenty-first in a series of micro craft essays exploring the finer points of writing. Check back each week for a new Craft Capsule.
***
Like most thoughtful people, I have noticed that the world is on fire and I want to use my skills to help extinguish the flames. To this end, I set out five years ago to write a novel that addresses the injustice of wrongful incarceration. I applied for and received a fellowship to the Radcliffe Institute and I became a dedicated researcher. I learned a lot, so much so that I got angry just watching Law & Order, my ex-favorite television show. I was informed, “woke,” and motivated, but I couldn’t write a novel because I had no story. The problem was that I was trying to write to the issue, and I can only write a story that is issue-adjacent.
I know I have a novel when I have a question to which I don’t know the moral/ethical answer. When it comes to wrongful incarceration, I am not torn. The state should not imprison innocent people. Full stop. Also without ambiguity: The prison system is cruel, corrupt, and in desperate need of reform, if not abolition.
So where was the novel?
The answer revealed itself in a food court where I spied a young couple. She was dressed in a lovely cashmere coat. He wore inexpensive khakis and a polo. They were clearly angry, and clearly in love. I overheard the woman say, “Roy, you know you wouldn’t have waited on me for seven years.” He shot back, “What are you talking about? This shit wouldn’t have happened to you in the first place.”
Just then, I knew I had a novel. The reason is that I understood that they were both probably right. I didn’t know him, but I couldn’t quite picture him waiting chastely by for seven years. At the same time, I couldn’t imagine her behind bars. But did he have a right to demand her loyalty when both seem to agree she would be in no position to demand the same? Was this question moot since she would not likely face this challenge? Was this a kind of privilege? Could she mitigate this privilege by waiting like a modern-day Penelope? Should she?
So we have a couple with a conflict, and at stake between them are issues of reciprocity, duty, and love. Yes, there is the injustice of mass incarceration. And yes, this injustice is fueled by racism and prejudice. Neither of them doubt this, and neither do I. But the question of “will you wait for me” is foremost on his mind.
The result is my new novel, An American Marriage. Roy and Celestial are newlyweds, married only eighteen months, when Roy is arrested for a crime he did not commit. When he is slapped with a twelve-year sentence, the questions of desire and responsibility are at the center of the characters’ lives. As a writer, I was genuinely torn: Roy needs Celestial to be a link to the life he left behind, and Celestial loves her husband, but she has only one life. I wrote this novel not only to satisfy my heart’s curiosity as to what they would do, but to also satisfy the part of my mind that wondered what should they do.
I realized that my passion for the issue of incarceration was the reason that I couldn’t write about it directly. A novel is not me, as a writer, telling the reader what I already know. And an honest novel is not about me pretending to take on “both sides” of an issue about which I have a clear opinion. I had to start with my issue and then walk away from it until I found the thing I didn’t know. To truly challenge the reader, I had to challenge myself as well.
Tayari Jones is a contributing editor of Poets & Writers Magazine. She is the author of four novels, including An American Marriage, forthcoming in February from Algonquin Books. Her website is www.tayarijones.com.
Craft Capsule: Gin and Scotch Tape
This is the eleventh in a series of micro craft essays exploring the finer points of writing. Check back each week for a new Craft Capsule.
***
Years ago a distinguished poet hosted our class’s workshops at her home in Virginia. The house was perched on an incline; down the hill was her writing cabin alongside a pond. We met at her dining room table and tried not to be distracted by the hawks swooping outside the windows.
A student brought in a draft that compared the scent of gin to Scotch tape. Setting aside all other matters of theme or craft, the discussion lingered on this comparison. The simile was bright and original. But was it accurate? That only a few in the room had ever sampled gin, and even then only of an aristrocrat variety, did not aid our analysis.
Reaching her limit, the professor sprang up from the table. “We’re settling this,” she said. She walked into the kitchen and retrieved a roll of Scotch tape. She went to a corner of the dining room, opened a cabinet, and pulled out a bottle. She walked the gin around the table so we could sniff accordingly.
Lesson one? To compare the scents of Scotch tape and gin doesn’t quite work, because the former obscures the latter’s floral qualities.
Lesson two? Always be prepared to have your simile put to the test.
Lesson three? Never let a turn of figurative language, no matter how vivid or clever, hijack what you’re trying to say. I can’t remember who wrote that poem, or where its heart lay. I only remember the gin and Scotch tape.
Sandra Beasley is the author of three poetry collections, including Count the Waves (Norton, 2015), and a memoir. Her website is SandraBeasley.com.
Craft Capsule: Left Brain, Right Brain
This is the tenth in a series of micro craft essays exploring the finer points of writing. Check back each week for a new Craft Capsule.
***
I attended a high school geared toward professions in science or technology, so I have an active analytical streak and crave objective rubrics for understanding the wildly creative poems, stories, and essays that I read. I suspect I’m not alone in this.
One of my mentors, Gregory Orr, articulated four “temperaments” of poetry in a 1988 essay titled “Four Temperaments and the Forms of Poetry.” You can envision these facets of craft as quadrants, positioned on an X-Y axis. To the left, limiting impulses: “Story” in the upper quadrant and, below it, “Structure.” To the right, impulses that extend limitlessness: “Music” in the upper and, below it, “Imagination.” Though designed for poetry, I find these temperaments useful for prose as well. As writers, we each typically favor two of the four in our work. Which temperaments bring you to the page? Which come easiest to you? Which do you need to consciously strengthen in your work?
This system gives us a way to articulate differences in aesthetic without ranking them. I’m relieved to set aside presumptive hierarchies. I suspect I’m not alone in this.
Sandra Beasley is the author of three poetry collections, including Count the Waves (Norton, 2015), and a memoir. Her website is SandraBeasley.com.
Craft Capsule: Beware the Indeterminate “It”
This is the eighth in a series of micro craft essays exploring the finer points of writing. Check back each week for a new Craft Capsule.
***
Beware the indeterminate “it,” I often say, when fine-tuning a draft.
But that word is so convenient. “It” carries the football from the previous sentence. Whatever “it” you just defined, you’re sticking with it for another ten yards, right?
Except that you’re fumbling the play. Too often, relying on “it” dissipates your language’s energy. Circle every “it” that leads off a sentence. Revising to avoid these instances will force your verbs into action, and clarify your intent.
This is not a hard-and-fast rule. Sometimes an indeterminate “it” will remain, one that has earned its place on the field. The pronoun can be strategic—signifying not just gender neutrality but an absence of comprehension or known name, a fumbling toward meaning, the building of suspense.
In the right hands, “It” can be a potent force. Just ask Stephen King.
Sandra Beasley is the author of three poetry collections, including Count the Waves (Norton, 2015), and a memoir. Her website is SandraBeasley.com.
Craft Capsule: The Art of Targeted Revision
This is the ninth in a series of micro craft essays exploring the finer points of writing. Check back each Tuesday for a new Craft Capsule.
***
“Too many hours of revising—to no clear end!” my student complains. He is tired. He feels like the poem never really gets better. There’s always more work to do.
Welcome to revision: the arbitrary realm in which we debate “the” versus “an,” “this” versus “that.” Spend an hour putting a comma in. An hour later, take it out.
Part of the problem is that we complicate the revision process by making our aims abstract. One big revision, we promise ourselves, will make the poem “better.” Don’t privilege “better,” which is a meaningless term. Assign clear and objective tasks. Devote one round of revision exclusively to heightening your imagery, another to reconsidering your verb choices, a third to playing with lineation or tense.
Think of each revision as an experiment. Often these experiments will feel like evolutionary progress, and you’ll keep their results intact. Not always, especially as you near the end of the revision process. When the new version fails to appeal—when you find yourself resisting, reverting, defending an earlier choice—you are locating the poem’s true form. You are identifying what makes this poem yours, and yours alone.
Sandra Beasley is the author of three poetry collections, including Count the Waves (Norton, 2015), and a memoir. Her website is SandraBeasley.com.
Craft Capsule: Find Your Metaphor
This is the seventh in a series of micro craft essays exploring the finer points of writing fiction. Check back each week for a new Craft Capsule.
***
A friend of mine, a poet, was trying to figure out what bothered him about a draft of my poem. “A poem should be like a wall,” he told me. “You build it brick by brick.” He pointed out that, in his opinion, key bricks were missing.
I didn’t share his vision, but I admired that he had one. I’ve come to value developing a metaphorical model for your genre. A model can help you identify your goals, name your struggles, and proceed toward success.
Perhaps you follow the lead of “stanza,” the Italian word for “room.” You come to think of each poem as a house. How do the rooms differ in function, size, and occupancy? Where does your central drama take place? What comprises your roof?
Perhaps you come to think of your essay as a harp. Each researched fact glimmers, an available string in a golden frame. But you can’t play them all at once. Only in choosing which notes to highlight, and how to sequence them, can you create music.
Personally, I always think of memoir as an egg. I’m protective of the inspiring memory, smooth and undisturbed in its surface. But I have to be prepared to break the egg. I have to make the idea messy before I can make a satisfying meal.
Perhaps your novel is a shark. Perhaps your villanelle is a waltz. Perhaps your short story is a baseball game. Don’t adopt my metaphors. Find one of your own.
Sandra Beasley is the author of three poetry collections, including Count the Waves (Norton, 2015), and a memoir. Her website is SandraBeasley.com.
Craft Capsule: The Egg in My Pocket
This is the first in a series of micro craft essays exploring the finer points of writing fiction. Check back each week for a new Craft Capsule.
***
As a project for school, my thirteen-year-old son, Will, spent several days carrying an egg around. His task was simple: Keep the egg from breaking.
The experiment was intended to show what it’s like to have a baby, to approximate the feeling of constant vigilance that never leaves you once you have a child. Ultimately, of course, it was supposed to make hormone-addled adolescents think twice before doing something stupid.
As a mother of three, though, I wasn’t convinced. A baby is nothing like an egg, unless it’s an egg that cries, wets itself, sucks on you constantly, and wakes you up four times a night. But as my son described the feeling of carrying his egg—he named it “Pablito”—I realized that it did remind me of something. “It’s always there,” Will said. “You can’t forget it or take it for granted. You feel protective and anxious all the time.”
Carrying an egg around is like writing a novel. No matter what else you’re doing, the fact of the novel is in the back of your mind. If you go too long without attending to it, you get nervous. It is always with you, a weight solid and yet fragile, in constant danger of being crushed. Like the egg, the weight of a book-in-progress is both literal and metaphorical. Within the accumulating pages, as inside the delicate eggshell, are the raw ingredients for something greater. Keeping it intact requires patience, time, attention—and, most of all, commitment. This concept applies to any stage of the process: The egg is both the idea that you nurture long before you begin to write, and the writing itself, which must be fostered and sustained.
Christina Baker Kline is the author of six novels, including A Piece of the World, published this month by William Morrow. Her website is christinabakerkline.com.
Craft Capsule: Deny the Accident
This is the third in a series of micro craft essays exploring the finer points of writing fiction. Check back each week for a new Craft Capsule.
***
Jackson Pollock’s reply to an interviewer’s question about how he composed his paintings of “accidental” splatterings has stuck with me. “I don’t use the accident,” he said. “I deny the accident.”
The sheer bravado of this is thrilling, and as a writer I find it to be a useful way to think about my work-in-progress. When I’m putting words on the page it’s easy to second guess, to question the often-unconscious choices I make as I go: the trajectories of characters’ lives, shifts in direction and focus, minor characters who gain traction as the story moves forward. The editor in my head starts whispering: You’re going in the wrong direction. Why are you spending so much time on that character? You need to focus, get back to the story you originally envisioned, stick to the plan.
Over time I’ve learned to trust my impulses. Whatever else they may be, these unanticipated detours are fresh and surprising; they keep me interested, and often end up adding depth to the work. Not always, of course—sometimes an accident is just an accident. But believing that these splatterings on my own canvas are there for a reason, as part of a larger process of conception, gives me the audacity to experiment.
Christina Baker Kline is the author of six novels, including A Piece of the World, published in February by William Morrow. Her website is christinabakerkline.com.
Craft Capsule: Good Sense
This is the second in a series of micro craft essays exploring the finer points of writing fiction. Check back each week for a new Craft Capsule.
***
The problem of beginning…
The Southern novelist and poet George Garrett, who was director of creative writing at the University of Virginia when I was a graduate student there, always said that if you’re having trouble getting into a chapter or a scene you should use all five senses right at the start, preferably in the first paragraph. Touch, taste, smell, hearing, sight. Your scene will jump to life, and you’ll have an easier time falling into the dream world of the story.
On a related note, Gustave Flaubert kept rotten apples in his desk drawer to evoke autumn when writing scenes that took place in that season….
Christina Baker Kline is the author of six novels, including A Piece of the World, published this month by William Morrow. Her website is christinabakerkline.com.
Craft Capsule: Good Sense
This is the second in a series of micro craft essays exploring the finer points of writing fiction. Check back each week for a new Craft Capsule.
***
The problem of beginning…
The Southern novelist and poet George Garrett, who was director of creative writing at the University of Virginia when I was a graduate student there, always said that if you’re having trouble getting into a chapter or a scene you should use all five senses right at the start, preferably in the first paragraph. Touch, taste, smell, hearing, sight. Your scene will jump to life, and you’ll have an easier time falling into the dream world of the story.
On a related note, Gustave Flaubert kept rotten apples in his desk drawer to evoke autumn when writing scenes that took place in that season….
Christina Baker Kline is the author of six novels, including A Piece of the World, published this month by William Morrow. Her website is christinabakerkline.com.
Craft Capsule: Good Sense
This is the second in a series of micro craft essays exploring the finer points of writing fiction. Check back each week for a new Craft Capsule.
***
The problem of beginning…
The Southern novelist and poet George Garrett, who was director of creative writing at the University of Virginia when I was a graduate student there, always said that if you’re having trouble getting into a chapter or a scene you should use all five senses right at the start, preferably in the first paragraph. Touch, taste, smell, hearing, sight. Your scene will jump to life, and you’ll have an easier time falling into the dream world of the story.
On a related note, Gustave Flaubert kept rotten apples in his desk drawer to evoke autumn when writing scenes that took place in that season….
Christina Baker Kline is the author of six novels, including A Piece of the World, published this month by William Morrow. Her website is christinabakerkline.com.
Craft Capsule: Tolstoy’s Short Chapters
This is the sixth in a series of micro craft essays exploring the finer points of writing fiction. Check back each week for a new Craft Capsule.
***
Anna Karenina is more than eight hundred pages long. So why does it feel shorter than many three-hundred-page books?
As I read this novel recently I noticed that Tolstoy cuts his long scenes into short chapters, usually no more than two or three pages. This makes sense, considering it was published in serial installments, from 1873 to 1877, in the Russian Messenger. Tolstoy often ends a chapter in a moment of suspense—a door opens, a provocative question is asked, a contentious group sits down to dinner, characters who’ve been circling each other finally begin to talk—which propels the reader forward into the next chapter.
The psychological effect of these short chapters is that this huge book is easy to get through. Reading in bed late at night (as I tend to do), I’m tempted to put it down, but then I riffle ahead to find that the next chapter is only three pages long. And I really want to find out who’s behind that door.
Three pages. I can do that—as a reader and as a writer.
Christina Baker Kline is the author of six novels, including A Piece of the World, published in February by William Morrow. Her website is christinabakerkline.com.
Craft Capsule: Visual Prompts
This is the fifth in a series of micro craft essays exploring the finer points of writing fiction. Check back each week for a new Craft Capsule.
***
For many writers, visual and tactile stimulation is an important component of the creative process. William Faulkner used to map his stories on the wall in his study. If you visit Rowan Oak, his home in Oxford, Mississippi, you can still see the notes for his 1954 novel, A Fable, in his precise, small handwriting. Edwidge Danticat has said that she has an evolving bulletin board in her workspace where she tacks up collages of photos of Haiti and images from magazines.
I, too, have a new board for each book I write. When I’m starting work on a novel I gather scraps like a magpie. My Orphan Train board was covered with postcards from the New York Tenement Museum depicting the interior of an immigrant Irish family’s cramped apartment, a black and white photograph of a young couple at Coney Island in the 1920s, a map of the village of Kinvara in Ireland. I hung a hand-carved Celtic cross on a green ribbon and a stone shamrock on a red ribbon from Galway; a Native American dreamcatcher from Maine; a silver train pin from a New York Train Riders’ reunion in Little Falls, Minnesota. I tacked up note cards: “Food in Ireland 1900s” was one (“wheatmeal, hung beef, tongue, barley”). Another listed ideas I wanted to explore (“links between misplaced and abandoned people with little in common”).
For A Piece of the World, I included a print of Andrew Wyeth’s painting Christina’s World; photos I took, inside and out, of Christina’s home in Cushing, Maine; some Emily Dickinson poems (“This is my letter to the world / That never wrote to me”); and postcards of other paintings Wyeth did at the Olson house, including Wind From the Sea and Christina Olson (both of which make appearances in my novel). I photocopied sketches Wyeth made for his portrait of Christina. I even included a small handful of grasses I’d plucked from the field Christina sat in.
I find these idea boards fun to assemble and inspiring as I work. My mantra, always: Find inspiration where you can.
Christina Baker Kline is the author of six novels, including A Piece of the World, published in February by William Morrow. Her website is christinabakerkline.com.

An outline of A Fable on the wall of William Faulkner’s study at Rowan Oak in Oxford, Mississippi. (Credit: Joe Bonomo)
Craft Capsule: Making Conversation
This is the fourth in a series of micro craft essays exploring the finer points of writing fiction. Check back each week for a new Craft Capsule.
***
Dialogue is hard to get right. It should sound like natural speech, but in fact it’s nothing like it. I like to send my creative writing students out to cafés and parks with notebooks to transcribe bits of overheard conversations. Then I ask them to type up these transcripts and turn them into dialogue between characters. Inevitably their written dialogue bears little resemblance to the overheard conversations. When you write dialogue you must eliminate niceties and unnecessary patter, and cut to the core of the exchange—unless the patter is crucial to the story, conveying a dissembling, depressed, incoherent, or boring personality. At the same time, it should sound natural, like something someone would actually say. The writer George Garrett called this dovetailing—trimming for verisimilitude and impact.
In direct and indirect speech, your characters should constantly be saying “no” to each other. Most of us (myself included) tend to avoid conflict in our real lives, but conflict is crucial in fiction. It keeps the story interesting.
Richard Price, in his novel Lush Life, allows his characters to talk and talk and talk. Price maintains a delicate balancing act; his characters’ words matter. What they say changes the direction of the story. But he never burdens his dialogue with exposition or forces it to convey plot points that don’t come up naturally. In Writing Fiction, Janet Burroway writes, “In order to engage us emotionally in a disagreement, the characters must have an emotional stake in the outcome.” Price’s characters are nothing if not emotionally invested.
Price’s dialogue is vital to the story because it moves the action forward. He constantly puts his characters in conflict with one another. Their conversations are full of surprises—self-revelation, inadvertent admissions, hearsay, evidence—and kinetic energy; they crackle with life. Real life.
Christina Baker Kline is the author of six novels, including A Piece of the World, published in February by William Morrow. Her website is christinabakerkline.com.
Craft Capsule: Making Conversation
This is the fourth in a series of micro craft essays exploring the finer points of writing fiction. Check back each week for a new Craft Capsule.
***
Dialogue is hard to get right. It should sound like natural speech, but in fact it’s nothing like it. I like to send my creative writing students out to cafés and parks with notebooks to transcribe bits of overheard conversations. Then I ask them to type up these transcripts and turn them into dialogue between characters. Inevitably their written dialogue bears little resemblance to the overheard conversations. When you write dialogue you must eliminate niceties and unnecessary patter, and cut to the core of the exchange—unless the patter is crucial to the story, conveying a dissembling, depressed, incoherent, or boring personality. At the same time, it should sound natural, like something someone would actually say. The writer George Garrett called this dovetailing—trimming for verisimilitude and impact.
In direct and indirect speech, your characters should constantly be saying “no” to each other. Most of us (myself included) tend to avoid conflict in our real lives, but conflict is crucial in fiction. It keeps the story interesting.
Richard Price, in his novel Lush Life, allows his characters to talk and talk and talk. Price maintains a delicate balancing act; his characters’ words matter. What they say changes the direction of the story. But he never burdens his dialogue with exposition or forces it to convey plot points that don’t come up naturally. In Writing Fiction, Janet Burroway writes, “In order to engage us emotionally in a disagreement, the characters must have an emotional stake in the outcome.” Price’s characters are nothing if not emotionally invested.
Price’s dialogue is vital to the story because it moves the action forward. He constantly puts his characters in conflict with one another. Their conversations are full of surprises—self-revelation, inadvertent admissions, hearsay, evidence—and kinetic energy; they crackle with life. Real life.
Christina Baker Kline is the author of six novels, including A Piece of the World, published in February by William Morrow. Her website is christinabakerkline.com.
Craft Capsule: Visual Prompts
This is the fifth in a series of micro craft essays exploring the finer points of writing fiction. Check back each week for a new Craft Capsule.
***
For many writers, visual and tactile stimulation is an important component of the creative process. William Faulkner used to map his stories on the wall in his study. If you visit Rowan Oak, his home in Oxford, Mississippi, you can still see the notes for his 1954 novel, A Fable, in his precise, small handwriting. Edwidge Danticat has said that she has an evolving bulletin board in her workspace where she tacks up collages of photos of Haiti and images from magazines.
I, too, have a new board for each book I write. When I’m starting work on a novel I gather scraps like a magpie. My Orphan Train board was covered with postcards from the New York Tenement Museum depicting the interior of an immigrant Irish family’s cramped apartment, a black and white photograph of a young couple at Coney Island in the 1920s, a map of the village of Kinvara in Ireland. I hung a hand-carved Celtic cross on a green ribbon and a stone shamrock on a red ribbon from Galway; a Native American dreamcatcher from Maine; a silver train pin from a New York Train Riders’ reunion in Little Falls, Minnesota. I tacked up note cards: “Food in Ireland 1900s” was one (“wheatmeal, hung beef, tongue, barley”). Another listed ideas I wanted to explore (“links between misplaced and abandoned people with little in common”).
For A Piece of the World, I included a print of Andrew Wyeth’s painting Christina’s World; photos I took, inside and out, of Christina’s home in Cushing, Maine; some Emily Dickinson poems (“This is my letter to the world / That never wrote to me”); and postcards of other paintings Wyeth did at the Olson house, including Wind From the Sea and Christina Olson (both of which make appearances in my novel). I photocopied sketches Wyeth made for his portrait of Christina. I even included a small handful of grasses I’d plucked from the field Christina sat in.
I find these idea boards fun to assemble and inspiring as I work. My mantra, always: Find inspiration where you can.
Christina Baker Kline is the author of six novels, including A Piece of the World, published in February by William Morrow. Her website is christinabakerkline.com.

An outline of A Fable on the wall of William Faulkner’s study at Rowan Oak in Oxford, Mississippi. (Credit: Joe Bonomo)
Craft Capsule: Visual Prompts
This is the fifth in a series of micro craft essays exploring the finer points of writing fiction. Check back each week for a new Craft Capsule.
***
For many writers, visual and tactile stimulation is an important component of the creative process. William Faulkner used to map his stories on the wall in his study. If you visit Rowan Oak, his home in Oxford, Mississippi, you can still see the notes for his 1954 novel, A Fable, in his precise, small handwriting. Edwidge Danticat has said that she has an evolving bulletin board in her workspace where she tacks up collages of photos of Haiti and images from magazines.
I, too, have a new board for each book I write. When I’m starting work on a novel I gather scraps like a magpie. My Orphan Train board was covered with postcards from the New York Tenement Museum depicting the interior of an immigrant Irish family’s cramped apartment, a black and white photograph of a young couple at Coney Island in the 1920s, a map of the village of Kinvara in Ireland. I hung a hand-carved Celtic cross on a green ribbon and a stone shamrock on a red ribbon from Galway; a Native American dreamcatcher from Maine; a silver train pin from a New York Train Riders’ reunion in Little Falls, Minnesota. I tacked up note cards: “Food in Ireland 1900s” was one (“wheatmeal, hung beef, tongue, barley”). Another listed ideas I wanted to explore (“links between misplaced and abandoned people with little in common”).
For A Piece of the World, I included a print of Andrew Wyeth’s painting Christina’s World; photos I took, inside and out, of Christina’s home in Cushing, Maine; some Emily Dickinson poems (“This is my letter to the world / That never wrote to me”); and postcards of other paintings Wyeth did at the Olson house, including Wind From the Sea and Christina Olson (both of which make appearances in my novel). I photocopied sketches Wyeth made for his portrait of Christina. I even included a small handful of grasses I’d plucked from the field Christina sat in.
I find these idea boards fun to assemble and inspiring as I work. My mantra, always: Find inspiration where you can.
Christina Baker Kline is the author of six novels, including A Piece of the World, published in February by William Morrow. Her website is christinabakerkline.com.

An outline of A Fable on the wall of William Faulkner’s study at Rowan Oak in Oxford, Mississippi. (Credit: Joe Bonomo)
Craft Capsule: The Art of Targeted Revision
This is the ninth in a series of micro craft essays exploring the finer points of writing. Check back each Tuesday for a new Craft Capsule.
***
“Too many hours of revising—to no clear end!” my student complains. He is tired. He feels like the poem never really gets better. There’s always more work to do.
Welcome to revision: the arbitrary realm in which we debate “the” versus “an,” “this” versus “that.” Spend an hour putting a comma in. An hour later, take it out.
Part of the problem is that we complicate the revision process by making our aims abstract. One big revision, we promise ourselves, will make the poem “better.” Don’t privilege “better,” which is a meaningless term. Assign clear and objective tasks. Devote one round of revision exclusively to heightening your imagery, another to reconsidering your verb choices, a third to playing with lineation or tense.
Think of each revision as an experiment. Often these experiments will feel like evolutionary progress, and you’ll keep their results intact. Not always, especially as you near the end of the revision process. When the new version fails to appeal—when you find yourself resisting, reverting, defending an earlier choice—you are locating the poem’s true form. You are identifying what makes this poem yours, and yours alone.
Sandra Beasley is the author of three poetry collections, including Count the Waves (Norton, 2015), and a memoir. Her website is SandraBeasley.com.
Craft Capsule: Beware the Indeterminate “It”
This is the eighth in a series of micro craft essays exploring the finer points of writing. Check back each week for a new Craft Capsule.
***
Beware the indeterminate “it,” I often say, when fine-tuning a draft.
But that word is so convenient. “It” carries the football from the previous sentence. Whatever “it” you just defined, you’re sticking with it for another ten yards, right?
Except that you’re fumbling the play. Too often, relying on “it” dissipates your language’s energy. Circle every “it” that leads off a sentence. Revising to avoid these instances will force your verbs into action, and clarify your intent.
This is not a hard-and-fast rule. Sometimes an indeterminate “it” will remain, one that has earned its place on the field. The pronoun can be strategic—signifying not just gender neutrality but an absence of comprehension or known name, a fumbling toward meaning, the building of suspense.
In the right hands, “It” can be a potent force. Just ask Stephen King.
Sandra Beasley is the author of three poetry collections, including Count the Waves (Norton, 2015), and a memoir. Her website is SandraBeasley.com.
Craft Capsule: Left Brain, Right Brain
This is the tenth in a series of micro craft essays exploring the finer points of writing. Check back each week for a new Craft Capsule.
***
I attended a high school geared toward professions in science or technology, so I have an active analytical streak and crave objective rubrics for understanding the wildly creative poems, stories, and essays that I read. I suspect I’m not alone in this.
One of my mentors, Gregory Orr, articulated four “temperaments” of poetry in a 1988 essay titled “Four Temperaments and the Forms of Poetry.” You can envision these facets of craft as quadrants, positioned on an X-Y axis. To the left, limiting impulses: “Story” in the upper quadrant and, below it, “Structure.” To the right, impulses that extend limitlessness: “Music” in the upper and, below it, “Imagination.” Though designed for poetry, I find these temperaments useful for prose as well. As writers, we each typically favor two of the four in our work. Which temperaments bring you to the page? Which come easiest to you? Which do you need to consciously strengthen in your work?
This system gives us a way to articulate differences in aesthetic without ranking them. I’m relieved to set aside presumptive hierarchies. I suspect I’m not alone in this.
Sandra Beasley is the author of three poetry collections, including Count the Waves (Norton, 2015), and a memoir. Her website is SandraBeasley.com.

Craft Capsule: Real Time vs. Page Time
This is the twentieth in a series of micro craft essays exploring the finer points of writing. Check back each week for a new Craft Capsule.
***
Several years ago I worked with a student who was writing a novel about a guy training for a career in the sport of mixed martial arts. The novel was exciting and interesting, and the writing was strong and compelling. Until the fighting began. The minute the bell rang and the fists and feet started flying, the pace of the narrative turned glacial.
This may come as a surprise to you; it certainly surprised me. The talented author was actually a former MMA fighter, so it seemed impossible that he was unable to write an exciting fight scene. Then I realized that fight scenes are rarely exciting on the page. I believe this is true for two reasons. First, a fistfight is a process, and processes rarely make for compelling reading. Second, fistfights are exciting because they unfold in real time, which is wholly different than page time.
I want to talk about process first. Process is part of our daily lives, and many of the processes we undertake are performed through rote memory: brushing our teeth, making coffee, pouring cereal. These processes aren’t very interesting, and they don’t really need to be written about in detail. Readers may need to know that your characters drink coffee, eat cereal, and brush their teeth, but they don’t need to see this happening. Telling them it happened is enough. This is an example of when telling should be privileged over showing. But sometimes you may want to show a process, especially if it proves a level of expertise. Perhaps you’re writing about a character who is skilled with firearms, and you want to show that level of knowledge and skill. Perhaps you should have a scene in which the character goes through the process of breaking down and cleaning a firearm.
Most often, when readers start down the road of reading about process they’re not interested in the process itself; they’re interested in the outcome. The fight scenes in my student’s mixed martial arts novel are a good example. While the scenes were very technical and showed the same level of skill and mastery that I just mentioned, as a reader I quickly became bogged down in the descriptions of the movements, and I lost a sense of the movements themselves. I found myself skipping through the process of the fight in order to discover whether or not our hero won the fight. I realized that as a reader I was more interested in the outcome than I was in the process. The scene hinged on the result of the fight as an event, not on the act of fighting.
Not only were the fight scenes weighed down by process, they were also slowed down by the act of reading. Let’s step out of the ring. Think about the fights or dustups or schoolyard shoving matches you’ve witnessed. How long did they last before someone stepped in or called the parents or the teachers came running? Thirty seconds? A minute? A few minutes, tops? These events almost always unfold very quickly. The movements are fast; words are exchanged at a rapid clip. Your eyes and ears are able to take in the movements and the verbal exchanges simultaneously. Now, imagine trying to portray these events verbatim on the page. Think about how many words would be required to nail down both the movements and the dialogue. It would take much longer to read that scene than it would to witness it.
There’s an old writerly saying that dialogue isn’t speech, but rather an approximation of speech. Sometimes, this is true of action, especially in terms of process.
Wiley Cash is the New York Times bestselling author of the novels The Last Ballad, A Land More Kind Than Home, and This Dark Road to Mercy. He currently serves as the writer in residence at the University of North Carolina in Asheville and teaches in the Mountainview Low-Residency MFA program. He lives with his wife and two young daughters in Wilmington, North Carolina. His website is www.wileycash.com.
Craft Capsule: The Art of Active Dialogue
This is the nineteenth in a series of micro craft essays exploring the finer points of writing. Check back each week for a new Craft Capsule.
***
When I work with new writers, one thing I often notice is their lack of faith in their dialogue: They don’t trust that it’s strong enough to stand on its own. They feel that they must add something to really get the point across. These writers add action words to their dialogue tags in an attempt to hide any flaws they fear may be hiding in their characters’ verbal interactions. In other words, they do everything they can to make certain that the reader gets the full import of what the characters are attempting, consciously or unconsciously, to communicate.
Often, and unfortunately, these action words take the form of gerunds. Let me follow this with a caveat: Gerunds in dialogue tags are not always a bad thing if they’re used purposefully and sparingly. I use them. Other writers I admire use them. But if I’ve used a gerund in a dialogue tag then I can defend it because I’ve already spent a good deal of time trying to consider whether or not to use it.
The gerunds in dialogue tags that bother me are the ones that are clearly there to underpin weakness in the dialogue. This happens when writers feel they need an action to complement a line of dialogue. Here’s an example:
“What do you mean?” he asked, shrugging his shoulders.
Let’s add an adverb and make that gerund really awful.
“What do you mean?” he asked, shrugging his shoulders nervously.
The writer (in this case, me) felt the need to add that gerund (and perhaps the adjective as well) because the dialogue itself was pretty weak. “What do you mean?” is a boring question. Anyone can ask this, but your character can’t just be anyone. He has to be a particular person with particular turns of phrase and particular movements (what are often called “beats” in dialogue) to flesh out what he means.
Let’s give it another try, and this time let’s write a better line of dialogue that essentially says the same thing as our original, just more clearly.
“What am I supposed to say to that?” He shrugged his shoulders. “What does that even mean?”
I tinkered a little with the original line and split it into two, but I divided the two lines with the beat of action. I feel like my two lines are pretty strong, and they seem particular to this person, whoever he is. Because my dialogue is strong, it doesn’t need the support of action. So my action can stand alone.
The action also does something the dialogue cannot do. It illustrates visually what the dialogue means verbally. The phrase “What am I supposed to say to that?” is a phrase of exasperation, so the action takes this a step further and shows exasperation. The follow-up question of “What does that even mean?” amplifies both the original question and the action.
If I had kept the gerund shrugging it would have combined the dialogue and the action, which crowds the reader’s mind in asking her or him to do two things at once: see and hear. Let’s focus on asking one thing of our reader at a time. The act of reading is not the act of movie watching, which often requires viewers both to see and hear at the same time. Literature and film cannot do the same things in the same ways.
The gerund shrugging is also a weak action word because it does not have a clearly demarcated time of beginning. How long has this guy been shrugging? After all, we enter the word “shrugging,” and presumably the dialogue, as the shrugging is already under way. On the other hand, when we read the line “He shrugged his shoulders” we are entering the action at the moment it begins. It has not been unfold-ing since an indeterminate moment in time. The action feels particular, as if it is caused by the line of dialogue that precedes it. It gives us a chance both to digest the dialogue and imagine the action. It does not ask us to do both at the same time with the confusion of wondering when the shrugging actually began. This is deliberate writing. We should all be deliberate writers.
I want to close with a few lines of dialogue from my upcoming novel, The Last Ballad. In this scene, a man has just come up a riverbank and met a small boy standing at a crossroad. The boy is staring down into a ditch where his injured dog is lying. The man asks the boy where they are.
The boy lifted his eyes from the ditch and looked around as if getting his bearings.
“Gaston,” the boy finally said.
“Gaston,” he repeated. He looked down at the boy. “Do you mean Gaston County?”
The boy shrugged.
“Mama just says ‘Gaston’ when she says ‘here.’”
I worked really hard on this scene. I wanted it to communicate an edge of laconic strangeness. The boy’s poverty has rendered him a bit provincial. The man’s travels have rendered him a bit wistful. I purposefully separated the actions from the lines of dialogue and cordoned them off in their own sentences.
But what if I’d used gerunds?
“Gaston,” the boy finally said, lifting his eyes from the ditch and looking around as if getting his bearings.
“Gaston,” he repeated, looking down at the boy. “Do you mean Gaston County?”
“Mama just says ‘Gaston’ when she says ‘here,’” the boy said, shrugging.
Written this way, the scene unfolds too quickly. The boy gives his answer about their location before getting his bearings. The man’s quizzical repetition of the word “Gaston” is marred by his deliberate action of looking down at the boy. The words and the actions do not go together. They must be separated and addresses and experienced on their own terms.
My advice is this: Trust your dialogue. If you don’t, make it stronger. Then, once your dialogue is strong, bring in action beats that amplify the speaker’s message, not messy gerunds that clutter it.
Wiley Cash is the New York Times bestselling author of the novels The Last Ballad, A Land More Kind Than Home, and This Dark Road to Mercy. He currently serves as the writer in residence at the University of North Carolina in Asheville and teaches in the Mountainview Low-Residency MFA program. He lives with his wife and two young daughters in Wilmington, North Carolina. His website is www.wileycash.com.
Craft Capsule: The Scourge of Technology
This is the twenty-second in a series of micro craft essays exploring the finer points of writing. Check back each week for a new Craft Capsule.
***
The cell phone is the worst thing to ever happen to literature. Seriously. So many great fictional plots hinge on one detail: The characters can’t connect. Most famous is Romeo and Juliet. If she just could have texted him, “R, I might look dead, but I’m not. Lolz,” then none of this would have happened.
In my new novel, An American Marriage, both e-mail and cell phones threatened my plot. Here is a basic overview: A young couple, Celestial and Roy, married only eighteen months, are torn apart when the husband is wrongfully incarcerated and given a twelve-year prison sentence. After five years, he is released and wants to resume his old life with her.
A good chunk of the novel is correspondence between our separated lovers. In real life, they probably would have used e-mail. But the problem, plot-wise, is that e-mail is so off-the-cuff, and there is so little time between messages. I needed to use old-fashioned letters. Their messages needed to be deep and thoughtful, and I wanted them to have some time to stew between missives. But who in their right mind (besides me) uses paper and pen when e-mail is so much faster and easier?
The fix was that Roy uses his allocated computer time in prison to write e-mail for the other inmates, for pay. As he says, “It’s a little cottage industry.” He also explains that he likes to write letters to his wife at night when no one is looking over his shoulder or rushing him.
So look how this fix worked: You see that even though he is incarcerated, his is still a man with a plan. The challenge was to figure out how to avoid e-mail in such a way that it didn’t read like I was just trying to come up with an excuse to write a Victorian-style epistolary novel.
The cell phone was harder to navigate. Spoiler: Celestial has taken up with another man, Andre, in the five years that her husband is incarcerated. A crucial plot point, which I will not spoil, involves Andre not being able get in touch with her. Well, in the present day there is no way to not be able to reach your bae, unless your bae doesn’t want to be reached. Trouble in paradise is not on the menu for the couple at this point, so what to do? I couldn’t very well have him drop his phone in a rest-stop commode!
To get around it, I had to put Andre in a situation in which he would agree not to call Celestial or take her calls—although he really wants to. Trust me. It’s killing him. But he makes an agreement with Roy’s father, who says, “Andre, you have had two years to let Celestial know how you feel. Give my son one day.” Andre agrees and has to rely on faith that their relationship can survive. The scene is extremely tense and adds suspense to the novel. I had to get up and walk around while I wrote it.
I predict that future novelists will not grapple with this quite as much as we do, as technological advances will be seen as a feature rather than a bug. But for now, you can still write an old-fashioned plot that doesn’t involve texting or tweeting—you just have to figure out a work-around that enhances the plot and understanding of your characters.
Tayari Jones is a contributing editor of Poets & Writers Magazine. She is the author of four novels, including An American Marriage, forthcoming in February from Algonquin Books. Her website is www.tayarijones.com.
Craft Capsule: Finding the Center
This is the twenty-third in a series of micro craft essays exploring the finer points of writing. Check back each week for a new Craft Capsule.
***
My new novel, An American Marriage, involves a husband and wife with an unusual challenge: Eighteen months after exchanging their vows, he is arrested and incarcerated for a crime he does not commit.
I was equally interested in both their stories, but for some reason early readers of the manuscript were way more interested in him (Roy) than her (Celestial.) At first, I was convinced that this was sexism, plain and simple. Men’s stories are considered more compelling. To try and make Celestial more appealing, I tried to give her a more vibrant personality. But regardless of the details I added to embroider her, beta readers still felt that she was “undeveloped” and that Roy was the character who popped. It almost drove me crazy. Finally, I realized that Roy held the readers’ attention because his problem was so huge. (He’s wrongfully incarcerated, for goodness sake!)
Undaunted (well, maybe a little daunted), I read stories by my favorite women writers who write beautifully about women’s inner lives. I checked out Amy Bloom, Antonia Nelson, Jennifer Egan. How did they manage to make emotional turmoil so visceral? In these writers’ hands, a small social slight can feel like a dagger. Why couldn’t I do this in my own novel?
I found the answer in the work of Toni Morrison, for all answers can be found there. It’s a matter of scale. There is a scene in The Bluest Eye where the lady of the house is distraught because her brother hasn’t invited her to his party, although she sent him to dental school. By itself, this is terrible and totally worthy of a story. However, in the same frame is Pauline, the maid who has suffered all manner of indignities in an earlier chapter. In the face of Pauline’s troubles, the matter of the party seems frivolous.
With this, I discovered a fundamental truth of fiction and perhaps of life: The character with the most pressing material crisis will always be the center of the story. Although Celestial’s challenges as a woman trying to establish herself in the world of art is intense, the fact of Roy’s wrongful incarceration makes her troubles seem like high-class problems and to center them in the novel feels distasteful to the reader, like wearing a yellow dress to a funeral and fretting over a scuffed shoe.
The solution: I made Roy the protagonist. Celestial’s voice is still there, but she is a secondary narrator. It was a hard choice because I was drawn to her story in the first place, but it was being drowned out by Roy’s narrative. Finally, I had to stop fighting it. The protagonist of An American Marriage is Roy Othaniel Hamilton.
It took me five years to figure this out. Of course, every craft solution makes for new craft obstacles. I’ll talk about the fall-out from this shift in my next (and final) Craft Capsule, next Tuesday.
Tayari Jones is a contributing editor of Poets & Writers Magazine. She is the author of four novels, including An American Marriage, forthcoming in February from Algonquin Books. Her website is www.tayarijones.com.
Epic: An Interview With Salman Rushdie
Once upon a time, on a day of many firsts, a writer who had lived nearly four decades on a rather wounded, uncertain planet met the writer she admired most, a writer who had lived almost exactly seven decades on that same battered earth.
It was the first hot day of the year, a week before the official start of summer (high of ninety-seven degrees in Manhattan, “record-breaking heat advisory,” every news outlet declared), and the first interview Salman Rushdie was giving for his new novel, The Golden House, published this month by Random House. It was also the first time I properly sat down with the author who has had more influence on me than any other living writer. The Golden House is his eighteenth book—his thirteenth novel, which has somehow been more quietly announced than one might expect—but I devoured it in a sitting and a half, my favorite Rushdie novel in years.
If F. Scott Fitzgerald, Homer, Euripides, and Shakespeare collaborated on a contemporary fall-of-an-empire epic set in New York City, the result would be The Golden House. Like Rome at its collapse, the America of Rushdie’s new novel—not unlike our own America—is bursting at the seams. Rushdie anchors us to a filmmaker narrator as he navigates a life in the city to which only the wealthiest have access, and ultimately intersects with its newest inhabitants, the mysterious Golden family—Nero Golden and his three adult sons—as well as a classic New York villain who embarks upon a boorish presidential campaign. Meanwhile, themes of race and ethnicity, gender and sexuality, immigrants and natives, outsiders and insiders, ambition and power, money and more money form the dizzying backdrop for this wildly satiric and yet piercingly real world of The Golden House. Rushdie isn’t just writing a New York parable though; this is very much a return to literary realism, but it’s largely a hyperreal reality of our own world, one that even his most celebrated madcap fabulism couldn’t top.
And so I found myself at his agent’s office: a maze of book-lined rooms belonging to the both renowned and notorious Andrew Wylie, just two blocks and yet worlds away from Trump Tower. One of Wylie’s assistants escorted me to a cozy (cramped) conference room with an ancient air conditioner trying to blast away the day’s sins of pollution and humidity. I was a bit nervous and excited and overheated and then overchilled; I put on and then took off my jacket, over and over, and this continued until, a few minutes later, in walked Rushdie.
He was shaking his head at the weather, armed with a perspiring iced coffee and wearing an expensive-looking gray suit with a pale blue dress shirt, mustering a New York mumble-apology as a greeting. He was a combination of flustered, amused, anxious, and exhausted, but he rather quickly turned charmingly enthusiastic about doing press, something one might imagine is cumbersome at best for a man with a literary career that spans more than four decades. He smiled gently through much of our interview but also at another first: his entry into a new decade. Salman Rushdie was just days away from turning seventy years old.
This was not my first encounter with him. I had seen him speak many times in my life—braved many metal detectors and a police presence at various times all around the world to hear him—but he and I also both moved to New York around the same time, two decades ago, and I’d occasionally seen him around town. One time, in my early twenties, at a fancy downtown party I’d drunkenly snuck into, I blurted to the astoundingly accessible New Yorker, “I love your work, but I’m from the country that tried to kill you, sorry!” (He didn’t say a thing but maybe laughed, and I did not remind him of this during our interview.)
In 2015 I met him at the PEN Literary Gala, for which I served as a table host and where fellow table hosts who were Bard colleagues of mine became known as parts of the “PEN Six” for boycotting the event, which rather controversially honored Charlie Hebdo, among others. I had not been a fan of their decision, as I felt very devoted to PEN, so I went on with my table host duties. But a few times on Twitter I’d been critical of Rushdie’s attitude toward those boycotting (Rushdie was a former PEN president and not shy about this anger at those walking away from the gala), so when I got to the event, several photographers kept nudging me to take a photo with him. I finally ended up shaking hands with Rushdie and introducing myself awkwardly as cameras snapped away. “I know who you are,” he said, and we exchanged niceties and I walked off staring into my champagne flute and eyeing the metal detectors and hordes of security at the Museum of Natural History, thinking to myself, “Well, if we all die tonight, at least I can die knowing Salman Rushdie is not that mad at me.”
Because long before I encountered him in person, I had been his fan. My work has long been compared to his, and that’s no coincidence. I first read The Satanic Verses just a few years after its publication in 1988 (I was ten). My Iranian family—Muslims who had fled during the Iranian Revolution—had been impressed by Rushdie’s bold confrontation of some dark aspects of Islam more than his literary prowess. In 1989, after a riot protesting the book in Pakistan, Iran’s Ayatollah Khomeini issued a still-in-place fatwa ordering the author’s death, and my aunt bought us a hardcover, noting it would be worth something one day. There had been so much on the news about it that I became obsessed with it—this was yet another instance in which my worlds of America and Iran collided. I was already dreaming of being a writer one day, and for the first time I learned that you might have to risk your life for art.
You could say that Salman Rushdie has changed the course of my life in many ways.
So on that blisteringly hot June day I was nervous to meet this hero of mine in this context. But what I found remarkable in the couple of hours we had together was not just that the titan of letters is full of sterling insights on everything from novel-writing to identity to social media to magical realism to modernism to New York—but that there is also something breathtakingly down-to-earth about Rushdie, who often seems both surprised and delighted by any praise, who seems as insecure as every writer I know (including me), and who feels as unsure of the state of our world as we all do.
Here you are now at your thirteenth novel. Or should I assume you are on to number fourteen now?
I’m not actually. I have no idea what’s next. I have a completely empty head. Which is not a good feeling actually. [Laughter.] I always feel happier when I’ve got a project to work on. This book took a lot out of me.
I was extra excited to read it, and I feel like this is one of your best books. I’ve been thinking a lot about your first book, Grimus, actually….
Nobody really liked it when it came out…except Ursula LeGuin. She’s been my loyal critic from the very beginning.
I think it’s a great first novel.
You do? Well, thank you. I’m not so sure myself. [Laughter.] After it came out and after its really quite poor reception, I did a lot of rethinking about what I think is wrong about it, never mind what other people said. And that process of rethinking is what led me eventually to Midnight’s Children. It was partially a way of rejecting what I was trying to do in my first novel, that I found my way. So in my head that’s a book I rejected in order to discover my path. I think it’s a book in which the author has not found his voice yet. I think it’s kind of erratic. There are passages that I think are really embarrassing. So I don’t look at it very often.
But it’s from there that you started this lifelong project of bringing in mythology and history from meta perspectives.
Well, yes, that’s been there from the beginning, I think. I presume you know Farid ud-Din Attar and The Conference of the Birds.
Yes, of course.
That was a text I’d really always liked. And so the book started there. I started to see how you might make some contemporary fiction out of that idea. That part of the book I’m okay about.
I used that book and the Shahnameh in my second novel, The Last Illusion, and it was you who taught me to how to do that.
Oh!
Taking in myth and mashing it up with contemporary New York and the American psyche and Muslim identity, balancing all that….
Oh, good. Well, the thing I always felt about the great stories, the myths, is how much they concentrated into a very small space. I remember much later, when I was writing The Ground Beneath Her Feet, where the Orpheus story is quite central to that—I mean, you could tell the story of Orpheus and Eurydice in under a hundred words, and yet there’s so much in there that if you start unpacking it you can write a six-hundred-page novel. I think that’s what the great myths do: They give you these incredibly concentrated pieces of meaning that you can unpack almost like Mary Poppins’s bag; endless stuff comes out of it. So I’ve quite often gone back there. Not so much in this book, but, for instance, in the novel before. I really tried to revisit those stories. Not just One Thousand and One Nights but stories of that sort. I’d written these two books for younger readers out of that same kind of sensibility, but if you read those stories they are not written for younger readers. I mean, One Thousand and One Nights is an adult book. It’s not a children’s book.
Definitely. But I sometimes think we of the East can handle more adult subject matter, just like we can handle darker humor a bit better.
Maybe. Growing up in India, with this kind of story material as the first fictional air that you breathe, was really a gift—and not just One Thousand and One Nights, but the animal fables and of course The Mahabharata and The Rubaiyat and all these grand narratives. It gave me a way of thinking that I’ve never entirely set aside. Although I’ve always slightly resisted the kind of magical realist tag because I believe that belongs properly to that group of South American writers, and it should be kept for them.
Yes, I feel that way too. What about the term fabulism?
Well, I think magical realism, fabulism, French surrealism, it’s kind of all the same thing. And then if you look at the history of literature, it’s all over the place all the time—I mean Kafka’s a magical realist and so is Gogol. The point is it’s a kind of writing that’s always been around. But then sometimes you don’t want to do it. With this book, I really didn’t want to do it. So I just think of it as one of the available ways of telling a story, and what you do depends on the story you want to tell.
I think a lot of people forget that fabulism is mainstream world literature—and that the domestic or psychological realism we have in the United States is the anomaly. As an Iranian, I used to find Cheever, Salter, Yates, and others so exotic. For me, they were the other.
Yes. Certainly, I mean, Cheever is quite exotic. [Laughter.] The thing about realism in its great heyday is that it depended on there being an agreement between writer and reader about the nature of reality. And so that when Trollope or George Eliot are writing, they can expect their reader to have, broadly speaking, the same worldview as themselves. They would agree about what the world was like. When you have that agreement, then you can build a realist novel on that. But we now live in a time when that consensus has very much broken down. We don’t have an agreement about the nature of reality. I mean, reality is now an argument. And sometimes it becomes a violent argument. So I don’t think you can write realism in the way that people used to because of this problem about consensus, about there not being a consensus about what is real. I mean, look what’s happening in this country. There are narratives about America now that have almost no meeting point. One man’s truth is another man’s lie. When you live in this kind of moment, you have to be aware of that. And so my view is that realism is very broad church—on one end of it you’ve got Raymond Carver, and on the other end you’ve got James Joyce. I mean, Ulysses is a completely realistic novel—it’s just that high modernism did something else with realism.
(Photo: Tony Gale)

The funny thing in this discussion is that we who are stylists and language writers—and I know that’s a dicey term too—get this questioning from readers and critics that centers around our style and its relation to substance. As in, why do you choose to tell it in the way you are telling it?
I think that’s a good question to ask yourself, actually. One of the things I do when I’m teaching people is I say, “There are a number of questions you have to ask when you are beginning a project: one is what are you writing about and what is the story you are telling; then you have to ask whose story is it; then you have to ask why are you telling it; and then the biggest and most important question is how are you doing it and why are you doing it that way?” The how question is what makes a work of literature work or not work. I mean, with Ulysses there is not much story. Man works around Dublin for a day. His wife is unfaithful to him. He meets a younger writer in the red-light district. I mean, really not very much happens. But the how is what makes it this gigantic work of literature.
We often talk of voice, of authority, which is also a nebulous concept for students, but the Rushdian storyteller voice is something I’ve grown up with and is so comforting to me. I always know it’s you. And I know my storyteller is actually my author. And I feel that with The Golden House, too.
One of the things that was a discovery for me here was the narrator. In the very early stages of working on this book, I had the very boring idea that he should be a writer. [Laughter.] And I started writing it like that and then I thought, “Stop it, this is so awful!” It would be better if he were a tax accountant than a writer. But then I thought, you know, I’ve always been very interested in cinema. I’ve maybe not written about it as much as I’d liked to have. I think actually a lot of my formative education was in the world of the art-house cinema. The moment I could think of him as a young filmmaker, it really opened a huge series of doors for me in the book—first of all, he’s more interesting that way, and second it allows me to use a whole number of cinematic tricks and devices. There are moments when the book slips into a sort of screenplay and it can have a kind of montage effect, collaging different kinds of scenes next to each other. That simple decision to make him not a writer but a young filmmaker allowed me some formal possibilities that otherwise the book wouldn’t have had. Then this thing happened that was even more surprising. I thought at first, even as a filmmaker, he’s been this eye-of-the-camera kind of figure just watching, and the story would be about this crazy family. And the more I got into it, the more I realized, actually it was about him—that actually the book was just as much his story as the story of the Golden family. And so it was something I didn’t set out to do, it started being a sort of bildungsroman, a novel that was about getting wisdom—this young man, through his engagement with these people, in a way learning how to be a man and being attracted to terrible deeds and having to survive his own misdeeds. I thought, “Oh, I didn’t know that—I’m writing a book about him.”
I thought about that choice and thought about Fitzgerald and The Great Gatsby and his decision to give us the novel in Nick’s point of view.
Everyone says Gatsby, but I don’t think I even thought of Gatsby except in the most tangential way. Because to me what’s interesting about Gatsby—I mean, many things are interesting about Gatsby—but one thing is that almost everyone in the novel is from the Midwest, and it’s about people from the Midwest coming to the East Coast and being screwed up! [Laughter.] And the survivor, which is Nick, goes home. So it seems to me Fitzgerald is talking about that. I mean, I suppose the obvious Gatsby thing is reinvention, which, after all, is the great subject for the American novel, from Huckleberry Finn. But I think the question of identity has become so central that [in writing] this book [I saw] it in all sorts of forms, you know: what happens to migrants, what happens in gender identity. I mean, the subject of identity has become huge, and in many parts of the world, as you know, it’s become heavily politicized. Like in India, identity and authenticity are now being interpreted by Hindu nationalists as meaning only one particular kind of Indian is an authentic person, and these other people are in some way what V. S. Naipaul might have called “mimic men.” And identity issues can become repressive. And so in another part of my head I felt I needed to get into that because this is what everybody is thinking about.
It’s amazing to read your new book in this time period. Will you find it frustrating, or will you be open to it being now constantly compared to life in Trumplandia?
I mean, yeah, of course, it does go from Obama to Trump. And I kind of guessed right. I mean, I’m sorry to say it. [Laughter.]
When was it written?
It was written last year. I mean, 99 percent of it was written before the election. I was also aware of the fact that if things had gone another way there may have had to be some reshaping done to it, which sadly I didn’t have to do. There’s also something about an arc that goes from a moment of great optimism to its opposite, which has a kind of shape…it has a good shape. It’s an awful thing to say: that this thing that is very bad for America is very good for the novel. It provides this light-into-darkness trajectory. Which is not the trajectory of the story—I thought that was good because otherwise it could be read as some kind of straightforward allegory, and I didn’t want it to be. I mean, obviously I can’t pretend there isn’t an echo of some Trump stuff in there, but it seems to me to be very much some kind of background, not foreground. It is not like an attempt to write a Trump novel. It doesn’t ignore that it’s happened, but it is not what the book is about.
Who do you think is your ideal reader these days? Do you think about that?
I don’t have an ideal reader, but I actually like who my readers are. Just in terms of who shows up. First of all, I’m happy to say lots of people show up. That’s good! But also they are a little bit of everybody. I mean, any publisher will tell you that without middle-aged white ladies there would be no fiction; there would be no publishing companies. [Laughter.] But I really like that my readership is extremely diverse. And also in terms of age there is a very wide range. There are always a lot of very young people. It’s kind of nice when you’re about to turn seventy to feel that there are people who weren’t born when you started publishing books, who have an interest in what you are doing.
I used to see my students discover you on Twitter all the time.
Yes. Well, I have abandoned Twitter. It was just the moment to stop. I started because somebody said why don’t you try it and you might find it interesting, and I did, and then you acquire all these people—I think it’s at one and a quarter million or something—I mean, it’s quite humbling when you look at Neil Gaiman or Stephen Fry and so on. Okay, so it’s only one and a quarter million. And then you get to the upper echelons like Justin Bieber, and then forget about it. But it was interesting to be able to have a way of talking to a million people directly, and then because of the phenomenon of retweeting you actually are talking to many more. And that was interesting. And then I just suddenly thought, “I don’t want this noise in my head.” Jonathan Franzen has always been sort of a denialist of all this stuff, and I remember he gave some statement somewhere saying writers should know better. And at the time I remember thinking, “Okay, Jonathan, you do that and I’ll do this,” but actually I’m more and more agreeing with him. I haven’t missed it for a nanosecond. I deleted the app.
Do you think you’ll come back?
I don’t know. If you are on a book tour and you’re going to be in San Francisco tomorrow, it’s quite useful to say I’m reading at such-and-such tomorrow, so I might do that. Twitter is a way of reaching a lot of people, but it’s also so bad-mannered. I think the anonymity is what does it. It allows people to be discourteous in a way they’d never be if they were sitting in the same room as you and if you knew their name.
A while ago I had someone tweet at me “Go kill yourself,” and then I met the person and said, “Hi, I am here now; how do you feel?” but of course the response was, quickly, “Oh no I didn’t mean it.”
Oh, yeah, now it’s a figure of speech! [Laughter.] I just think somehow we’re bringing up a generation of rude people because of the ease of it and lack of accountability and lack of consequences. So I just thought, “I don’t like it; I don’t like the tone or voice of it,” so I stopped doing it.
I do appreciate that you are very much engaged with your audience. When I moved here twenty years ago, I’d see you at parties. You’re a writer who’s very much in the world and you haven’t done that thing that writers sometimes do, which I think of as an obsessive glorification of an introversion that might be more misanthropy.
Yeah, I’m not like that. I’m not like that as a person, so why would I be like that as a writer? I mean, I admire writers who can just shut the world out, but I think the great thing about the novel is that it plunges its hands deep into what’s happening. I’m into the idea of trying to know as much about as many parts of the world as possible. Don’t just sit in your own comfort zone. Try and be in rooms that are different no matter what happens in those rooms. Get deep into the matter of life, you know? And you can’t do that in an ivory tower—you have to be in the world. And certainly this city. Who can write about it if you don’t get into it? You can’t just sit in your little apartment and imagine New York. I’ve been here a long time—it’s been almost twenty years now. And the way I’ve written about it has changed in that time. Before I was living here I wrote The Ground Beneath Her Feet, about another New York that doesn’t exist anymore. It’s about when I first discovered New York—I first came here in the early seventies, I must have been twenty-six or so. That’s that other city: CBGB, Max’s Kansas City, dirt, and muggings.
When I wrote Fury, I thought it was a novel of arrival, about coming here. I can’t write the novel in the way Don DeLillo would write New York; that wouldn’t be possible. But there was another kind of New York novel about coming here; most people in this city came from somewhere else, so I thought I’d write about that. And The Golden House—I think because I really have been here a long time—it is just probably the most New York New York novel I’ve ever written.
You not only refer to but you create a mythology of New York City.
Well, you notice almost all the major characters are immigrants. Everybody is from Argentina or India or Burma. And that’s on purpose. I tried to create a kind of New York that feels like it’s mine, that feels like a city for me to write about.
I often think there’s a way New York City embraces those of us who are from other places, perhaps even better than some white people—say, the rural white America the New Yorker Trump tried to appeal to.
I always thought of myself first of all as a kind of big-city writer. I spent almost all my life in Bombay, London, or here. I think if that’s your frame of mind, it’s not so difficult to adjust from one big city to another because you know how it is to live in a big city. But if you’re coming from some small rural community, I think there are journeys that are from the depths of America to the big cities that are maybe more complicated than from another country to here, as long as it’s one metropolis to another. So I know I fit very easily into any kind of big-city environment—I know how it goes. For me the opposite has been difficult, which is to write about outside the city. When I wrote Shalimar the Clown, a lot of which takes places in a Kashmiri village, I really set myself the task of saying, “You have to be able to write about this.” Because certainly in India the reality of the village is very, very important; because of the way the population is distributed, most people still live in villages. Two-thirds of the population lives in villages of less than two hundred people. So one could argue, and people do argue, that the urban reality of India is not typical—and actually the rural reality is the real one. So I made myself enter into that other reality, which doesn’t come naturally to me.
This goes back to your saying earlier what is the real—what is the real experience, what is the authentic person—and I think especially today we have to complicate that question and the narratives.
Well, I think we are just living in a moment when we are being asked to narrow ourselves—you know, when we are asked to frame ourselves more and more narrowly. That’s true of political identity, gender identity, cultural identity. The Museum of Identity in the novel is obviously made up, but I’m amazed that it doesn’t exist.
I almost had to look it up.
And I’m sure it will exist. Two years from now there will be a Museum of Identity. I mean, it’s a comic device to explore all this, but I think one of the great things that the novel has always known is that our identities are very plural. You know, “Do I contradict myself? / Very well then I contradict myself.” That idea that we are not unitary selves, that we are very polymorphous. To make characters in a book interesting and alive they have to be like that—if they are only one thing then they are dead. I tried to explore that over the years quite a lot. We all have this capacity to shift ourselves according to our circumstances. All the time. To say you’ve got to choose one of those things, to me, it’s a straitjacket.
I often use the example of pillow talk with people I teach. That voice that very few of us hear, that private self. What then if your mother suddenly calls you in the middle of it? What will your voice sound like then?
Yes, when your selves collide.
Some young people worry that this is a big problem. And I often have to tell them it’s not a problem.
I don’t like to offer a utilitarian view of reading literature, but one of the uses of literature is that it shows you what human beings are really like. And they are not like that. And thank goodness we’re not, because we would be much less interesting if we were. And I don’t like that there is a kind of rhetorical pressure that, I think you’re right, young people feel quite strongly right now. Although I wonder if there’s already a backlash against it. I think we live in a time when the world moves so fast that yesterday’s orthodoxy is today’s unorthodoxy. I worry about the fact that now numbers of young people for what seems to them to be virtuous reasons become prepared to espouse ideas of censorship—that certain things should not be said because they don’t agree with them. And they don’t see what a dangerous choice that is. But again, everyone talks about what’s happening in the academy, and I have to say I have been teaching in the American academy for twenty years now and I have not had a single experience of that sort. Not one person has ever tried to say these things are improper thoughts. But what I’m saying is that I’m not sure there is as much of it as we have been led to believe—it might be more exceptional than we think. Certainly in classes I’ve taught, there has been absolute interest in that way of thinking.
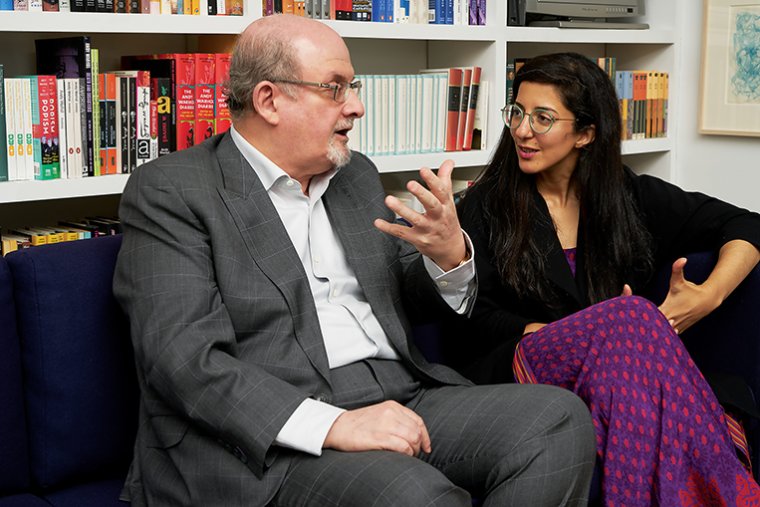

Salman Rushdie and Porochista Khakpour in the Manhattan office of Rushdie’s literary agent, Andrew Wylie. (Credit: Tony Gale)
I’ve mostly had students reject trigger warnings.
Exactly. I’ve had the same experiences—students really dislike the idea of trigger warnings, as they should. Being surprised by a book is one of the good things about it.
I saw an interview you gave in late March that made me reflect again on The Satanic Verses and your experience there. You talked about how there is humor in all you do, something I was drawn to in all your work. And one of the things you discussed in the interview that moved me was that having the fatwa made people actually forget how funny The Satanic Verses is.
Yeah, nobody says it’s a funny book…except people who read it. But I think what happened is that it colored people’s expectations of what sort of writer they thought I was. And because it was such a dark event: In a way the characteristics of the attack were assumed to be also the characteristics of the writing. But that’s been a cloud that still hovers around me. I think for some people it gets in the way of picking up the book, like, “Oh no, that’s not my kind of thing,” because of assumptions made because of what happened.
And our names, I’ll bet. They see foreign names and think, “Oh, no, this must be some heavy thing.”
Yes, exactly. All I can do is continue to write. I mean, The Satanic Verses was my fifth published book, and this is my eighteenth. I certainly tell people not to read that book first—to read almost anything else first.
I found myself recommending to a student to read Joseph Anton first.
Well, I’m happy, obviously, but I just think of that as having done what I wanted it to do. When I started out as a writer, if you had asked me whether I would ever write an autobiography, I would have said absolutely not. That would be the least interesting thing in the world. And then I acquired an interesting life. Then I thought, “Given what happened, I don’t want somebody else to be the person telling that story,” so at some point I felt I had to do it. But still, I don’t think of myself as a nonfiction writer even though that’s the longest book I’ve written.
Do you have people read your work before it goes out?
Nobody sees anything until I’m finished. Then it goes here [to Andrew Wylie], and then it goes to the publishers. Then I do have a few friends I show it to, yeah. I really find it too frightening to reveal a work-in-progress. It’s so fragile. If I show you something and I know it’s not quite there yet and you say this is interesting and it’s not quite there yet, I get depressed. I mean once, years ago, when I was much younger, I went to a reading of John Irving’s in London in which he said this is a first draft and invited the audience to make suggestions. And I thought, “That’s so scary.” I could have never done that. So what I consider to be finished is where there’s a point at which I’m not really making it better anymore. I’m just pushing things around and making them different, and then I think, “Now I need to know what other people have to say.”
With all the many hats that you wear—humanitarian work, an appointment at NYU, the talks, the traveling—are you writing every day?
When I’m writing a novel, yes. The novel comes first and everything else has to take a number. I’ve always had this view that you wake up every day with a little nugget of creative juice for the day and you can either use it or you waste it. My view is, therefore, you write first. Get up, get out of bed, get to your desk, and work. Usually a couple of hours, until I know what I’m doing that day. Then I can go have a shower and the rest and then go back to it. Do the work first; otherwise it doesn’t get done. I’ve always thought of the novelist as a long-distance runner; that’s the marathon. It doesn’t mean a marathon runner is a more gifted athlete than a sprinter, but it’s just that kind of athletics. It’s long-form, you have to chip away at it, let the mark posts go by and trust that one day the finish line will come. You can’t even think about the finish line when you start.
I wonder if that’s why your work has a consistency to it that I feel. I can really see your project as an author. There’s a logic to it all.
That might be easier for you to see than me. Me, I don’t want to do the same thing every time. I’m always looking for some way to get at it in a way I haven’t done before. For example, the last novel came after Joseph Anton and was in many ways a reaction to it—because after this immense piece of nonfiction, I wanted to do something very, very fictional, something on the other end of the pendulum. And then I thought, “Well, that book goes as far into that as you could, so what else can I do that I haven’t done before?” And this kind of modernist way of approaching reality is where The Golden House came from. It came out of thinking about modernism.
I do think of you as a modernist author.
Well, if you think about it, modernism is a hundred years old. You know, modernism isn’t modern.
I love it so much. I tend to feel less aesthetically interested in a lot of what was categorized as postmodern.
I remember doing an event with Edward Said at Columbia, and in the Q&A this gentleman stood up who was clearly a member of the faculty—and he seemed very agitated—and he said, “We’ve always claimed you as postcolonialist; are you still with us?” And I said, “Well, you know, we just met!” I think the thing about postcolonialism is that, yes, obviously there was a period where it was very important, especially in India, and there is an obvious sense in which Midnight’s Children is postcolonialist. But it was seventy years ago. Nobody in India thinks very much about the British Empire. The subject is gone. So now you’re in a moment that’s post-postcolonial. I think the same thing is true for postmodernism. That we’ve gone a few steps more than that now—there isn’t a name for it, but there doesn’t need to be.
A modernist fan and writer friend of mine, Can Xue, calls her work neoclassical experimental instead of, say, avant-garde.
Well, I just don’t like labels. If someone tries to put me in a particular box, I immediately want to be in a different box. I’ve never been a great gang member. There are writers who like to travel in packs—I don’t like that. The thing about magical realism is, those guys really were thinking together in a way. They actually had a kind of project in the way the French surrealists had a project. But I have the Groucho Marx position: not wanting to be a member of any club that would have me as a member. I just think what is great about this art form is that it’s one single intelligence saying, “Here’s how I see it.” An intelligence that nobody owns. It’s just this one person saying, “I will tell you this.” And you can be lucky or unlucky—the point of that is it’s a big gamble. But the desire to be that individual voice I think is what makes a novelist. Every novelist I’ve ever loved has that thing where you know it’s them. You pick up a random page of DeLillo and it’s nobody else.
This reminds me of your reactions when people bring up the Nobel Prize. I’ve seen you laugh at the idea, though I personally think you should be up for it already.
But look at who gets it. [Laughter.] You know, I’ve been lucky with prizes a lot of the time, and unlucky a lot of the time, and that’s just the game. But I don’t think of it as serious.
You’re not perched by your phone on Nobel announcement day?
No. I mean, of course it’s nice when you win and it’s not so nice when you don’t, but I don’t really care. The thing that is much more of a prize to me is what we were saying earlier, which is that the books endure. If you are writing this kind of work, not pop fiction, the purpose is to write something that will endure, that hopefully will be around long after you’re not around. Martin Amis has this nice phrase that I always quote—what you want to do is leave behind a nice shelf of books. You know, Midnight’s Children is a really old book now—when I started writing it, it was 1976. The fact that it has managed to remain interesting to people two or three generations later, that’s a prize. Books survive only because people love them—there’s no other reason why a book survives ever. Books don’t survive because of scandal. If The Satanic Verses survives, it won’t be because of scandal. People forget scandal. Affection is the only thing that makes literature survive. That’s all there is.
Porochista Khakpour is the author of the novels Sons and Other Flammable Objects (Grove, 2007) and The Last Illusion (Bloomsbury, 2014) and the memoir Sick (Harper Perennial, 2018). Her writing has appeared in many sections of the New York Times, the Guardian, the Los Angeles Times, the Wall Street Journal, Bookforum, Elle, Virginia Quarterly Review, and other publications around the world.
(Photo: Tony Gale)

A Talk in the Woods: Barbara Kingsolver and Richard Powers
Behind the farmhouse in the Appalachian Mountains of southwestern Virginia where Barbara Kingsolver lives and writes, surrounded by trees, ruby-throated hummingbirds are constant companions, darting here and there, pollinating the orange jewelweed and other flowering plants. But on the recent, sunny afternoon the best-selling author spent talking with novelist Richard Powers, who drove a few hours north from his home in the Smoky Mountain foothills of northern Tennessee to see her, the hummingbirds seem more interested in the almost-empty feeder that hangs above the table on her terrace, where we chat following a lunch of homegrown cucumbers, tomatoes, and red peppers along with olives and smoked-trout pâté with chips.
The humming is so loud, in fact, that at one point late in the conversation, Powers remarks, “Let the record show that what sounds like nearby automobiles are actually hummingbirds.”
Powers, whose list of awards covers just about every major honor available to a writer, including the National Book Award for The Echo Maker (FSG, 2006) and a MacArthur “Genius” Fellowship, is the author of twelve novels, most recently The Overstory, which is, to repeat the word Kingsolver herself used in a front-page encomium in the New York Times Book Review upon its release by W. W. Norton in April, a “monumental” achievement. Through eight intersecting and overlapping narratives, Powers expertly assembles a supporting cast of characters who, through their individual stories, reveal the novel’s real protagonists: trees.
Kingsolver is the author of nine best-selling works of fiction, including the novels Flight Behavior, The Lacuna, The Poisonwood Bible, and Animal Dreams, as well as books of poetry, essays, and creative nonfiction. Her list of honors and awards is even longer than that of Powers and includes the Orange Prize for Fiction, the National Humanities Medal, and the Dayton Literary Peace Prize. Her novel The Poisonwood Bible was selected for Oprah’s Book Club in 2000, the same year Kingsolver established what is now known as the PEN/Bellwether Prize for Socially Engaged Fiction.
Her new novel, Unsheltered, is the tale of two families who live, in different centuries, in Vineland, New Jersey, a real town built as a utopian community in the 1860s. Kingsolver masterfully blends historical and fictional characters to frame twin narratives of people coping with a paradigm shift. The story of Willa Knox and her family, who inherit a ramshackle house whose disrepair is in step with the family’s declining fortunes, is juxtaposed with the narrative 150 years earlier of Thatcher Greenwood, a science teacher who comes under attack for furthering the controversial theories of Charles Darwin, and his neighbor Mary Treat, a scientist who corresponds with Darwin.
I invited Powers and Kingsolver to talk not only because they are both giants of contemporary American literature, but also because they’d never met, despite having much in common. Both pursued academic fields of study in the sciences (Kingsolver has a master’s degree in ecology and evolutionary biology, and Powers studied physics); they both moved overseas as children (the Powers family moved from Illinois to Bangkok for five years when Richard was eleven, and the Kingsolvers moved from Kentucky to what was then called Léopoldville, Congo, for a year when Barbara was seven); both live in southern Appalachia; and both have a deep, abiding, infectious fascination with and love for the natural world.
What would happen if they were given an open forum with no expectations, no preconceived editorial angle, other than recording their conversation? What would they talk about? Before I even started recording, they were exchanging strategies for observation in service of the fictional narrative.
Barbara Kingsolver: I always feel that I’ve seen a thing after I’ve described it. My notebooks that I carry with me when I’m researching a place are not full of drawings—only if there’s a map or something to help me orient myself—but when I’ve written a thorough physical description of something, then I feel like I’ve seen it and I’ll remember it. I’ve never been one to take pictures when I travel, even when I was younger. I always feel that taking pictures interferes with my being somewhere—
Richard Powers: —with actually being present. You are either in the scene or you have framed the scene. They are two different cognitive processes.
BK: They are. And I suppose that when I’m writing, taking notes on something, I am also outside of it. I’m framing it, but words are the way that I take something in.
RP: Although you are converting it into another kind of semantic unit. It’s not like saying, “Here’s my composition.” It’s just a stab at something. It’s an associative mnemonic, and it has these endless repercussions of association that ripple outward from it.
BK: Right. There are a million ways that you could look at this thing or understand this thing, and you’ve mastered one of them. And that’s enough to hold on to it, I guess.
RP: But what about the visual? Your characters are insanely palpable and present and integral and coherent. You must have a visual fix on them too.
BK: When I’m writing I’m watching a movie in my head, but of course I’m also generating the movie in my head. Unlike some writers who claim that they just channel them or something. I think it’s Alice Walker, in the beginning of The Color Purple, who thanks all of these characters for showing up. I read that and thought, “Lucky you! I had to chisel mine out of cold, hard clay, and they weren’t that happy about it either.” What about you? Are your notebooks full of drawings?
RP: They are. I dearly love to draw and paint. I’m horrible at it. I can barely sign my name. When I do my compositing…when I bring my commonplace books into a kind of annotated outline, I need a visual prompt because maybe I can’t do quite as strongly what you’re able to do, which is to really summon up those visual cortex high-granularity, high-resolution images. So I’ll be on the lookout during composition for things—people, places, and things—in my consumption of visual images or in my travels that I can use as a stand-in, as a little bit of a bookmark.
BK: I do use visual prompts as well. I have a giant bulletin board in my office—probably a five-by-five-foot bulletin board—on the wall next to my desk. And right now, in the middle is a map of Vineland. It’s my Unsheltered visual composite. Just having that bulletin board full of photographs helps anchor me to that place—especially the nineteenth-century place, which is harder. It’s harder to visualize a scene in a time you’ve never lived. Like when people sit down to dinner: What are they eating? Who made it? Who cooked it? Is it cold? Is it greasy? So many details you have to look up. It’s so much harder to visualize.
RP: But there was more joy for you than challenge in terms of living in that time period? You’ve done historical fiction before, but this may be the furthest away temporally.
BK: The furthest back I’d gone before is the twentieth century. And it was harder for that reason.
RP: As you were talking I realized you can get strength from the fact that there is a world to go to that you can find and build out of documents. But there is always that qualified sense of am I doing this in an arch fashion? Am I overlooking some obvious anachronism? There’s a terror associated with trying to make it credible.
BK: Absolutely. And you could discover something just as you’re finishing your last draft that makes everything moot. That’s the hardest thing about historical fiction: the terror of anachronisms.
RP: On occasion I’ve made things far more difficult for myself than I ever should have. For instance, in my novel Gain, I try to tell the history of a single company over the course of two centuries. And the challenges of a fixed time period that is not your time period are multiplied because now you have to set the whole process in motion. That luxury of making yourself expert over twenty decades.
BK: Yeah, that sounds miserable. [Laughter.]
RP: But also that sense of trying to grasp a large process, to cast a narration on something other than personal time, which was one of the great joys of working on The Overstory—finding narrative techniques that allow you the equivalent of time-lapse photography.
BK: And to knock a reader out of a personal time scale.
RP: Yes, which you do [in Unsheltered] by unity of place, in the crosscutting over 150 years. So that’s also an estrangement. And you have this lovely overlapping, almost like an Oulipo device, where the last words of each chapter become part of the next.
BK: As novelists we’re looking for the universal that makes a reader understand that a human person is a human person regardless of where and when and how.
RP: The lumping and splitting, as the taxonomists say.
BK: Exactly, but if we’re in the empathy business, that’s the first challenge: to get a reader to just forget themselves and be there in another body, another time, another set of worries.
RP: When you composed the book…you had to do a fair amount of top-down planning in order for all of the joints to work out. Were you to able to work consecutively, or were you doing a lot of discursive back and forth?
BK: I always do a lot of jumping around. I do a lot of architecture. I do an enormous amount of planning. I write things on legal pads: sort of narrative-arc stuff, the architecture of the story. Then I’ll just write almost like a movie treatment—a few sentences about what happens in each chapter—and then I’ll break each of those out into a computer file, and that way if I start seeing a scene that’s happening at the end, I can just go to that chapter and write whatever I want to write.
RP: I’m almost picturing an eighteenth-century proto novel: “Chapter 18, in which…”
BK: Or A. A. Milne, “in which Pooh and Piglet discover…” Yeah, very much like that. So I have pretty much all of it plotted out and outlined, then I’ll try to do a continuous first draft, but I still do a lot of jumping around.
RP: What you just said explains a bit of something that I just marvel at and that fills me with horrific envy at how well you do this. Very few people writing now are as absolutely, viscerally persuasive at the level of the scene and the character and the transactional vignettes while still in the service of grand architecture and a thematic preoccupation that manifests itself in all kinds of ingenious ways across the journey. And I just think, “How does she do that when it does not feel constructed?” And yet when you step back and you realize where you’ve been, to quote Horace, “the instruction and the delight,” or the top down and the bottom up, just mesh. You’re not hitting that in the first draft presumably.
BK: That is sort of the manifold challenge of the process: to start with that architecture and then you put on the sheet rock and then you put on the paint and then you put in the furniture. And by the end of it hopefully none of the I-beams are visible, but they’re all there.
RP: Absolutely, but there are things that pop up on page 370 of the nineteenth-century frame that are a kind of retrospective correspondence to things that are happening on page 20 of the twenty-first-century frame. You know, I think, “She sold her soul to the devil to get this!”
BK: Bless you for having the memory to notice. I just love those letters I get from people who say, “I read [your book] four times and I’m starting my fifth,” because you put so much more into a book than any one person is going to get out of it. But that’s okay because that’s the form, and it needs to be many things to many people. And anyway I’m not trying to please anybody really, am I? I’m trying to say this thing right. But I think what you’re referring to, the cross-referential nature of it, is the beauty of revision. I feel like once I’ve gotten a draft nailed down, then I can breathe. Then I can accept the advance. Now I know for sure I can do this thing. But the real art comes from revision. Because you can take that ending and pull it back through the whole thing, and the minute you know for sure where you’re going to end up, then you can start angling, holding up mirrors in different scenes that lead the reader in the right direction without giving away too much.
RP: There’s a great villanelle by Theodore Roethke, “The Waking.” And the refrain is: “I learn by going where I have to go.”
BK: Exactly.
RP: But of course that means two completely inimical things.
BK: And it is fascinating that every writer has a different process; many, I know, say, “Well I just start writing and I don’t have any idea where I’m going to end up, and it’s like I wander through the woods.” I think if I did that it’d be trash.
RP: I think you can get away with that if your primary concern were simply to manifest some local aspect of consciousness.
BK: You’re right.
RP: Some private thing, some psychological, small-scale thing, but you’re not doing that. You are working on at least three levels at once. You’ve got the psychological going, you have the social and the political going, and you have this larger…. I think of it as the three kinds of love: eros, philia, and agape. I think Kingsolver is the one who gets all three plates in the air every time with no sacrifice.
BK: You’re really making me blush. [Laughter.] That’s what I love about your work. Like the first chapter of The Overstory, the chestnut chapter. I thought that was a perfect short story. It’s a story of a man, it’s the story of a family, it’s a story of the species, and the last paragraph just shoots you through the heart. And a human gets to feel for once—for most humans, once in a lifetime—what a tragedy this was for the chestnuts, that they lost their whole family, and it mattered. That was just beautiful.
RP: You’re also a plant person, and you have spent a great deal of your life finding ways of joining human stories to nonhuman stories, so you are the ideal reader for this, and my fairy godmother put the book into your hands.
BK: Well, I was thrilled. There is no more enjoyable assignment than reviewing a book you love and no more miserable than reviewing a book you didn’t like. I haven’t reviewed that many books that I didn’t like, but the effort I put into it was far and away more than anything else. It’s so hard. It’s just not worth taking up column inches to say, “Don’t read this book.” It’s just wrong.
RP: That’s never a very useful function of a review. I had a teacher who said, “Here’s one way you can approach this question of reviewing: Rather than superimpose your preexisting values on the thing, why not ask, to the extent that you can, ‘Who would I have to be to find this magnificent and moving?’ Now start looking at that list. Can I get there from here? Do I want to go there? Would I like myself if I were that person? What would it teach me to not be the person I am but to be that person?” It behooves the reviewer to move toward that world to decide what the values of that world are. But this act of becoming the right person for the other end of that contract—the act of imagining yourself into who you need to be to like the book or for the book to be useful to you—isn’t dissimilar to what you were talking about earlier with the act of character creation and narrative testing, where you’re basically saying, “Yes, I’m here.” I know where I would like this to go, but I do have to defer to some other temperament that is not my temperament.
BK: I know where they all have to end up. So I get to cast this story and I put the people in it who I know will go the distance, who will do the things that I need them to do. Once in a while they may balk and say, “I don’t want to do that.” So then you have to light a fire under them, you back up, and that’s one of the many things I love about revision: Any weak parts, if their motivations aren’t clear you can back up all the way to the beginning, and you can begin building up motivation right from the start. And you get to connect things across time, across place. I would so much rather revise. I wish I could just pay someone to write my first draft, and then I would just revise. [Laughter.]
RP: But there’s that sense when, okay, [the work] has somewhat set in concrete—I’m not doing major surgery at this point—but I realize, my goodness, “He’s not saying that; she’s saying that,” and this happens at the eleventh hour, ten minutes to midnight. I must have known at some level that I just headed in the wrong direction, or that if I use this metaphor instead of the metaphor I was using, then I have a correspondence that wasn’t there before. I must have been leaving bread crumbs for myself, and I’m now just getting to the point where I can detach enough from it to see the signals that I was sending.
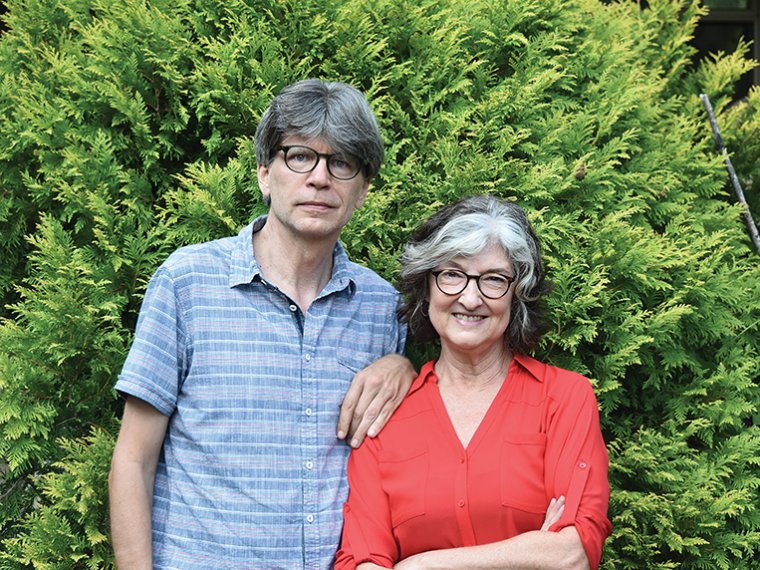

Richard Powers and Barbara Kingsolver. (Credit: Kevin Larimer)
BK: What do you do?
RP: Cry and be grateful I guess, when you manage to find something that you can make much more resonant through small changes. And sometimes they’re cosmetic and sometimes they’re subterranean, but so much has to do, again, with that humility of backing off from your original plan and being open to your actions as well. There’s a genome that drives the expression, but you also have an environment that has to allow all kinds of things to express.
BK: That’s a book title: Enormous Changes at the Last Minute, Grace Paley. But when I sign a contract I’m way ahead of where they think I am. That’s a secret. [Laughter.] So I know that I won’t be stressed by a deadline. There’s just no reason to do that to myself or to anybody else. I want to be sure this is exactly the book that I want it to be before I let go of it. So I don’t often have these great reckonings at the eleventh hour. I believe if I did I would just call my editor and say, “Are you sitting down? Barbara is going to miss her first deadline.” I couldn’t let go of a book if I felt it was not—I don’t want to say perfect; it’s never perfect—but exactly what I want it to be. Although I am grateful for deadlines because I reach a point of diminishing returns. I know that during the last three drafts of this thing I probably changed eighty words throughout, and they were all changed back from the last draft. Now I’m just fiddling. Then I’m glad I have to turn it in because I’m such a perfectionist. I would just keep messing.
RP: You just reminded me of George Sand talking about the way Chopin would write a short piece. She said he would start out, and it would be beautiful, it would be lovely. And then there would follow this incredible stretch of torture and agony. Everything came apart. It became something else. He hated it. He would throw it all away, and eventually he’d work his way back to what he had at the beginning.
BK: Well, I don’t start with perfection, unlike Chopin. I start with a mess. I want to ask you how much architecture do you do at the beginning?
RP: I’ll honestly say that when I started out as a wee boy—my first book was published in 1985, so just a couple years before your first book—I was definitely a top-down guy. I mean my tastes were all for the avant-garde. They were all for structured literature. They were all for constrained literature. I really loved the literature of the mind. And I remain somewhat unapologetic about that now, although I’ve lived most of my life in a culture and at a time where that’s not going to speak to a lot of people. And my journey has been toward the bottom up and has, over the course of thirty-five years and twelve novels, been toward the joys of the organic and the affective and the emotional and the unstructured. So I still think there’s something in me that wants to work on large-scale architecture. But I think I might be much more open to the idea of surprising myself along the way and being open to more substantial course correction. But again, if you’re looking for this triple-layer cake—if you want the psychological and the social and the political to line up, if you want your eros and philia and agape all to be pulling or adding to the sense of coherence for the work—you can’t be above structuring it. It has to be there. Despite this present-day obsession with “Don’t show anything that looks like architecture.”
BK: I don’t think it has to be either/or. As long as you’re good at disguise.
RP: And you’re the best. That’s why I love your stuff. There was a well-known Shakespearean critic who said, “It’s amazing, in the Elizabethan audience, how much poetry they would stomach on the way to blood and thunder.” I would say that slightly differently about a Kingsolver novel. How much incredibly deep education we get about the living world on our way toward understanding more about ourselves. So the seduction is there. The conventional pleasures of a character-driven novel, but superimposed on that is this whole superstructure of meaning that goes beyond the individuals and beyond the private transactions.
BK: Well, if you don’t start with that, it’s not going to be there. I haven’t taught writing very much—it’s not my gift—but when I did, a question I would often ask is, “What does this mean?” And if the answer is you don’t know, then how the hell do you think I’m going to know? It can’t be random. You can’t just leave it to the reader to guess what your story is about, even though that has been much in fashion for most of our lives. When I finish writing like that I feel like I’ve consumed empty calories. I just feel like I need to go work out or something. And yet of course I understand that people read novels because they want to enter another life—the life of another human, not a tree, not a Venus flytrap—but they can be there.
RP: You have a magnificent protagonist who feels passionate toward carnivorous plants in the way that the ordinary person can only feel passionate toward other people. So in a sense you finesse this difficulty of opening up a nonhuman to the human, via the human.
BK: Exactly, as you did with people who love trees. And that’s our contract. I know I’m an odd bird, but some of the passages in fiction that I love best are those that don’t have any people. And they’re still clear in my mind. The first one I think I ever read was in Steinbeck’s Cannery Row. I loved Steinbeck when I was younger, when I was first sort of teaching myself to write, because there’s just so much instruction there. And in Cannery Row there is a complete chapter told from the point of view of a groundhog. And it just blew out the windows when I read that. I thought, “I could do this? I could do this in a novel?” My goal in life was to do “the groundhog,” as I called it to myself. But it’s a huge risk. I think the first time I ever really tried to pull it off is at the beginning and the end of Prodigal Summer.
RP: The coyote.
BK: You are experiencing the world through the eyes and mostly the nose of a coyote, and that’s really where I want to take people—out of their humanness. It is the ultimate act of empathy. If you can imagine yourself in some other life that’s not human.
RP: In Unsheltered you tackle head-on the direct fear of what science might be telling us about our importance or place in the world, or the way that we have to think about our relationship to the nonhuman. And I hit this line where Thatcher Greenwood is talking to Mary Treat. He says to Mary: “You and I are not like other people. We perceive infinite nature as a fascination, not as a threat to our sovereignty, but if that sense of unity in all life is not already lodged in a person’s psyche I’m not certain it can ever be taught.” I read that first half and I just thought, “It has taken me some years to get around to this, but that’s the club I want to belong to.” And you’ve been there for a while. When he says that if you’re not born with that sense of unity maybe you can’t learn it, I think your book is a spectacular example of the opposite, both in its narrative and in your use of that narrative to move people who are somewhere on that spectrum closer to this idea that what we can take away from this astonishing revolution that the people in your nineteenth century are just feeling the forward edge of. And what we in our twenty-first century are just feeling a very late edge of: If we can’t take away from the fact that this is a huge augmentation and enhancement of the reverence of life and the urgency of life—if instead it feels like a diminishment to us—we’re doing something wrong.
BK: And we’re sunk. But this understanding that natural law applies to us as well—we don’t get to rewrite it. We can try our best, but it wins. Physics—I don’t use the word trumps anymore; it used to be a good word—but physics takes all.
RP: But what you’ve done is juxtapose the story where that initial dramatic dislodging of anthropocentrism—you’re juxtaposing that story, that trauma, with the trauma of the present, which is a dislodging of the same kind of what George Lakoff has called Western paternalism: men above women, white above black, Americans above all other nationalities, and humans above all other creatures of the earth. The rejection of Darwin because we’re no longer the center is also the kind of rejection that’s being promulgated by our political leaders right now because we can’t think of ourselves as centrist or as urgent or as essential as we perhaps once were.
BK: Right. Nationalism and patriotism and patriarchy and all of these things are sort of crass attempts to hold on to the same thing that Thatcher and Mary’s compatriots were trying to hold on to: supremacy in the face of a complete failure of the paradigm. Well, it’s really hard to understand a paradigm shift. It’s impossible, by definition.
RP: Not when you’re in the middle of it.
BK: So that’s why I really wanted to write about paradigm shift, and I thought the only way to do it would be to compare this moment with some equivalent moment in history when people were really struggling with a paradigm shift that just oriented them completely. And I’ve always wanted to write about Darwin. I thought he would be a character in this novel…but it just wasn’t going to work because I had this device of the house and the people, then and now, living in the same house. You think it’s the same house. And of course it’s falling down. When you start with all of this structure it seems like, oh, that’s going to be so obvious: a falling-down house as a metaphor for a crumbling paradigm, but you just keep at it until the house is the place. You know, you’re talking to the contractor and you’re in the house and you’re feeling like, I got to fix this house.
RP: In the act of reifying that place in your own imagination and seeing every timber in the floor plan and what rooms have caved in and where they have retreated to, you’re also animating that house in an almost pantheistic way for the characters in the story. I mean it is no longer a placeholder in your intellectual scheme about the intersecting themes of Unsheltered. It actually has a visceral urgency to your protagonist. And as a result that urgency is transferred to the reader.
BK: I’m just thinking about sentences when I’m writing. I mean, once I’ve done all of this planning, then, well, then the fun begins. And just thinking about the internal alliteration. I read sentences aloud as I write them. That’s where 90 percent of the work is—and the fun. What moves me utterly in The Overstory, when I understand I’m in the company of greatness, is when I feel like I’m being asked to be a larger person, a larger brain, than I was when I started. And I think we reach for wisdom, don’t we?
RP: We also write for wisdom; we sneak our way toward it I think.
BK: I always start with questions that I can’t answer. Otherwise you get bored halfway through if you already know the answers. If you’re asking what seem to be unanswerable questions, then you have to keep showing up. It is so interesting to me that people, in what they’re calling the attention economy, and people are chronically short of time, or so they say—as if people weren’t short of time when they had to dig up their own food or shoot it or whatever, it’s a sort of artificial urgency—but people don’t buy and read poetry. I mean masses of people don’t read poetry; they don’t read short stories. I know if I went to my publisher, which I would love to do, if I went to my publisher and said my next book is going to be poems or short stories, I think they would just smile, leave the room, and then keel over. They wouldn’t be happy. Why not? If people don’t have much time, why do they prefer novels?
RP: We want to be part of something bigger than ourselves. And yet to have a keyhole in a door that’s on our scale to get into this larger place. And you almost need the real estate of the novel to bridge that, from little to big and back again. That’s one possibility. This isn’t you, although you certainly channel this woman at various places in your career: “I was something that lay under the sun and felt it, like the pumpkins, and I did not want to be anything more.” That’s Willa Cather in My Antonia. “Perhaps we feel like that when we die, and become a part of something entire, whether it is sun and air, or goodness and knowledge. At any rate that is happiness; to be dissolved into something complete and great.” I’m not saying the novel is a sure way to get that. It just allows that strange mismatch of scale. It also allows that strange distortion of time. You know, Peter Brooks says we have a curious relationship to the logic of time in a novel: We read in anticipation of retrospect, and we know that page 400 is going to change page 20 forever. And we love the fact that page 20 is disappearing under our feet as we move forward to this ending that has already been written. It reverses our relationship to the fixity of future and past. We want that immersion. We want to feel like we’ve gone into a world, and when we turn that last page it’s hard for us to come back from that world into this world.
BK: Half of it is about entering into the other world, and the other half is self-forgetting. I think self-forgetting is really important and really valuable, and in times past it was for most people a function of religion, spirituality, culture, music…. Participatory music was a really standard way that ordinary people all the time would just stop being themselves and become part of the human chorus—self-forgetting—and so the novel gives you the space to leave yourself and go be someone else and really just go inside another human brain and see through other eyes and hear through other ears. It’s something we must crave because the novel as a form has remained pretty consistent for hundreds of years.
RP: Reading as a confirmation or as a provocation. Reading as telling us what we already knew. So we come to the final page having journeyed not all that far from where we went into it, or having been taken out of ourselves into other selves in other places and other hierarchies. I do believe that a book can trouble and delight us at the same time.
BK: And should, ideally.
RP: I wonder—though it’s a horrible thing to ask, because it’s only a deep commitment to commodity culture that would make any interviewer ask, “So what are you working on now?”
BK: I know. And don’t you love when you’re on book tour, and in the signing line people ask, “What are you working on?” And you want to say, “Signing your book! That’s what I’m writing: my name.” [Laughter.]
RP: I’ve always been restless. Every book has seemed to run its course and present new questions that take me to some new place and make me want to commit for another three or four years to some new place, to become knowledgeable about some new domain. But this time I thought, “Now wait a minute—I want to stay here. I like these woods.” We’ll see.
BK: Interesting. So you don’t have any idea what your next novel might be? Do you think you’re going to stay in the woods?
RP: I don’t think the apple is going to fall too far from the tree.
BK: That is wonderful news. It is interesting though, as you say, our vocation is to love and to leave…but your readers and the media want to keep you where you were. We did a book about local food, and I still get five invitations a week to go talk about local food economies. I say no to all of them, but then it’s like you’re betraying a sacred trust. But it’s our joy—and an urgent requirement of our vocation—to move on, to not get so associated with the subject matter of one book that we can never write another. And it’s really difficult in the modern era to set those boundaries. You’re going to be the go-to forestry guy now.
RP: There are worse fates.
Kevin Larimer is the editor in chief of Poets & Writers, Inc.
Episode 22: Susan Orlean, Barbara Kingsolver, Natasha Trethewey & More
In the twenty-second episode of Ampersand, editor in chief Kevin Larimer and senior editor Melissa Faliveno discuss the work of superstar nonfiction writer Susan Orlean, best-selling novelists Barbara Kingsolver and Richard Powers, and Pulitzer Prize–winning poet Natasha Trethewey. Orlean is the subject of our November/December 2018 cover profile; Kingsolver and Powers spent an afternoon in conversation for a feature titled “A Talk in the Woods,” and Trethewey’s new book, Monument: Poems New and Selected, is feature in this issue’s Page One: Where New and Noteworthy Books Begin.
00:01 Susan Orlean reads an excerpt of The Library Book.
The opening spread of the cover profile of Susan Orlean by Kate Tuttle. Photo by Tony Gale.
02:40 The cover of the new issue features New Yorker staff writer and author Susan Orlean, whose seventh book, The Library Book, is out now from Simon & Schuster. In The Library Book Orlean investigates the unsolved mystery of the largest library fire in American history—the massive 1986 fire that destroyed the Los Angeles Public Library—while showcasing the crucial role libraries play in our lives. “It was a challenging book,” she tells contributor Kate Tuttle. “And I went into it thinking how easy it would be.” Simon & Schuster Audio shared with us an excerpt from the audio book, read by the author herself.
Richard Powers and Babara Kingsolver. Photo by Kevin Larimer.
10:34 Kevin took a trip down to Virginia to meet Barbara Kingsolver and Richard Powers, whose in-depth, hours-long conversation about the art of fiction writing, the architecture of novels, the joy of planning, and more is featured in “A Talk in the Woods.” Kingsolver is the author of nine best-selling works of fiction, including the novel Unsheltered, published this month by Harper, and Powers has written twelve novels, including The Overstory, published in April by W. W. Norton. The authors spent an afternoon on the terrace behind Kingsolver’s farmhouse in the woods, and Kevin made sure his tape recorder was on to capture two masters of the art form talking shop.
Natasha Trethewey. Photo by Terry Thomas.
21:55 Former two-term U.S. poet laureate Natasha Trethewey reads two poems from her Pultizer Prize–winning book, Native Guard (2007), both of which are also included in her new book, Monument: Poems Selected and New, forthcoming in November from Houghton Mifflin Harcourt and featured in this issue’s Page One.
25:58 Kevin and Melissa look ahead to the next episode of Ampersand, which will be released a couple weeks before the end of 2018—a year that, when viewed solely through the lens of national news and political headlines, can best be described using one of our favorite terms: dumpster fire. Fortunately, the world’s poets and writers are there to save us from ourselves. Here’s to work that matters and dreams of a better tomorrow.
This episode is brought to you in part by the MFA in Writing Program at California College of the Arts in San Francisco. Our two-year program has launched Molly Prentiss, Adam Nemett, and Julie Lythcott-Haims. Come write with us! Learn more about CCA’s den of poets, raconteurs, playwrights, and novelists at cca.edu/writingmfa.
Susan Orlean audio excerpt courtesy of Simon & Schuster Audio from The Library Book by Susan Orlean, read by the author. Copyright © 2018 by Susan Orlean. Reprinted by permission of Simon & Schuster, Inc.
Ampersand: The Poets & Writers Podcast is a production of Poets & Writers, Inc., and is edited and mixed by Melissa Faliveno. Music for this episode is provided by Chris Zabriskie, YACHT, Broke for Free, and Black Ant. Comments or suggestions? E-mail ampersand@pw.org.
Vagrant & Vulnerable: Dawn Lundy Martin, Nicole Sealey
The poets whose work I return to again and again answer a call that compels them, meaning their poems cannot not exist. I can’t escape them, even though what I want from poetry is lightless, weightlessness, to be untethered. The poems—for the writer and for me, the reader—create the feeling, however temporarily, that I am free.
Nicole Sealey is one such poet. Born in St. Thomas and raised in Apopka, Florida, she is the author of Ordinary Beast, published this month by Ecco, and The Animal After Whom Other Animals Are Named, winner of the 2015 Drinking Gourd Chapbook Poetry Prize. She is also the executive director of Cave Canem, a nonprofit organization in Brooklyn, New York, that cultivates the artistic and professional growth of African American poets. In fact, in mid-June we spent a week together at Cave Canem’s retreat at the University of Pittsburgh in Greensburg. There we had our first substantial conversation, though we’ve been in each other’s orbit and mutual admirers of each other’s work for years. Despite the sweltering heat that hit us in that special landlocked way, we talked about poetry and craft, our new books—I, too, have a new collection, Good Stock Strange Blood, out in August from Coffee House Press—aesthetics and language, vulnerability and vagrancy, luxury and yearning, drag and systematic repression.
Somewhere in my thoughts I held Sealey’s poem “A Violence,” from Ordinary Beast, as we spoke. I thought of how it feels like a poem for our times; at the end, it references what the mind cannot sustain. We are left to imagine what that is, exactly, though she gives us good direction. In Between the World and Me (Spiegel & Grau, 2015), Ta-Nehisi Coates writes of the art that he was coming to love as a young man, how it “lived in this void, in the not yet knowable, in the pain, in the question.”
Our discussion spanned several days, and I felt the calling that compels us both through our focus on the craft of our poetry and how we think meaning gets made. As our conversation spread (during the week of the retreat, the Minnesota police officer on trial for the killing of Philando Castile was acquitted of all charges in the July 2016 shooting), we never overtly said the names of those people who have been unjustly killed by police, but they are ever-present nonetheless. While at the retreat, we all heard of legal absolutions that confuse the rational mind. But the conversations between most of us who attended remained focused on poetry. Why? I think—and this is what I noticed in my talk with Sealey—that the art that moves us does something else entirely than speak to the thing at hand. What we do as poets is figure out how to negotiate the limits of the so-called rational world. This is a means of survival. And it is also, finally, where weightlessness might be found.
Nicole Sealey: I don’t know if you remember, but about a decade ago I wrote a review of your debut collection for Mosaic magazine. I wrote:
Just as the great American folklorist Zora Neale Hurston encouraged readers—through her mother’s words—to “jump at the sun,” so does poet Dawn Lundy Martin urge in A Gathering of Matter / A Matter of Gathering. It is the leap, not necessarily the landing, that forces risk and invention. Martin has taken such a leap and, in the process, invented new ways in which to engage and experience language. A Gathering of Matter…does not consult with convention, but rather vehemently argues with it.
I didn’t think it possible, but Good Stock Strange Blood takes even greater leaps and risks even more. Can you trace your journey from A Gathering of Matter / A Matter of Gathering to Good Stock Strange Blood?
Dawn Lundy Martin: When I was writing A Gathering of Matter / A Matter of Gathering, I was doing two things. One, I was figuring out how to speak to childhood traumas; and second, I was thinking of black displacement—like our relationship to a postcolonial continent. So I was trying to make work about something really big and something really small, and do it via a poetics that was interested in language’s inexactitude. Language feels too bulky to speak to trauma. What happens when we open our mouths to speak it? Out comes dust. Blathering. A cry. A stammer. A circling, a return again and again to try to say what happened.
I was working from the idea that language was not enough, that it fails us—often even in regular communication, like, say, an argument with a lover—and that where poetry enters is in the re-formation and ratcheting of language, so that it does its best job at speaking. This is especially important when it comes to trauma, which has no language, and the displacement of an entire people, which is almost unimaginable. By the time I got to Good Stock Strange Blood I’d been working in the art world and influenced by the ways utterance happens in art by folks like Kara Walker, Carrie Mae Weems, and Lorna Simpson. I’d also been working a lot in the prose poem and attending to the sentence.
The sentence is such a curious method toward utterance for me. It really wants to control us with its yoke of grammar. In Discipline and Life in a Box Is a Pretty Life, the prose poem becomes a way of thinking through the concerns of freedom—both internal and external, individual and collective. In my mind, however, Good Stock is my strangest work to date. The approach to language is ranging—lots of lyric poems extracted from Good Stock on the Dimension Floor, the libretto I wrote for the politically trouble-making global artist’s collective HowDoYouSayYamInAfrican? And other approaches: essays, journaling, prose poems, poems that are poems and poems that approximate poems. Which is to say, the aesthetic approach is less contained, less namable. More vagrant.
Vagrant is the word I would use to describe Good Stock Strange Blood. But if I had to describe your work in one word, I would use “vulnerable.” Immediately, when reading Ordinary Beast, I’m struck by the opening poem’s gorgeous and stinging vulnerability. How does this kind of nakedness impact how you think about writing poetry? And when I say “vulnerable” or “naked,” I mean I feel a rawness in your work—the poems feel stripped of artifice, even as they make themselves available to us as crafted poems. This is a rare and gorgeous balance.
Sealey: Straight out of the gate there’s an assumed familiarity between the reader and myself, void of pretense. Part of the pleasure I take in being a writer and reader of poetry is this instant intimacy. By the first page, we’re practically what one would refer to as family—at this point, I’m comfortable in my nightclothes and headscarf. As you know, the relationship between reader and writer is reciprocal. We bring with us all that we are, the sum total of our experiences up to that point. There’s an exchange happening—one that encourages vulnerability, one that can transform strangers into kin. Which is why, without a second thought, I’m comfortable opening the collection with “Medical History,” its lines: “I’ve been pregnant. I’ve had sex with a man / who’s had sex with men. I can’t sleep.”
I read somewhere that in order to be likable, one mustn’t share too much too soon. I’m not convinced that this rule applies to art, particularly poetry, as some of the best work is some of the most exposed and indicting early on—take Sympathetic Little Monster by Cameron Awkward-Rich, Rummage by Ife-Chudeni A. Oputa, and Beast Meridian by Vanessa Angélica Villarreal, for instance. All that to say, when poets sit down to write, we don’t think about being vulnerable. We just are.
But I so admire this idea of vagrancy. Did you consciously give yourself permission to be “more vagrant,” or was this an unconscious evolution? And I’m in love with the italicized voices that interrupt the “narrative” of Good Stock. Who are they?
Martin: Vagrancy just evolved. I’m less interested in doctrine than I used to be and more compelled by uncertainty. I know so little about how to write an essay but have been teaching myself how to write them, which is very exciting, like learning a new language. And the essays teach me about wandering. As much as I feel like the books are an evolution over time, I feel like they are also one big utterance—always circling around the same haunting themes in an attempt to get it down better. I think of that thing my mother does when she’s listening. She doodles by tracing a word or scribbles over and over, making a deep imprint.
In terms of the italicized voices, sometimes they are an interior voice I want to gift the reader. It’s the voice in my head—or a fabrication of it—or a certain register, which in a way is an invitation into my heart. In other moments, it can be like singing into one’s own ear. I happen to be, probably to my own detriment, a fairly abstract thinker—meaning the voice I whisper into my own ear is like a clock questioning time. When I write, however, “Something larger than ourselves to hold us,” I am writing about black people and thinking very concretely about how we as black people have historically always been left to build our own apparatuses for our own support, defense, relaxation, and protection.
And speaking of support, answer this: If someone you don’t know approaches you with an open hand and that open hand, you understand, is open for you to place a poem into, which poem do you place into it from Ordinary Beast and why? You know nothing about the person or what they need, just that their hand is open, and that they are desperate.
Sealey: Without a doubt I’d place “Hysterical Strength” in the hand. The first half of the poem describes true accounts of superhuman strength—a child lifts a car, a woman fights a bear, etcetera. These accounts are then juxtaposed with the strength black people have had to harness to exist in a world that, I would argue, has for centuries tried (and failed) to kill us. The poem speaks to our struggle and to our strength. I need that someone to know that they’re not imagining things, that this is not normal and that they’re stronger than some people would have them believe. Yes, I would hand over “Hysterical Strength.”
When I hear news of a hitchhiker
struck by lightning yet living,
or a child lifting a two-ton sedan
to free his father pinned
underneath,
or a camper fighting off a grizzly
with her bare hands until someone,
a hunter perhaps, can shoot it dead,
my thoughts turn to black people—
the hysterical strength we must
possess to survive our very
existence,
which I fear many believe is, and
treat as, itself a freak occurrence.
There have been so many poems that have saved me in this same way. The most significant being Claude McKay’s “If We Must Die.” Whenever I get to thinking otherwise, that poem affirms that I’m not imagining things, that this is not normal, and that I’m stronger than some people would have me believe.
What about you? If someone approaches you for a poem, which from Good Stock Strange Blood do you give that person?
Martin: There are these lines in the middle of the new book—a square block of italicized text:
Symptomatic of being a slave
is to forget you’re a slave, to
participate in industry as a
critical piece in its motor. At
night you fall off the wagon
because it’s like falling into
your self.
This is a reminder that we have to be vigilant, especially now with people running the country who are explicit in their disdain for black people, women, queer people, and the poor. The other day I was listening to this heartbreaking podcast about the resurgence of predatory home-lending practices. Instead of buyers acquiring mortgages, mortgage companies are offering “contracts” and telling buyers that this is a cheap route toward home ownership. “Buyers” never accumulate equity, so as soon as they miss a payment they’re out. Ta-Nehisi Coates writes about this in “The Case for Reparations.” This was one way black people were kept from owning homes in the 1960s and ’70s. The practice is back. And guess who’s the secretary of treasury. A guy who has made billions from people losing their homes. Playing the game often doesn’t work—you know, being a good citizen, pulling yourself up by your bootstraps.
But turning back to aesthetics, I’m energized by the ranging approaches to telling stories in Ordinary Beast and the range of forms you inhabit and invent. How did you develop these multiple means toward narrative? And I’m interested in how drag and gender is configured in the work. I love the emergence of all these drag queens who speak up through the interstices of the book via epigraph.
Sealey: In the movie Love Jones, the character Darius Lovehall says, “When people who have been together a long time say that the romance is gone, what they’re really saying is they’ve exhausted the possibility.” I say this to say, these multiple means toward narrative is my attempt to keep the relationship I have with poetry interesting…yet manageable. Writing is hard, at least for me. Having an architectural plan with which to imagine and engage poems makes the process less so. I love form for precisely this reason and find the constraints ironically freeing—the restrictions actually lend themselves to specific music, associations, and imagery that probably wouldn’t happen otherwise. This is definitely true of the various forms in the collection.
For the last decade I’ve been at work on “Legendary,” a series of personae sonnets inspired by the queens featured in Paris Is Burning, a documentary film about drag pageants in 1980s Harlem. Thus far I’ve drafted about a half dozen poems—only three of which were solid enough to make it into Ordinary Beast. What most interested me is the double interiority of it all, the idea of being a subgroup of an already marginalized community. In a perfect world—one free of racism, sexism, classism, homophobia, and transphobia—these queens, who were at the top of their game and art, might have lived the fabulous lives they emulated; instead, their high-ranking status was limited to makeshift ballrooms. The series acknowledges their restricted authority and, in so doing, is as much an assertion of their power as it is commentary on the lack thereof.
I’m interested in the way you use fragment and fracture as tools to reconstruct “truth” in Good Stock Strange Blood. “—The Holding Place—” is a great example of this.
Martin: When I look back at some of my earlier work and the way I used the em dash, I understand the usage to be a literal stutter, cut speech that won’t come out. Like trying to speak with a hand around the neck. In Good Stock, the fragment is a disruptive force to the poem itself. “—The Holding Place—” in particular is meant to self-destruct in the speaker’s attempt to grapple with her own blackness. Originally this piece was in the libretto, and the speaker, NAVE, I imagined, had been born from the head of Sarah from Adrienne Kennedy’s one-act play Funnyhouse of a Negro. Being born black on earth has rendered NAVE both mutant—her body made of many arches and windows—and crazy. NAVE’s is a madness meant to speak to what racism can produce. The truth is the poem can’t hold all of this, so it falls apart in these places of radical ellipses. I’m more than willing to let the poem slip out of the reader’s grasp at times to get as close as possible to the utterance that enacts the near impossibility of our simply being.
A little game I’ve played over the course of my four books is to borrow a line or two from a previous book in each new book. In this case “matter that matters” is extracted with slight variation from A Gathering of Matter / A Matter of Gathering and in its new location doing completely different work on what “good stock” might mean to American black bodies.
Ordinary Beast is such a striking title—hard and soft at the same time. I noticed how beasts and animals find several locations in the book. In the last poem, that beautiful moment, “There’s a name for the animal / love makes of us” still resonates in my imagination. What is the beast to you?
Sealey: Those lines from “Object Permanence,” the final poem in the collection, speak to how love can transform someone into something wholly unrecognizable—if we’re lucky, into something better. Whatever “better” looks like. The speaker seems surprised by her own affection for her beloved, by her own capacity to love, which suggests a shift in the way the speaker now engages with “love.” I can’t imagine her having similar thoughts about the love that came before the one she muses over in the poem.
I just did a quick roll call in my mind of all the animals in Ordinary Beast—fish, horses, tadpoles, a bear, scarabs, goats, elephants, locusts, dogs, caterpillars, unidentified “strays” as well as a variety of birds, one of which is made of fire. Fun fact about me is that back in the day I was studying to become a veterinarian. Obviously, that didn’t pan out, but I’ve maintained my interest in animals, human beings included. I think we’d like to think that we’re more evolved than ordinary beasts, but the truth is we’ve got some growing to do. As a species that prides itself on its consciousness, there are many who are content to live in the dark. And even more who would have us join them. What is the beast to me? At the moment, it is mankind—some men more than others.
Dawn Lundy Martin teaches in the writing program at the University of Pittsburgh and is codirector of the Center for African American Poetry and Poetics. She is the author of several books and chapbooks, including A Gathering of Matter / A Matter of Gathering (University of Georgia Press, 2007), winner of the Cave Canem Poetry Prize; Discipline (Nightboat Books, 2011), which was selected for the Nightboat Books Poetry Prize and was a finalist for the Los Angeles Times Book Prize; Candy, a limited-edition letterpress chapbook (Albion Books, 2011); The Main Cause of the Exodus (O’clock Press 2014); The Morning Hour, selected by C. D. Wright for the 2003 Poetry Society of America’s Chapbook Fellowship; and Life in a Box Is a Pretty Life (Nightboat Books, 2015), which won the Lambda Literary Award for Lesbian Poetry. Her latest collection, Good Stock Strange Blood, was published by Coffee House Press in August. Her nonfiction writing has been published in the New Yorker, Harper’s Magazine, and boundary 2.

Dawn Lundy Martin (left) and Nicole Sealey at Cave Canem’s 2017 retreat at the University of Pittsburgh in Greensburg. (Credit: Richard Kelly)
Q&A: Nicole Sealey Leads Cave Canem
Cave Canem was established by Cornelius Eady and Toi Derricotte in 1996 to nurture black poets both on the page and in the publishing marketplace. The Brooklyn, New York–based organization’s many programs include writing workshops, master classes, a reading series, publication prizes, and an annual retreat, which brings together more than fifty poets, or “fellows,” each year. In January Nicole Sealey, previously Cave Canem’s programs director, became the organization’s new executive director. A veteran arts administrator (including a previous role as the assistant director of Poets & Writers’ Readings & Workshops program), Sealey is also a poet; her first full-length collection, Ordinary Beast, will be published by Ecco in September. A couple of months into her new position, Sealey spoke about the future of Cave Canem.
Can you tell me a little bit about your relationship to Cave Canem?
Almost ten years ago I participated in Cave Canem’s eight-week fall workshop in New York City, facilitated by Marilyn Nelson. I was a very young writer and it ended up being a formative experience in my life. We got serious about craft and made lifelong connections in the process. I’ve met many of my closest friends through Cave Canem, the closest of all being my husband, John Murillo. The very least I can do for an organization that has served me well for the last decade is to return the gesture.
How does being a writer influence the way you will lead the organization?
Cave Canem has always had a “poets first” philosophy, which has served the organization well for the last twenty-plus years. Remember, the organization was founded by rock-star poets and directed for the past decade by Alison Meyers, also a poet. In that tradition, I plan to lead with both head and heart, which are the qualities I value most in poetry.
What’s ahead for Cave Canem and for you as the new executive director?
In May we’ll be capping off our twentieth-anniversary year with Cave Canem 20/20: A Panoramic Vision of Black Poetry, a two-and-a-half day poetry forum at Weeksville Heritage Center in Brooklyn. The forum will offer readings, skill-building panels, artist conversations, and more. I’m also looking forward to my first retreat as executive director. The retreat takes place in June at the University of Pittsburgh in Greensburg, Pennsylvania. It’s our flagship program, and where, as Harryette Mullen says, “black poets, individually and collectively, can inspire and be inspired by others, relieved of any obligation to explain or defend their blackness.”
So much has changed since Cave Canem faculty member Elizabeth Alexander recited “Praise Song for the Day,” the inaugural poem for Barack Obama in 2009. What do you see as the role of Cave Canem, and poetry more broadly, in the new political climate?
“So much has changed” is a very gracious way to describe the political climate in which we now find ourselves. In “Praise Song for the Day,” the speaker asks, “What if the mightiest word is love?” I have no doubt that it is love, but the new administration would have me believe that the mightiest word is fear or, worse yet, the president’s name. It is neither. It is love. And what is love if not a society based on justice and equality? With this in mind, the role of Cave Canem in particular, and poetry in general, is and will be to comfort the afflicted and afflict the comfortable. With love. Bigly.
Are there any outreach programs on tap to connect poetry with readers?
Cave Canem’s Poets Tour, a nonprofit speakers bureau, connects national audiences with Cave Canem fellows through readings and workshops. This year we hope to increase the number of participating fellows and reach out to presenting institutions, including high schools, universities, museums, libraries, and prisons. We want to bring black poets to diverse communities.
Tayari Jones is a contributing editor of Poets & Writers Magazine.

Nicole Sealey (Credit: Murray Greenfield )
A New Center for Black Poetics
From late nineteenth-century poet Paul Laurence Dunbar to Harlem Renaissance icon Langston Hughes to contemporary poetry stars Rita Dove and Toi Derricotte, the influence of African American poets on America’s literary culture cannot be overstated. But until recently there was no center that had significant institutional support and was specifically dedicated to sharing and studying the legacy of African American poetry.* Earlier this year, poets Dawn Lundy Martin, Terrance Hayes, and Yona Harvey decided it was high time to start one. The trio launched the Center for African American Poetry and Poetics (CAAPP) as a creative think tank to spark conversation and collaboration among poets and other artists, and to promote and archive the work of African American poets for future generations.
“We recognized that there was this huge impact that African American and African diasporic poets were making on American arts and letters,” says Martin, who codirects the center alongside Hayes. “We wanted there to be a place where we could really think and work through what that means.” Housed at the University of Pittsburgh, where both Martin and Hayes teach in the MFA writing program, the center held its first event in March—a set of conversations and readings about race, poetry, and the humanities—and will host similar events throughout the academic year. Its first course on African American poetry and poetics, led by Lauren Russell, the assistant director of CAAPP and an English professor, will be offered to undergraduate and graduate students during the 2017–2018 academic year and will feature visiting speakers each week. Hayes and Martin also plan to launch a residency and fellowship program, through which poets, artists, and scholars can work at the center for periods between a month and a year.
Part of CAAPP’s core mission is to archive and document the work of African American poets, which will be accomplished through both a physical collection of books and an online archive of lectures, readings, and discussions. While organizations like Cave Canem create space to nurture new work by African American poets, and other university centers such as Medgar Evers College’s Center for Black Literature and Chicago State University’s Gwendolyn Brooks Center work to promote black literature, CAAPP will focus specifically on the research and scholarship of black poetics, particularly as it relates to historical, artistic, and cultural repression, as well as corresponding social justice movements. “Cave Canem is twenty years old, and there still hasn’t been a large body of work about how it came into being or archival work around it,” says Hayes. “Our organizations historically haven’t had an opportunity to take care of our own information, to build our own insights around that work…. Now we are in a position to be our own historians and our own archivists, and write our own biographies about the importance of these roots.”
The University of Pittsburgh has long been a home for the work of African American poets. The university press, with editor Ed Ochester at the helm, has published notable titles by both emerging and established African American poets, recently Derricotte, Ross Gay, Rickey Laurentiis, Nate Marshall, and Afaa Michael Weaver. Hayes and Martin hope to work with the press on a book prize, and harness other university resources. “What a university can do is provide infrastructure, in a way that’s just not set up in most sectors of our society,” says Hayes. “Infrastructure and research capabilities.” The pair have enlisted faculty from other departments, including English and Africana Studies, to advise CAAPP and possibly teach future courses. “We think of ourselves as a start-up,” says Martin. “And like innovators in tech, we want to be open and inclusive as we generate new ideas about what it means to work in the fields of African American poetry and poetics. This seems especially important in these trying and divisive times.”
A significant part of CAAPP’s work will also intersect with the university’s MFA program. Graduate writing students will be able to take courses offered by the center and have the opportunity to help curate, design, and teach these courses. This goes hand in hand with how Hayes sees the MFA as an opportunity to teach students the tools and skills needed to hold positions of power in poetry and arts organizations. “A person who is interested in getting an MFA and being a poet can learn how to live in the world, whether they are directing centers or working as librarians, archivists, or critics,” says Hayes. “Just to alert and inspire a poet to do that is a possibility. Maybe you want to run a press or be an editor of a press. I don’t see why the MFA can’t be an opportunity to begin that conversation, as opposed to assuming that all you can do is write or teach.”
*Editor’s Note: After this article went to print, it was brought to our attention that a center dedicated to studying African American poetry was already established before the launch of CAAPP. The Furious Flower Poetry Center, housed at James Madison University and founded by Joanne Gabbin, has been cultivating and promoting African American poetry since 1994. We regret the error.

Hayes and Martin hope that the center will also help make the university’s MFA program a more welcoming space for writers of color, an important effort in light of increased discussion about race and diversity in MFA programs. For Martin, this means creating and maintaining a space of cultural inclusion. “Pittsburgh is a place where there are other students of color, and the graduate faculty is extremely diverse. There’s already some understanding between folks who are there, so you can start from a place of not having to work through your values and struggle to articulate your cultural perspective.”
The CAAPP directors plan to offer courses that intersect with visual art and music, in order to explore how thinking across disciplines can parallel thinking across cultures and perspectives. “Certainly, we feel like if anyone is prepared to build those new conversations, it would be African American poets and poets of color in general,” says Hayes, adding that CAAPP aims to include non-black people of color and other marginalized communities in the conversation. “We talk about collage and hybridity—that’s what people of color are. [We’re] not thinking about segregation, not thinking about fences around what we do, but looking across those bridges, saying, ‘Well, how are these people across the street interested in what I’m doing?’ even if they’re not poets. They might be architects, they might be scientists.”
Moving forward, the center will hold a community workshop, reading, and exhibition from November 9 to November 11 on poetry and politics titled “Black Poets Speak Out,” featuring Jericho Brown, Mahogany Browne, and Amanda Johnston. The directors also hope to host a reading by emerging women and trans poets. Martin and Hayes are optimistic about the social impact of the center’s work. “As far as I’m concerned,” says Martin, “especially given the state of violence in this country—violence against queer people, violence against black people, violence against women—it makes sense to take up things like African American literature, African American culture, African American history, African American poetry and art as a part of making the world better.”
Tara Jayakar is the founder and editor of Raptor Editing. She lives in New York City.


Karen Russell, author of the story collection Orange World. (Credit: Dan Hawk)
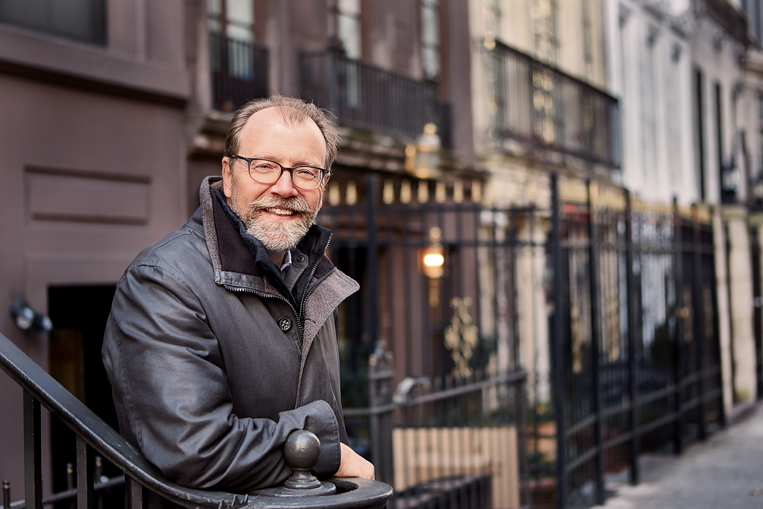
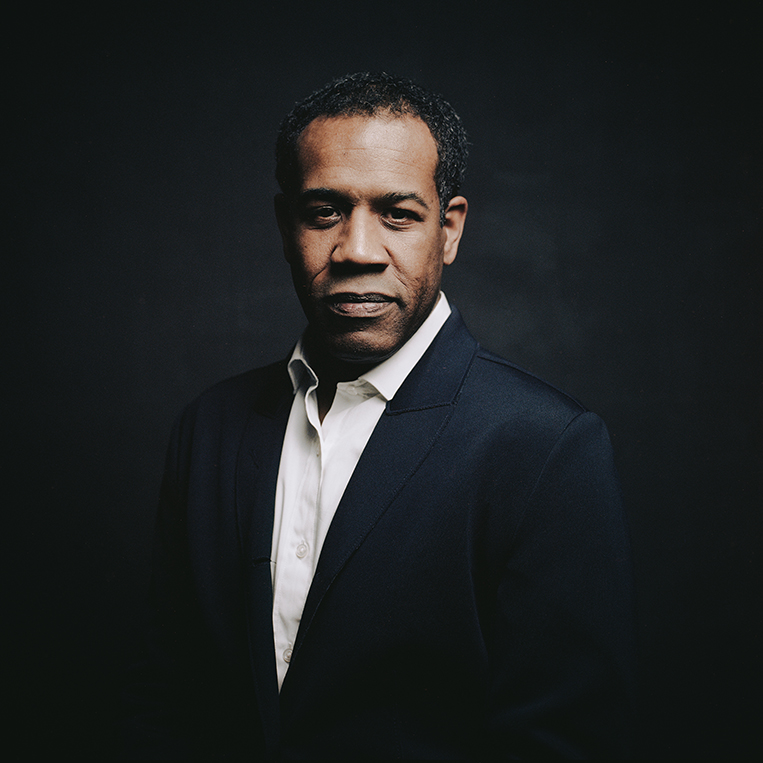
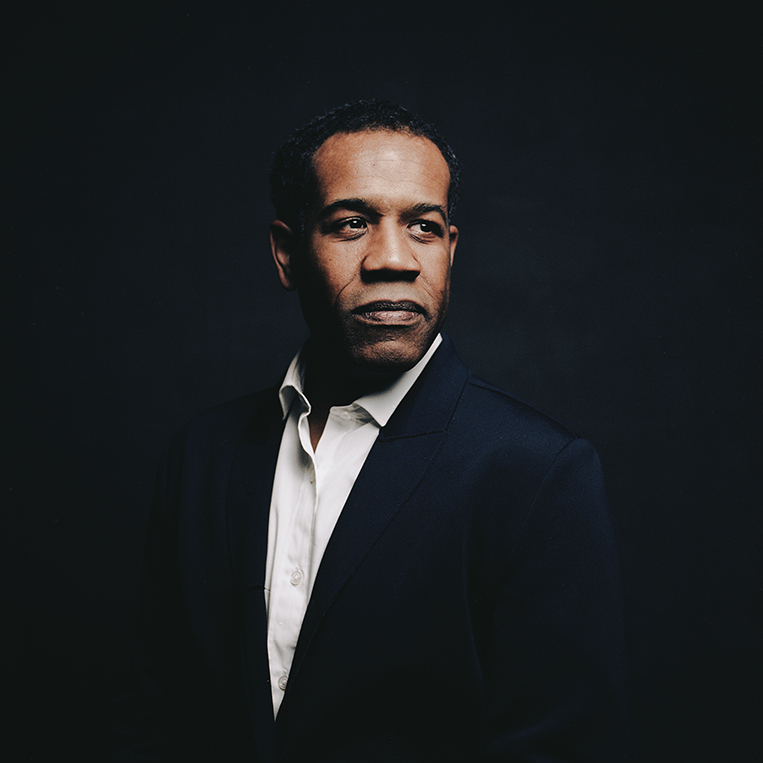
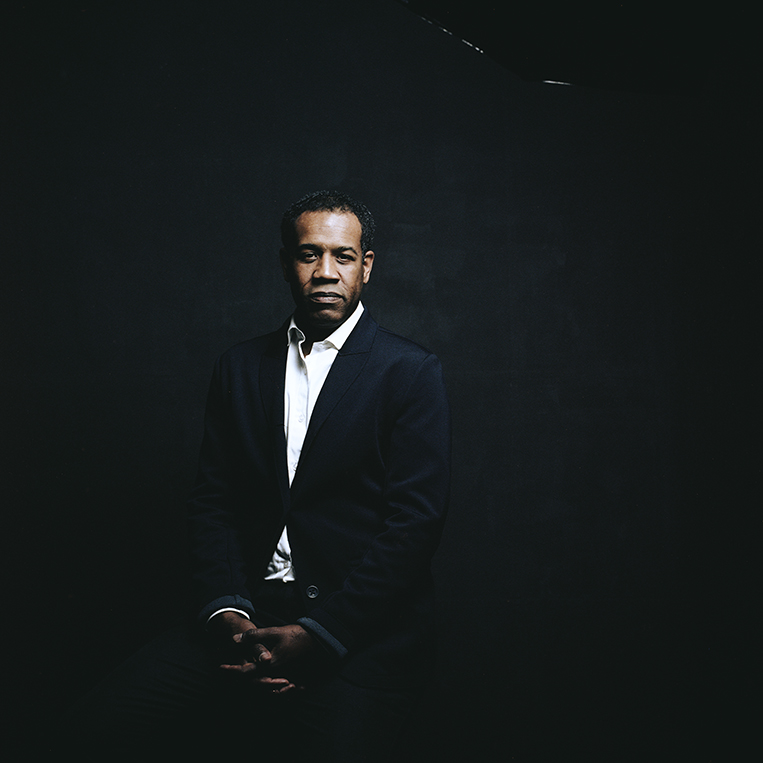
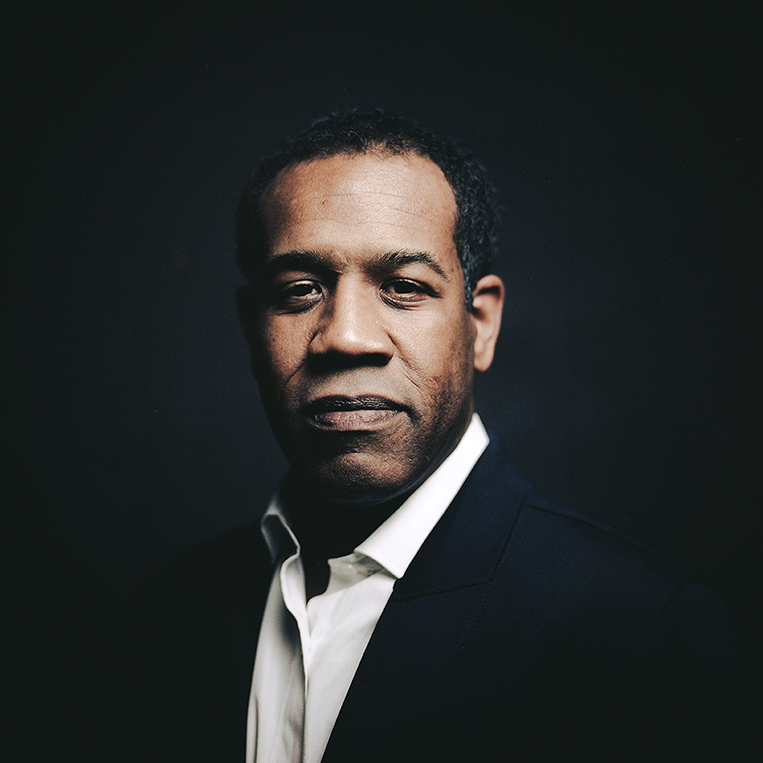
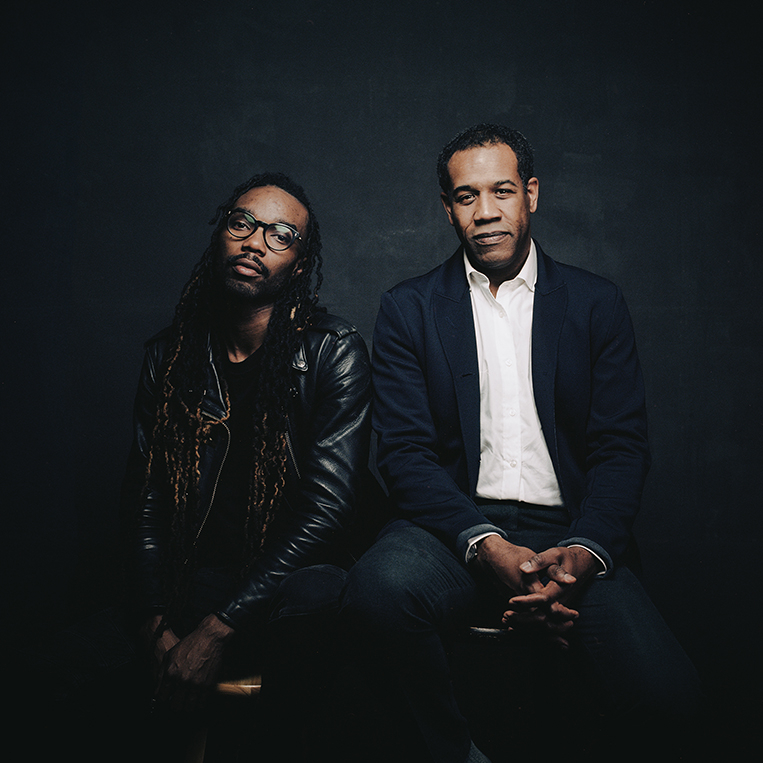
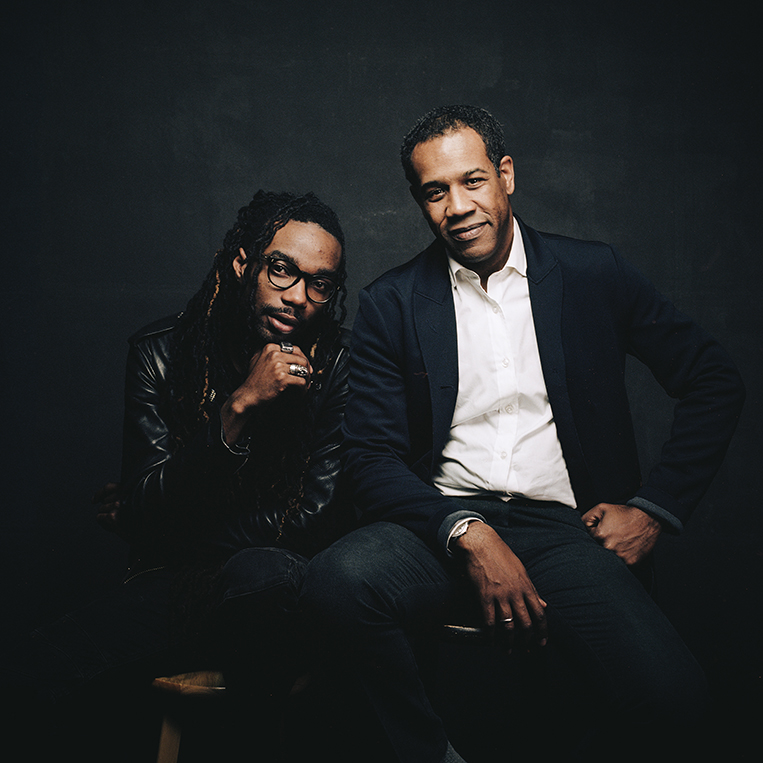
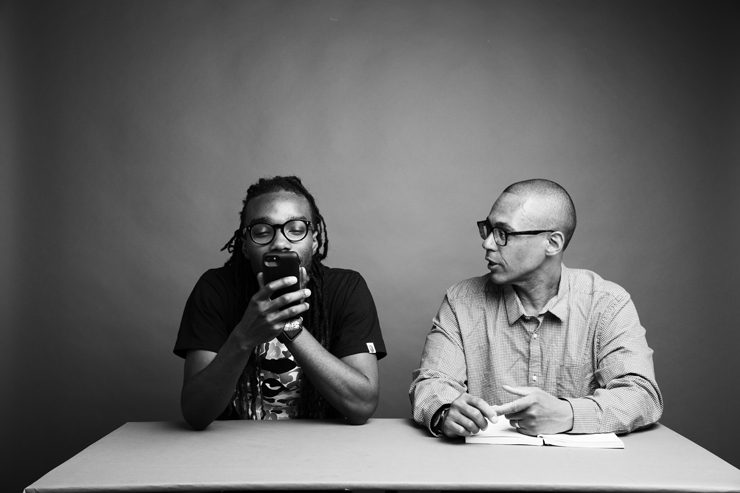
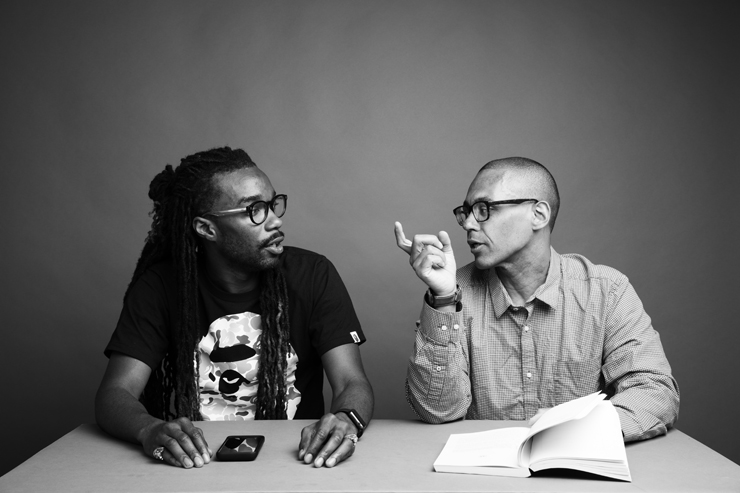
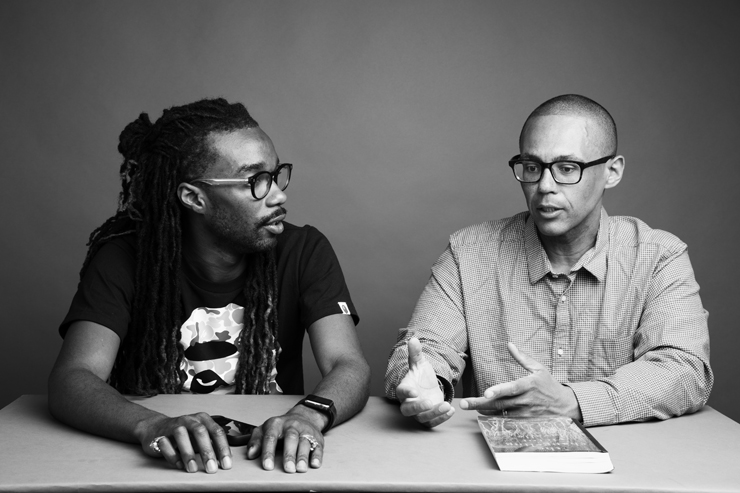
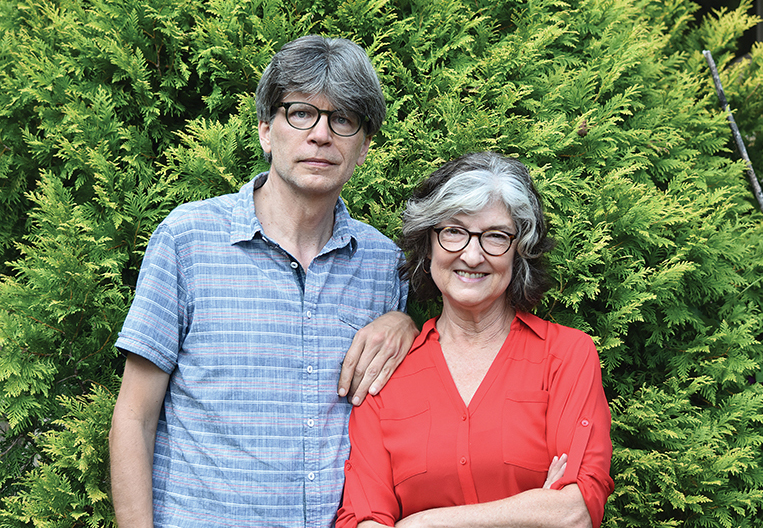
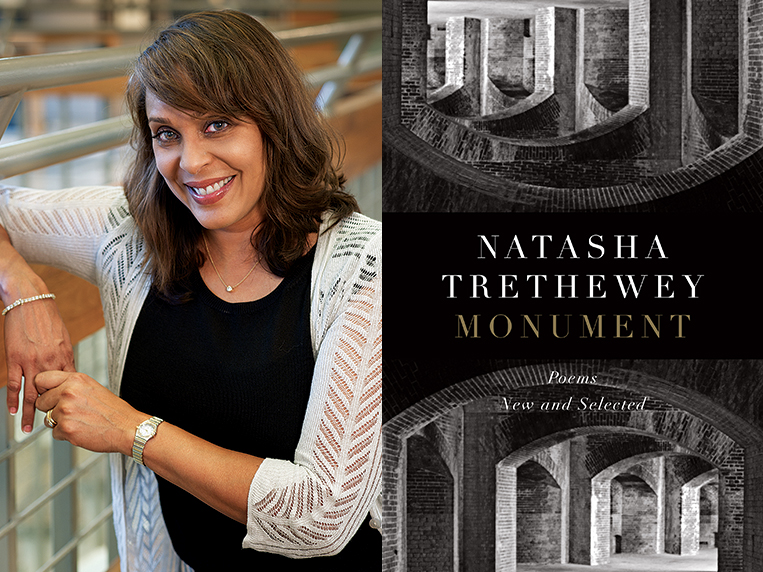






























 How has Amistad changed or grown in the past thirty years?
How has Amistad changed or grown in the past thirty years?




